- C Programming Examples
- C Programming Examples
- C Print Hello World
- C Get Input from User
- C Print Integer
- C Add Two Numbers
- C Add Subtract Multiply Divide
- C Add n Numbers
- C Area Perimeter of Square
- C Area Perimeter of Rectangle
- C Area Circum of Circle
- C Fahrenheit to Celsius
- C Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C Inches to Centimeters
- C Kilogram to Gram
- C Reverse a Number
- C Swap Two Numbers
- C Interchange Numbers
- C Print ASCII Value
- C Print Fibonacci Series
- C Check Palindrome or Not
- C Check Armstrong or Not
- C Find Armstrong Numbers
- C Find nCr and nPr
- C Find Profit Loss
- C Sum of their Square
- C First & Last Digit Sum
- C Sum of All Digit
- C Product of All Digit
- C Print Total Digit in Number
- C Check Perfect Number
- C Find Basic Gross Salary
- C Round Number to Integer
- C Print Series upto n Term
- C Find Factors of Number
- C if-else & Loop Programs
- C Check Even or Odd
- C Check Prime or Not
- C Check Alphabet or Not
- C Check Vowel or Not
- C Check Leap Year or Not
- C Is Reverse Equal Original
- C Make Calculator
- C Add Digits of Number
- Count Positive Negative Zero
- C Largest of Two Numbers
- C Largest of Three Numbers
- C Smallest of Two Numbers
- C Smallest of Three Numbers
- C Find Factorial of Number
- C Find LCM & HCF
- C Find LCM of n Numbers
- C Find HCF of n Numbers
- C Find Arithmetic Mean
- C Find Average, Percentage
- C Find Student Grade
- C Print Table of Number
- C Print Prime Numbers
- C Find Discount Purchase
- C Calculate Parcel Charge
- C Calculate Wage of Labor
- C Print Phone Bill
- C Conversion programs
- C Decimal to Binary
- C Decimal to Octal
- C Decimal to Hexadecimal
- C Binary to Decimal
- C Binary to Octal
- C Binary to Hexadecimal
- C Octal to Decimal
- C Octal to Binary
- C Octal to Hexadecimal
- C Hexadecimal to Decimal
- C Hexadecimal to Binary
- C Hexadecimal to Octal
- C Pattern Programs
- C Pattern Printing Programs
- C Print Diamond Pattern
- C Print Floyd's Triangle
- C Print Pascal's Triangle
- C Array Programs
- C 1D Array Programs
- C Linear Search
- C Binary Search
- C Largest Element in Array
- C Smallest Element in Array
- C Second Largest/Smallest
- C Count Even Odd
- C Array Element at Even
- C Array Element at Odd
- C Print Even Array Elements
- C Print Odd Array Elements
- C Sum/Product of Even/Odd
- C Reverse an Array
- C Insert Element in Array
- C Delete Element from Array
- C Merge Two Arrays
- C Bubble Sort
- C Selection Sort
- C Insertion Sort
- C Print Common Elements
- C 2D Array Programs
- C Add Two Matrices
- C Subtract Two Matrices
- C Transpose a Matrix
- C Multiply Two Matrices
- C Sum All Matrix Elements
- C Largest Element in Matrix
- C Print Row Column Total
- C 3D Array Programs
- C String Programs
- C Print String
- C Find Length of String
- C Compare Two String
- C Copy a String
- C Concatenate String
- C Reverse a String
- C Count Vowels Consonants
- C Replace Vowel in String
- C Delete Vowels from String
- C Delete Word from String
- C Frequency of Character
- C Count Word in String
- C Remove Spaces from String
- C Sort a String
- C Sort String in Alphabetical
- C Sort Words in Ascending
- C Sort Words in Descending
- C Uppercase to Lowercase
- C Lowercase to Uppercase
- C Swap Two Strings
- C Check Anagram or Not
- C Check Palindrome String
- C Print Number in Words
- C Print Successive Character
- C Character without Space
- C File Programs
- C Read a File
- C Write Content to File
- C Read & Display File
- C Copy a File
- C Merge Two Files
- C Reverse File
- C Count All Character in File
- C List Files in Directory
- C Encrypt & Decrypt a File
- C Delete a File
- C Misc Programs
- Generate Random Numbers
- C Print Date Time
- C Print Message with Time
- C Get IP Address
- C Print Smiling face
- C Pass Array to Function
- Add Two Numbers using Pointer
- C Address of Variable
- C Shutdown Computer
- C Programming Tutorial
- C Tutorial
C Program to Subtract Two Matrices
In this article, you will learn and get code for matrix subtraction in C. There are two programs available here:
How does matrix subtraction get performed?
There is a separate tutorial on it, namely, matrix subtraction. You will learn everything there is to know about matrix subtraction in a very short period of time. However, for the time being, the subtraction of any two 3*3 matrices is performed as follows:
matSub[i][j] = mat1[i][j] - mat2[i][j];
where i and j indicate a row and a column, respectively. When the values of i and j are set to 0:
matSub[0][0] = mat1[0][0] - mat2[0][0];
As the above statement shows, the first number (or element) of the second matrix gets subtracted from the first number of the first matrix and initialized as the first element of the third matrix (that holds the subtraction result of both the matrices).
The number in the first matrix's 0th row and 0th column is subtracted from the number in the second matrix's 0th row and 0th column. And its subtraction result gets initialized as the value of the 0th row and 0th column of the resultant matrix. All of the elements are subtracted using the same method.
Subtract two 3x3 matrices using a C program
To subtract two matrices in C programming, you have to ask the user to enter the two 3*3 matrices. That is, enter nine elements for the first matrix, and then nine elements for the second matrix. Now subtract the second matrix from the first. Print the subtraction result on the output as shown in the program given below.
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int mat1[3][3], mat2[3][3], matSub[3][3], i, j; printf("Enter First 3*3 Matrix Elements: "); for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) scanf("%d", &mat1[i][j]); } printf("Enter Second 3*3 Matrix Elements: "); for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) scanf("%d", &mat2[i][j]); } for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) matSub[i][j] = mat1[i][j] - mat2[i][j]; } printf("\nThe Subtraction Result is:\n"); for(i=0; i<3; i++) { for(j=0; j<3; j++) printf("%d ", matSub[i][j]); printf("\n"); } getch(); return 0; }
This program was built and runs in the Code::Blocks IDE. Here is its sample run:
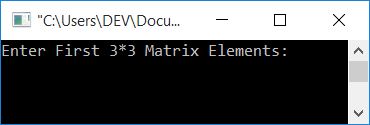
Now enter any 9 numbers for the first matrix, and then 9 numbers for the second matrix. Then press the ENTER key to see the subtraction of two given matrices. The subtraction gets performed in such a way that the first matrix gets subtracted from the second one:

If you enter nine elements for the first matrix, say mat1[][]. Then these elements are stored in a way that:
- The first element gets stored at mat1[0][0].
- The second element gets stored at mat[0][1].
- The third element gets stored at mat1[0][2].
- The fourth element gets stored at mat1[1][0].
- The fifth element gets stored at mat1[1][1].
- and so on.
The same happened with the second matrix. Now, using the for loop, subtract two matrices as follows:
- The outer for loop evaluates or executes three times.
- And at every execution of the outer for loop, the inner for loop executes three times.
- As a result, the inner for loop executes three times during the first execution of the outer for loop. Therefore:
- matSub[0][0] = mat1[0][0] - mat2[0][0]
- matSub[0][1] = mat1[0][1] - mat2[0][1]
- matSub[0][2] = mat1[0][2] - mat2[0][2]
- gets executed. The inner for loop is executed three times during the second execution of the outer for loop. Therefore again:
- matSub[1][0] = mat1[1][0] - mat2[1][0]
- matSub[1][1] = mat1[1][1] - mat2[1][1]
- matSub[1][2] = mat1[1][2] - mat2[1][2]
- gets executed. The same things happened with the third execution:
- matSub[2][0] = mat1[2][0] - mat2[2][0]
- matSub[2][1] = mat1[2][1] - mat2[2][1]
- matSub[2][2] = mat1[2][2] - mat2[2][2]
- As a result, the matrix matSub[][] contains the subtraction result of both the given matrix.
- Print the value of matSub[][] now.
Here [0][0] means the very first element corresponding to the matrix written before it. And [0][1] means the second element, [1][0] means the fourth element, and [2][2] means the last element.
The for loop works like this: first, and only once its initialization part executes, Then it checks the condition; if the condition evaluates to true, then the program flow executes all the statements present in the block of this for loop. Then update the loop variable, or the program flow goes to the update part. After updating the value, check the condition. If it again evaluates to be true, then program flow again does the same job of executing its block of code. The procedure is repeated until the condition evaluates to false.
Subtract two matrices of a given size using a C program
This program has an extra feature. That is, it allows the user to define the size for both matrices.
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int rowSize1, colSize1, rowSize2, colSize2, i, j; int mat1[10][10], mat2[10][10], matSub[10][10]; printf("Enter Row and Column Size of First Matrix: "); scanf("%d%d", &rowSize1, &colSize1); printf("Enter Row and Column Size of Second Matrix: "); scanf("%d%d", &rowSize2, &colSize2); if(rowSize1==rowSize2 && colSize1==colSize2) { printf("\nEnter First %d*%d Matrix Elements: ", rowSize1, colSize1); for(i=0; i<rowSize1; i++) { for(j=0; j<colSize1; j++) scanf("%d", &mat1[i][j]); } printf("Enter Second %d*%d Matrix Elements: ", rowSize2, colSize2); for(i=0; i<rowSize2; i++) { for(j=0; j<colSize2; j++) scanf("%d", &mat2[i][j]); } printf("\nThe Subtraction Result is:\n"); for(i=0; i<rowSize1; i++) { for(j=0; j<colSize1; j++) { matSub[i][j] = mat1[i][j] - mat2[i][j]; printf("%d ", matSub[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } } else printf("\nSubtraction can't be Performed!"); getch(); return 0; }
Here is its sample run:
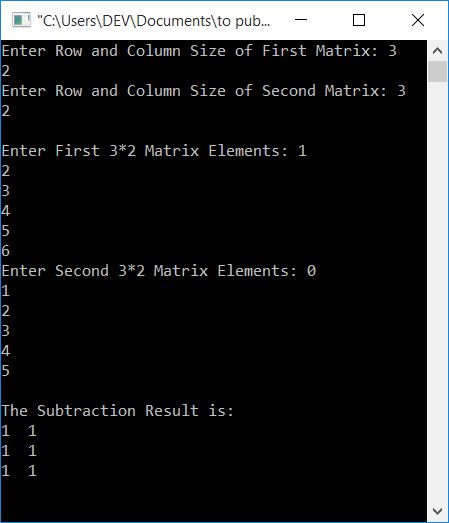
Note: If sizes are mismatched, then subtraction can't be performed. Subtraction cannot be performed if the row size of the first matrix is not equal to the row size of the second matrix or the column size of the first matrix is not equal to the column size of the second matrix.
In the above program, at the time of subtraction, we have printed the element after each subtraction.
The same program in different languages
« Previous Program Next Program »