- C Programming Examples
- C Programming Examples
- C Print Hello World
- C Get Input from User
- C Print Integer
- C Add Two Numbers
- C Add Subtract Multiply Divide
- C Add n Numbers
- C Area Perimeter of Square
- C Area Perimeter of Rectangle
- C Area Circum of Circle
- C Fahrenheit to Celsius
- C Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C Inches to Centimeters
- C Kilogram to Gram
- C Reverse a Number
- C Swap Two Numbers
- C Interchange Numbers
- C Print ASCII Value
- C Print Fibonacci Series
- C Check Palindrome or Not
- C Check Armstrong or Not
- C Find Armstrong Numbers
- C Find nCr and nPr
- C Find Profit Loss
- C Sum of their Square
- C First & Last Digit Sum
- C Sum of All Digit
- C Product of All Digit
- C Print Total Digit in Number
- C Check Perfect Number
- C Find Basic Gross Salary
- C Round Number to Integer
- C Print Series upto n Term
- C Find Factors of Number
- C if-else & Loop Programs
- C Check Even or Odd
- C Check Prime or Not
- C Check Alphabet or Not
- C Check Vowel or Not
- C Check Leap Year or Not
- C Is Reverse Equal Original
- C Make Calculator
- C Add Digits of Number
- Count Positive Negative Zero
- C Largest of Two Numbers
- C Largest of Three Numbers
- C Smallest of Two Numbers
- C Smallest of Three Numbers
- C Find Factorial of Number
- C Find LCM & HCF
- C Find LCM of n Numbers
- C Find HCF of n Numbers
- C Find Arithmetic Mean
- C Find Average, Percentage
- C Find Student Grade
- C Print Table of Number
- C Print Prime Numbers
- C Find Discount Purchase
- C Calculate Parcel Charge
- C Calculate Wage of Labor
- C Print Phone Bill
- C Conversion programs
- C Decimal to Binary
- C Decimal to Octal
- C Decimal to Hexadecimal
- C Binary to Decimal
- C Binary to Octal
- C Binary to Hexadecimal
- C Octal to Decimal
- C Octal to Binary
- C Octal to Hexadecimal
- C Hexadecimal to Decimal
- C Hexadecimal to Binary
- C Hexadecimal to Octal
- C Pattern Programs
- C Pattern Printing Programs
- C Print Diamond Pattern
- C Print Floyd's Triangle
- C Print Pascal's Triangle
- C Array Programs
- C 1D Array Programs
- C Linear Search
- C Binary Search
- C Largest Element in Array
- C Smallest Element in Array
- C Second Largest/Smallest
- C Count Even Odd
- C Array Element at Even
- C Array Element at Odd
- C Print Even Array Elements
- C Print Odd Array Elements
- C Sum/Product of Even/Odd
- C Reverse an Array
- C Insert Element in Array
- C Delete Element from Array
- C Merge Two Arrays
- C Bubble Sort
- C Selection Sort
- C Insertion Sort
- C Print Common Elements
- C 2D Array Programs
- C Add Two Matrices
- C Subtract Two Matrices
- C Transpose a Matrix
- C Multiply Two Matrices
- C Sum All Matrix Elements
- C Largest Element in Matrix
- C Print Row Column Total
- C 3D Array Programs
- C String Programs
- C Print String
- C Find Length of String
- C Compare Two String
- C Copy a String
- C Concatenate String
- C Reverse a String
- C Count Vowels Consonants
- C Replace Vowel in String
- C Delete Vowels from String
- C Delete Word from String
- C Frequency of Character
- C Count Word in String
- C Remove Spaces from String
- C Sort a String
- C Sort String in Alphabetical
- C Sort Words in Ascending
- C Sort Words in Descending
- C Uppercase to Lowercase
- C Lowercase to Uppercase
- C Swap Two Strings
- C Check Anagram or Not
- C Check Palindrome String
- C Print Number in Words
- C Print Successive Character
- C Character without Space
- C File Programs
- C Read a File
- C Write Content to File
- C Read & Display File
- C Copy a File
- C Merge Two Files
- C Reverse File
- C Count All Character in File
- C List Files in Directory
- C Encrypt & Decrypt a File
- C Delete a File
- C Misc Programs
- Generate Random Numbers
- C Print Date Time
- C Print Message with Time
- C Get IP Address
- C Print Smiling face
- C Pass Array to Function
- Add Two Numbers using Pointer
- C Address of Variable
- C Shutdown Computer
- C Programming Tutorial
- C Tutorial
C Program to Print a Diamond Pattern
In this article, you will learn and get code about the printing of a diamond pattern in the following ways:
Print a diamond pattern of stars
Let's create a program that asks the user to enter the row size of the upper-half diamond to print the diamond pattern of stars. For example, if the user enters 5 as the row size, then a diamond of stars of size 5*2-1 or 9 rows gets printed.
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int i, j, row, space; printf("Enter Number of Rows: "); scanf("%d", &row); space = row-1; for(i=1; i<=row; i++) { for(j=1; j<=space; j++) printf(" "); space--; for(j=1; j<=(2*i-1); j++) printf("*"); printf("\n"); } space = 1; for(i=1; i<=(row-1); i++) { for(j=1; j<=space; j++) printf(" "); space++; for(j=1; j<=(2*(row-i)-1); j++) printf("*"); printf("\n"); } getch(); return 0; }
This program was built and runs under the Code::Blocks IDE. Here is its output:
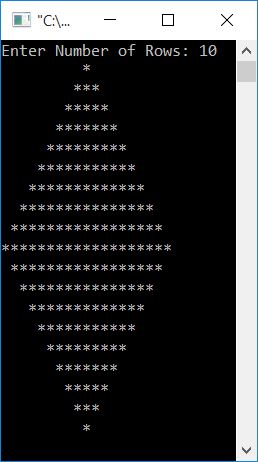
Now enter the number of rows, say 10, to print a diamond pattern that expands up to the row-1 line. That is, with row number 10, it will print a diamond pattern with 9 lines, as shown in the output given below:
Program Explained
If the user enters 10 as the size of the diamond, then always remember these things to print the upper half of the diamond:
- In the first row, print 9 spaces and one star.
- In the second row, print 8 spaces and three stars.
- Print seven spaces and five stars in the third row.
- Print six spaces and seven stars in the fourth row.
- Print five spaces and nine stars in the fifth row.
- Print four spaces and eleven stars in the sixth row.
- Print three spaces and thirteen stars in the seventh row.
- In the eighth row, print 2 spaces and fifteen stars.
- Print one space and seventeen stars in the ninth row.
- Print nineteen stars in the tenth row.
And for the diamond's lower half:
- Print one space and seventeen stars in the first row.
- Print two spaces and fifteen stars in the second row.
- Print three spaces and thirteen stars in the third row.
- Print four spaces and eleven stars in the fourth row.
- Print five spaces and nine stars in the fifth row.
- Print six spaces and seven stars in the sixth row.
- Print seven spaces and five stars in the seventh row.
- Print eight spaces and three stars in the eighth row.
- At the ninth row, print nine spaces and one star.
The following is the dry run of the above program: suppose user input is 10.
- The variable row is initialized with 10.
- Using the statement
space = row-1;
9 gets initialized to "space." - The for loop is now being executed.
- At the first run of the for loop with i = 1, the dry run goes like this:
- Inside the loop, 1 gets initialized to i and checks whether it is less than or equal to row or not
- Inside the loop, 1 gets initialized to i, and it is checked whether it is less than or equal to "row" or not.
- Because the value of i (1) is obviously less than the value of row (10), the condition evaluates to true.
- Therefore, program flow goes inside the loop's body and executes another for loop.
- This time, 1 gets initialized to j and checks whether it is less than or equal to the value of space (9) or not.
- The condition is satisfied.
- Therefore, program flow goes inside the loop body and executes only one statement, that is,
printf(" ");
that prints a space. - Now the variable j gets incremented, and again, program flow goes to the loop's condition part and checks whether the updated value or incremented value of j (2) is less than or equal to the value of space (9) or not.
- The condition is again evaluated as true. Therefore, program flow again goes inside the loop and prints another space.
- In this way, the printing of space continues until the value of j becomes greater than the value of space.
- As a result, the first row contains a total of 9 spaces.
- And then decrement the value of space to print one less space on the next row than the previous one.
- Now the program flow goes to the second for loop part (present inside the first outer for loop).
- There, 1 gets initialized to j and checks whether it is less than or equal to the value of ((2*i)-1) or not.
- Because the value of i was 1 in the first run, compare j to (2*i)-1, (2*1)-1, or 1.
- The condition is satisfied.
- Therefore, program flow goes inside the loop and prints a star (*).
- Then it increases the value of j and compares it to ((2*i)-1).
- This time, the value of j (2) is not less than or equal to (2*i)-1, which is 1.
- Therefore, the condition evaluates to false, and the program flow exits the loop.
- The program flow now begins the next output (printing) thing from the new line by using the newline character ('\n').
- At the second run of the for loop with i = 2, the dry run goes like this:
- Print 8 spaces using first for loop.The process goes the same from step no. 1 to step no. 10 as mentioned above, with an updated value of i.
- Again, decreasing the value of space to print one less space next time. Now space=8.
- This prints three stars by using second for loop.The process continues from step 12 to step 19 as described above, but with an updated value of i.
- Then proceed to step 20.
- At the third run of the for loop with i=3, the dry run looks like this:
- Process the similar operation from step no. 1 to step no. 10 with the new value of i (3). That is, 7 spaces are printed.
- Reduces the value of space. Now space=7.
- Process the similar operation given from step no. 12 to step no. 19 with the new value of i (3). That is, print 5 stars.
- Process step no. 20
- Continue executing the loop until the value of i becomes 11.
- Because 11 is not less than or equal to row 10, the condition evaluates to false, and the program flow exits from this loop.
- Print the lower half of a diamond in the same manner with the initial value of space as 1.
- Because we only need to print one space in the first row of the lower half.
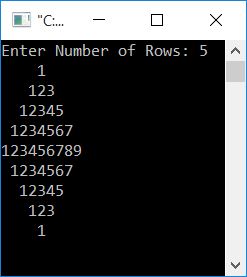
Print a diamond pattern of numbers
Here is another program for printing diamond-shaped numbers. In each row, the number starts with 1. The program is similar to the previous one. Except, in place of the star, print the number using a variable named "num" (initialized with 1 at the start of the program). Increment the value of num after each print.
Remember to always initialize num with 1 after the statement printf("\n"); to begin with 1 for each row.
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int i, j, row, space, num=1; printf("Enter Number of Rows: "); scanf("%d", &row); space = row-1; for(i=1; i<=row; i++) { for(j=1; j<=(space); j++) printf(" "); space--; for(j=1; j<=(2*i-1); j++) { printf("%d", num); num++; } printf("\n"); num=1; } space = 1; for(i=1; i<=(row-1); i++) { for(j=1; j<=(space); j++) printf(" "); space++; for(j=1; j<=(2*(row-i)-1); j++) { printf("%d", num); num++; } printf("\n"); num=1; } getch(); return 0; }
Here is the output produced by the above program, assuming that the user has entered 5 as the size of the diamond:
Print a Diamond Pattern of Alphabets
This program is nearly identical to the previous one. In place of a number, use a character using a variable, say, ch of the char type. Initialize it with A. The rest of the program is similar to the previous one.
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { int i, j, row, space; char ch='A'; printf("Enter Number of Rows: "); scanf("%d", &row); space = row-1; for(i=1; i<=row; i++) { for(j=1; j<=(space); j++) printf(" "); space--; for(j=1; j<=(2*i-1); j++) { printf("%c", ch); ch++; } ch='A'; printf("\n"); } space = 1; for(i=1; i<=(row-1); i++) { for(j=1; j<=(space); j++) printf(" "); space++; for(j=1; j<=(2*(row-i)-1); j++) { printf("%c", ch); ch++; } ch='A'; printf("\n"); } getch(); return 0; }
Here is its output, assuming the user input is 5:

The same program in different languages
« Previous Program Next Program »