- C Programming Examples
- C Programming Examples
- C Print Hello World
- C Get Input from User
- C Print Integer
- C Add Two Numbers
- C Add Subtract Multiply Divide
- C Add n Numbers
- C Area Perimeter of Square
- C Area Perimeter of Rectangle
- C Area Circum of Circle
- C Fahrenheit to Celsius
- C Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C Inches to Centimeters
- C Kilogram to Gram
- C Reverse a Number
- C Swap Two Numbers
- C Interchange Numbers
- C Print ASCII Value
- C Print Fibonacci Series
- C Check Palindrome or Not
- C Check Armstrong or Not
- C Find Armstrong Numbers
- C Find nCr and nPr
- C Find Profit Loss
- C Sum of their Square
- C First & Last Digit Sum
- C Sum of All Digit
- C Product of All Digit
- C Print Total Digit in Number
- C Check Perfect Number
- C Find Basic Gross Salary
- C Round Number to Integer
- C Print Series upto n Term
- C Find Factors of Number
- C if-else & Loop Programs
- C Check Even or Odd
- C Check Prime or Not
- C Check Alphabet or Not
- C Check Vowel or Not
- C Check Leap Year or Not
- C Is Reverse Equal Original
- C Make Calculator
- C Add Digits of Number
- Count Positive Negative Zero
- C Largest of Two Numbers
- C Largest of Three Numbers
- C Smallest of Two Numbers
- C Smallest of Three Numbers
- C Find Factorial of Number
- C Find LCM & HCF
- C Find LCM of n Numbers
- C Find HCF of n Numbers
- C Find Arithmetic Mean
- C Find Average, Percentage
- C Find Student Grade
- C Print Table of Number
- C Print Prime Numbers
- C Find Discount Purchase
- C Calculate Parcel Charge
- C Calculate Wage of Labor
- C Print Phone Bill
- C Conversion programs
- C Decimal to Binary
- C Decimal to Octal
- C Decimal to Hexadecimal
- C Binary to Decimal
- C Binary to Octal
- C Binary to Hexadecimal
- C Octal to Decimal
- C Octal to Binary
- C Octal to Hexadecimal
- C Hexadecimal to Decimal
- C Hexadecimal to Binary
- C Hexadecimal to Octal
- C Pattern Programs
- C Pattern Printing Programs
- C Print Diamond Pattern
- C Print Floyd's Triangle
- C Print Pascal's Triangle
- C Array Programs
- C 1D Array Programs
- C Linear Search
- C Binary Search
- C Largest Element in Array
- C Smallest Element in Array
- C Second Largest/Smallest
- C Count Even Odd
- C Array Element at Even
- C Array Element at Odd
- C Print Even Array Elements
- C Print Odd Array Elements
- C Sum/Product of Even/Odd
- C Reverse an Array
- C Insert Element in Array
- C Delete Element from Array
- C Merge Two Arrays
- C Bubble Sort
- C Selection Sort
- C Insertion Sort
- C Print Common Elements
- C 2D Array Programs
- C Add Two Matrices
- C Subtract Two Matrices
- C Transpose a Matrix
- C Multiply Two Matrices
- C Sum All Matrix Elements
- C Largest Element in Matrix
- C Print Row Column Total
- C 3D Array Programs
- C String Programs
- C Print String
- C Find Length of String
- C Compare Two String
- C Copy a String
- C Concatenate String
- C Reverse a String
- C Count Vowels Consonants
- C Replace Vowel in String
- C Delete Vowels from String
- C Delete Word from String
- C Frequency of Character
- C Count Word in String
- C Remove Spaces from String
- C Sort a String
- C Sort String in Alphabetical
- C Sort Words in Ascending
- C Sort Words in Descending
- C Uppercase to Lowercase
- C Lowercase to Uppercase
- C Swap Two Strings
- C Check Anagram or Not
- C Check Palindrome String
- C Print Number in Words
- C Print Successive Character
- C Character without Space
- C File Programs
- C Read a File
- C Write Content to File
- C Read & Display File
- C Copy a File
- C Merge Two Files
- C Reverse File
- C Count All Character in File
- C List Files in Directory
- C Encrypt & Decrypt a File
- C Delete a File
- C Misc Programs
- Generate Random Numbers
- C Print Date Time
- C Print Message with Time
- C Get IP Address
- C Print Smiling face
- C Pass Array to Function
- Add Two Numbers using Pointer
- C Address of Variable
- C Shutdown Computer
- C Programming Tutorial
- C Tutorial
C Program to Encrypt and Decrypt Files
In this article, you will learn and get code about how to encrypt or decrypt a file using the C programming language. But before going through the program of encryption and decryption, let's first understand what it actually means when encrypting or decrypting a file.
What exactly are encryption and decryption?
Data encryption means converting the original data into a form or code that cannot be read or understood by anyone (the public). Because encrypted data can only be accessed by authorized people, Here "authorized person" means a man who knows its decryption key (or formula or password). A decryption key is a password or formula that is used to convert the ciphertext to plaintext or the original text.
Note: Encrypted data is known as "cyphertext," whereas unencrypted data is known as "plaintext."
Encrypt or Decrypt a File in C
Encrypting a file means, we will convert the plaintext (original content of file) to cyphertext, so that our credential information stored in a file gets converted into ciphertext, whereas decrypting a file means getting our content back to its original form.
Things to Do Before the Program
Here are the things that must have to do, before going through the program given below. Because, we have created a program to encrypt a file and then created another program to decrypt the same file. Then we must have to create a file in the same directory where program's source code is going to be saved.
For example, create a folder named "c programs" to the parent directory named "Documents". And create a file named "codescracker.txt" with following content:
my usernamed is codescracker my password is 1234@cc
Here is a snapshot of the "c programs" folder present in the parent directory of "Documents":
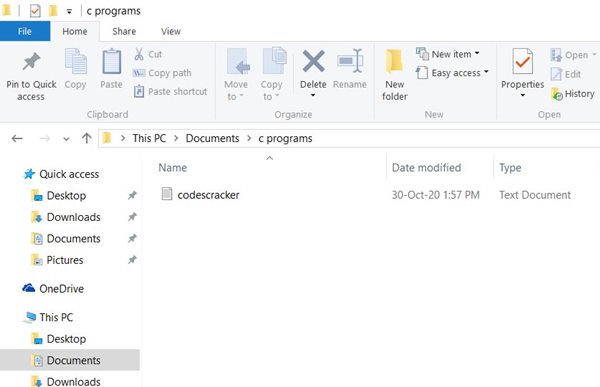
As you can see from the above snapshot, there is a file named codescracker.txt in the folder "c programs." Now let's move on to the program to encrypt the content of this file using the C program given given below.
Program to Encrypt a File in C
To encrypt a file in C programming, you have to open that file and start reading the file character by character. At the time of reading, create some algorithm to encrypt the content of the file, and place the content in a temporary file, character by character. Finally, copy the content of the temporary file to the original file as shown in the program given below:
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { char fname[20], ch; FILE *fps, *fpt; printf("Enter Filename: "); gets(fname); fps = fopen(fname, "r"); if(fps == NULL) return 0; fpt = fopen("temp.txt", "w"); if(fpt == NULL) return 0; ch = fgetc(fps); while(ch != EOF) { ch = ch+100; fputc(ch, fpt); ch = fgetc(fps); } fclose(fps); fclose(fpt); fps = fopen(fname, "w"); if(fps == NULL) return 0; fpt = fopen("temp.txt", "r"); if(fpt == NULL) return 0; ch = fgetc(fpt); while(ch != EOF) { ch = fputc(ch, fps); ch = fgetc(fpt); } fclose(fps); fclose(fpt); printf("\nFile %s Encrypted Successfully!", fname); getch(); return 0; }
This program was written in the Code::Blocks IDE. Before running the preceding program, save it by going to the File->Save file as... menu (in Code::Blocks).Save the file in the same directory where codescracker.txt was saved earlier in this article, namely the "c programs" folder.
Now build and run the above program after saving it. Because we have used "w" as the file opening mode (for the file temp.txt), that is used to write. And if the file does not exist, then a new one gets created with the same name, which in this case is temp.txt. Now here is the sample run of the above program:
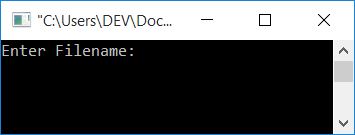
Enter the filename codescracker.txt and press the ENTER key to encrypt it. Here is the second snapshot of the same sample run:
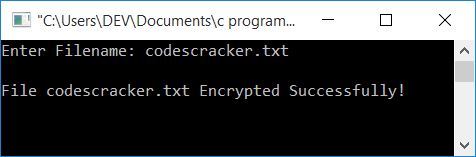
Now your file, codescracker.txt, gets encrypted. Here is a screenshot of the "c programs" folder. You will see that a new file, text.txt, automatically gets created inside the same folder:
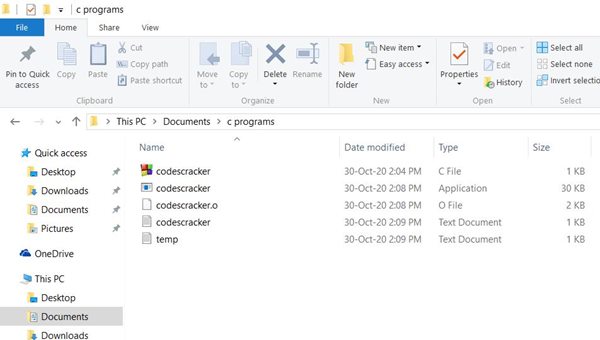
The content of the file, codescracker.txt, before encryption is:
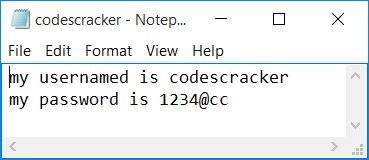
And the following is the content of the same file, codescracker.txt, after encryption:
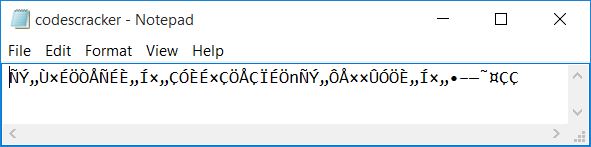
Algorithm used to encrypt files in previous programs
This is the simple encryption key that was used in the above program to encrypt the content of the file codescracker.txt:
ch = ch+100;
It means:
- We've added 100 to each character.
- If the first character of the file codescracker.txt is A and the ASCII value of A is 65, adding 100 means that a character whose ASCII value is 165 gets placed in the temp.txt file as its first character.
- Similarly, process the second character of the codescracker.txt file and save it to the temp.txt file.
- Continue the process for all the characters.
- Finally, overwrite the contents of the codescracker.txt file with those of the temp.txt file.
Now let's go through the program that decrypts the same file that was encrypted using the above program.
Program to Decrypt a File in C
The question is: write a program in C that decrypts the file encrypted using the previous program. The answer to this question is given below:
#include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> int main() { char fname[20], ch; FILE *fps, *fpt; printf("Enter Filename: "); gets(fname); fps = fopen(fname, "w"); if(fps == NULL) return 0; fpt = fopen("temp.txt", "r"); if(fpt == NULL) return 0; ch = fgetc(fpt); while(ch != EOF) { ch = ch-100; fputc(ch, fps); ch = fgetc(fpt); } fclose(fps); fclose(fpt); printf("\nFile %s Decrypted Successfully!", fname); getch(); return 0; }
Here is the sample run of the previous program (just above this sentence):
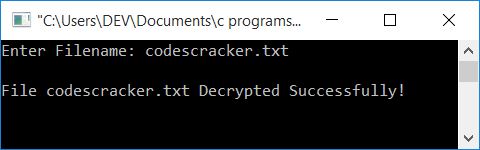
If you look at the file codescracker.txt, you will see its original content, which was:
my usernamed is codescracker my password is 1234@cc
That is, if you see your file's content, then you will find that your file's content will be decrypted, i.e., you will get back your original content.
Note: You can use a lot of algorithms and techniques (including your own) to encrypt and decrypt your file's content.
The same program in different languages
« Previous Program Next Program »