- Java Basic Programs
- Java Programming Examples
- Java Print Hello World
- Java Get Input from User
- Java Print Integer
- Java Add two Numbers
- Java Check Even or Odd
- Java Check Prime or Not
- Java Check Alphabet or Not
- Java Check Vowel or Not
- Check Reverse equal Original
- Java Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Java Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Java Perfect Number Program
- Java Find Quotient Remainder
- Java Days to Seconds
- Java Count Digits in Number
- Java Binary Number Addition
- Java Discount Program
- Java Compute Courier Charge
- Java Find Telephone Bill
- Java Print ASCII Values
- Java Check Palindrome or Not
- Java Check Armstrong or Not
- Generate Armstrong Numbers
- Add two Numbers using Pointers
- Java Mathematical Programs
- Add Subtract Multiply & Divide
- Java Make Calculator
- Java Add Digits of Number
- Java Check Leap Year or Not
- Java Check Divisibility
- Java Find Simple Interest
- Java Find Compound Interest
- Java Print Fibonacci Series
- Java Find nCr nPr
- Calculate Average & Percentage
- Java Calculate Arithmetic Mean
- Java Calculate Student Grade
- Java Print Table of Number
- Java Print Prime Numbers
- Java Add n Numbers
- Java Interchange two Numbers
- Java Reverse Numbers
- Java Swap two Numbers
- Count Positive Negative & Zero
- Find Largest of two Numbers
- Find Largest of three Numbers
- Java Find Factorial of Number
- Java Find HCF & LCM
- Area & Perimeter of Square
- Area & Perimeter of Rectangle
- Area & Circumference of Circle
- Java Conversion Programs
- Java Decimal to Binary
- Java Decimal to Octal
- Java Decimal to Hexadecimal
- Java Binary to Decimal
- Java Binary to Octal
- Java Binary to Hexadecimal
- Java Octal to Decimal
- Java Octal to Binary
- Java Octal to Hexadecimal
- Java Hexadecimal to Decimal
- Java Hexadecimal to Binary
- Java Hexadecimal to Octal
- Java Pattern Programs
- Java Pattern of Stars
- Java Pattern of Alphabets
- Java Pattern of Numbers
- Java Pyramid of Stars
- Java Pyramid of Alphabets
- Java Pyramid of Numbers
- Java Print Diamond Pattern
- Java Print Floyd Triangle
- Java Print Pascal Triangle
- Java Array Programs
- One Dimensional Array Program
- Java Linear Search
- Java Binary Search
- Find Largest Element in Array
- Find Smallest Element in Array
- Java Reverse Array
- Insert Element in Array
- Delete Element from Array
- Java Merge two Array
- Java Bubble Sort
- Java Selection Sort
- Java Insertion Sort
- Java Find Common Elements
- Java Count Even/Odd Number
- Two Dimensional Array Program
- Java Add two Matrices
- Java Subtract two Matrices
- Java Transpose Matrix
- Multiply two Matrices
- Three Dimension Array Program
- Java String Programs
- Java Print String
- Find Length of String
- Java Compare two String
- Java Copy String
- Java Concatenate String
- Java Reverse String
- Delete Vowels from String
- Delete Words from Sentence
- Find Occurrence of a Character
- Java Find Occurrence of a Word
- Occurrence of Each Character
- Java Occurrence of Each Word
- Java Count Repeated Characters
- Java Count Repeated Words
- Java Capitalize Each Word
- Java Count Vowels/Consonants
- Java Extract Numbers
- Java Count Word in String
- Remove Spaces from String
- Java Sort a String
- Java Uppercase to Lowercase
- Java Lowercase to Uppercase
- Java Swap two Strings
- Java Check Anagram or Not
- Java Check Balance Parentheses
- Java Check Password Strength
- Java File Programs
- Java Read File
- Java Write to File
- Read & Display File Content
- Java Copy File
- Java Append Text to File
- Java Merge two File
- List files in Directory
- Java Delete File
- Java Miscellaneous Programs
- Generate Random Numbers
- Java Print Time & Date
- Java Get IP Address
- Java Shutdown Computer
- Java Programming Tutorial
- Java Tutorial
Java Programming Examples
Java programming is a language that is still dominating the Android world. There are almost a ton of famous Android applications written in Java. Some world-famous applications that use Java are Google, Amazon, LinkedIn, Uber, Spotify, etc.
I know, as a programmer, how to learn a language efficiently. We need to practice as much as possible. Therefore, I've written around 500 Java codes here, separated into more than 100 Java program articles.
Since there are a lot of programs, I've written them in Java. And of course, all those programs cannot be included in a single article. Therefore, I've divided those programs into separate articles.
This is basically the home page of Java programming examples. All the programs written here are well-tested and executed using or under one of the most famous Java IDEs, the Apache NetBeans IDE. This series of Java programming examples is designed to take care of beginners too. So that, in most of the article, I've first included the basic version of the code, then written the complete version of the same program.
And I assure you, after practicing all the programs written here, that you will be successful. You'll feel much better than ever before. Therefore, it becomes important to experiment with all the Java programs written here. As much as you practice, the more you build your skill in Java.
Simple Java Programs for Beginners
Here is a list of some simple Java programs written for beginners: So if you're a beginner Java programmer, then you must practice these Java programs before visiting the other Java programs. These Java programs may boost your knowledge in the field of Java so that you can easily get started.
- Java program to print "Hello World"
- Java Program to Add Two Numbers
- Java Program to Check an Even or Odd Number
- Java Program to Check Prime Numbers or Not
- Java Program to Check the Alphabet or Not
- Java Program to Check Vowels or Not
- Java Program to Check Leap Year or Not
- Java Program to Find the Sum of N Numbers
- Java Program to Reverse a Number
- Java Program to Swap Two Numbers
- Java Program to Find the Factorial of a Number
- Java Program to Print a Table of a Given Number
- Simple Calculator Program in Java
- Java Program to Calculate Arithmetic Mean
- Java Program to Find the Area and Perimeter of a Square
- Java Program to Find the Area and Perimeter of a Rectangle
- Java Program to Find the Area and Circumference of a Circle
List of the Top 100 Java Programs
Here is the list of the top 100 Java programs. The series of Java programs provided here is not limited to this list of Java programs. You'll get much more than this. But these are the common programs that are almost available in most of the projects and assignments.
- Java Program to Get Input from the User
- Java Program to Find the Sum of Digits of a Number
- Java Program to Calculate the Grade of a Student
- Java Program to Interchange the Digits of a Number
- Java Program to Find the Largest of Two Numbers
- Java Program to Find the Largest of Three Numbers
- Java Program to Find the HCF and LCM of Two Numbers
- Java Program to Convert Temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Java Program to Convert Temperature from Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Java Program to Find Quotient and Remainder
- Java Program to Convert Days into Seconds
- Java Program to Count the Number of Digits in a Number
- Java Program to Add Two Binary Numbers
- Java Program to Calculate Discount and Price to Pay
- Java Program to Compute Courier Charges to Send the Parcel
- Java Program to Find Telephone Bills
- Java Program to Find Simple Interest
- Java Program to Find Compound Interest
- Java Program to Print ASCII Values
- Java Program to Print the Fibonacci Series
- Java Program to Check Palindromes or Not
- Java Program to Check Armstrong or Not
- Java Program to Generate Armstrong Numbers
- Java Program to Find nCr and nPr
- Java Program to Convert Decimal to Binary
- Java Program to Convert Decimal to Octal
- Java Program to Convert Decimal to Hexadecimal
- Java Program to Convert Binary to Decimal
- Java Program to Convert Binary to Octal
- Java Program to Convert Binary to Hexadecimal
- Java Program to Convert Octal to Decimal
- Java Program to Convert Octal to Binary
- Java Program to Convert Octal to Hexadecimal
- Java Program to Convert Hexadecimal to Decimal
- Java Program to Convert Hexadecimal to Binary
- Java Program to Convert Hexadecimal to Octal
- Java Program to Print the Pattern of Stars
- Java Program to Print the Pattern of Alphabets
- Java Program for Patterns of Numbers
- Java Program to Print a Pyramid of Stars
- Java Program to Print a Pyramid of Alphabets
- Java Program to Print a Pyramid of Numbers
- Java Program to Print the Diamond Pattern
- Java Program to Print Floyd's Triangle
- Java Program to Print Pascal's Triangle
- Linear Search Program in Java
- Binary Search Program in Java
- Java program to add two numbers using pointers
- Java Program to Find the Largest Element in an Array
- Java Program to Find the Smallest Element in an Array
- Java Program to Find the Reverse of an Array
- Java Program to Insert an Element in an Array
- Java Program to Delete an Element from an Array
- Java program to merge two arrays
- Bubble Sort Program in Java
- Selection Sort Program in Java
- Insertion Sort Program in Java
- Java Program to Find Common Elements Between Two Arrays
- Java Program to Count Even and Odd Numbers in an Array
- Java Program to Add Two Matrices
- Java Program to Subtract Two Matrices
- Java Program to Transpose Matrix
- Java Program to Multiply Two Matrices
- Java Program to Find the Length of a String
- Java Program to Compare Two Strings
- Java Program to Copy a String
- Java Program to Concatenate Strings
- Java Program to Reverse a String
- Java Program to Delete Vowels from a String
- Java Program to Delete Words from Strings
- Java Program to Find the Occurrence of a Character in a String
- Java Program to Find the Occurrence of a Word in a String
- Java Program to Find the Occurrence of Each Character
- Java Program to Find the Occurrence of Each Word
- Java Program to Count the Number of Repeated Characters
- Java Program to Count the Number of Repeated Words
- Java Program to Capitalize Each Word in a String
- Java Program to Count Vowels and Consonants
- Java Program to Extract Numbers from Strings
- Java Program to Count the Number of Words in a String
- Java Program to Remove Spaces from Strings
- Java Program to Sort a String
- Java Program to Convert Uppercase to Lowercase
- Java Program to Convert Lowercase to Uppercase
- Java Program to Swap Two Strings
- Java Program to Check Anagram or Not
- Java Program to Check Balance Parentheses
- Java program to check password strength
- Java Program to Generate Random Numbers
- Java Program to Read a File
- Java Program to Write to a File
- Java Program to Read and Display the Content of a File
- Java Program to Copy the Content of a File
- Java program to append the text to a file
- Java program to merge two files
- Java Program to List Files and Folders in a Directory
- Java Program to Delete a File
- Java Program to Print Time and Date
- Java Program to Get Local and Public IP Addresses
- Java Program to Shutdown a Computer
Now, before starting the series of Java programming examples, let's first take a look at some of the basic Java programs along with their explanations.
Java Program Example No. 1
The Java program written below is the very basic and simplest program that can be written in Java. Let's see the code and its output. Then its explanation, to get some idea about what is going behind the code written in Java.
public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("Hey, Java is Fun!"); } }
This program produces the output as shown in the snapshot given below:
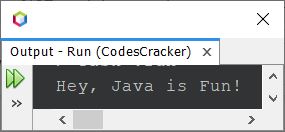
In the above program, the following code:
public class CodesCracker
tells that a class named CodesCracker is defined using the keyword class. This class is declared public using the public keyword. Here, public is an access modifier. Declaring the class "public" means the class CodesCracker is accessible to all. And the following code:
public static void main(String[] args)
refers to the definition of the main() method. Every Java program must have this method. The execution of the program starts within the main() method.
Before the method main(), the keyword void refers to the return type of the method. Declaring a method void as its return type means the method does not return any value. And of course, we did not want the main() method to return any value.
Using the method as a static type means that we do not need to create an object to invoke the method. And of course, the main() method is to be called without any object; therefore, it is defined using static. And the keyword public is again an access modifier.
And the String[] args indicate an array of a sequence of strings that are passed to the method main(). This happens when the program is executed. For example, if you execute the Java program using or via the command line:
java CodesCracker Hey, Java is Fun!
Then, the array will store: ["Hey,", "Java", "is", "Fun!"].
And finally, inside the main() function, the code System.out.println() is used to print content on the output screen. For example, in the above program, I've passed the string "Hey, Java is Fun!". Therefore, this string gets printed on the output screen.
The above program can also be written as:
public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "Hey, Java is Fun!"; System.out.println(str); } }
You'll get the same output as the previous program's output.
Now, in short, if I say that every Java program contains a main() method inside the class with a name the same as the Java application's or program's source code name, that is:
public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { // your Java code goes here } }
where CodesCracker is the name of the class. In your case, the only change that may occur is this name. Other things would be the same. And in the section // your Java code goes here, you'll write your Java code to do whatever you want. Now let's take a look at some more Java program examples, given below.
Java Program Example No. 2
This is the second version of a program written in Java. This program uses a loop to execute a statement multiple times.
public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0; i<10; i++) System.out.println(i); } }
The output produced by this Java program will be:
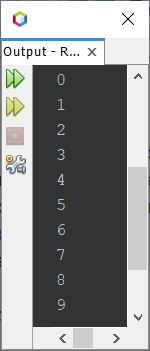
As already told, the execution of the Java program starts with the main() method. Therefore, inside the main() method, there is a for loop defined. The for loop starts its execution in such a way that the first statement gets executed initially and only once. Therefore, using the first statement, that is:
int i=0;
a variable i gets defined, which is of the int type. And initialized with a value of 0. Now, while entering the body of the loop, every time the compiler checks the condition of the loop, That is, the second statement (condition-checking) gets executed.
i<10;
now the variable i gets replaced with its value. Since its value for now is 0, 0<10 evaluates to be true. Since the condition evaluates to be true, program flow goes inside the loop. Now inside the loop, the statement:
System.out.println(i);
gets executed. That prints the value of i on the output screen. Therefore, 0 gets printed on the output. When the statement of the loop gets executed, the compiler goes to the third statement of the loop, that is:
i++
The value of i gets incremented by 1. So i = 1 now. As already told, before entering the loop, the condition-checking statement (the second statement) gets evaluated. Since i<10 or 1<10 again evaluates to be true, program flow again goes inside the loop and prints the new value of i. That is, 1 this time. This process continues until the condition is evaluated as false.
Java Program Example No. 3
Now let's create another program in Java that receives the name of a user and prints some string on the output, along with the entered name:
import java.util.Scanner; public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { String name; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter Your Name: "); name = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("\nHey,"); System.out.println(name); System.out.println("Are you excited ?"); } }
The snapshot given below shows the sample run of the above Java program, with user input James as the name:
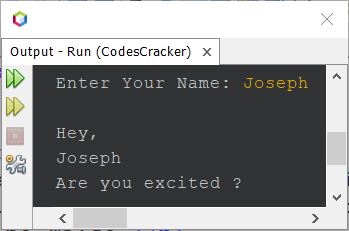
Because in Java, to scan input from the user, we need to use the Scanner class. And the Scanner class is defined inside the java.util package. Therefore, before using the Scanner class to scan the input, I've imported the package and then defined an object scan of the Scanner class to scan input from the user. Don't worry, you'll learn everything, step by step, in this series of Java program examples.
In the above program, the \n used in the second System.out.println() statement is an escape sequence. That inserts a newline to the output screen so that the next output thing will get printed from the next line. Therefore, the string Hey gets printed one line after the user's input. Also from the above program, the last three System.out.println() statements can be written as:
System.out.println("\nHey,\n" +name+ "\nAre you excited ?");
That is, in the above statement:
"\nHey,\n" +name+ "\nAre you excited ?"
is composed of three strings; the first one is:
"\nHey,\n"
which is the string itself. And the second one is:
name
which is indirectly equal to "Joseph" entered by the user, according to the sample run given above. Since the entered string is stored in the name variable. Therefore, wherever you write a name inside the main() method, it evaluates to "Joseph". And the third one is:
"\nAre you excited ?"
which is itself a string. And using the + operator, I've added all these three strings. So the output will be the same as in the previous program's sample run.
Java Program Example No. 4
This program does not receive any input from the user. This program only declares four variables of the int type. And initialized some values to the three variables, and the summation of all three variables' values gets initialized to the fourth variable. The value of the fourth variable gets printed on the output screen using the System.out.println() statement.
public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { int a, b, c, res; a = 10; b = 20; c = 30; res = a+b+c; System.out.println(res); } }
The output produced by the above Java program will be:
60
Java Program Example No. 5
This is the same program as the previous one. The only difference is that the values of three variables are received by the user at run-time of the program:
import java.util.Scanner; public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter Three Numbers: "); int a = s.nextInt(); int b = s.nextInt(); int c = s.nextInt(); int res = a+b+c; System.out.println("\nResult = " +res); } }
The output produced by the above Java program, with user input of 10, 20, and 30 as three numbers, is shown in the snapshot given below:
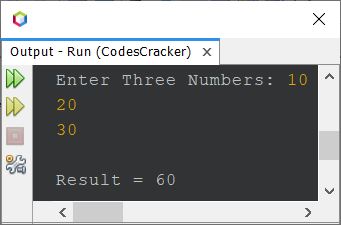
Java Program Example No. 6
Here is the same program as the previous one, except this program works with both int and float type values. That is, if the user enters a whole number or a real number, this program works for both.
import java.util.Scanner; public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter Three Numbers: "); float a = s.nextFloat(); float b = s.nextFloat(); float c = s.nextFloat(); float res = a+b+c; System.out.println("\nResult = " +res); } }
Here is its sample run with user input (10.43, 20.53, and 30.53):
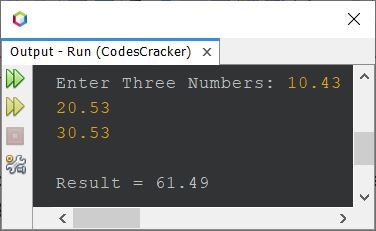
Java Program Example No. 7
Here is another program written in Java that receives two values of different types.
import java.util.Scanner; public class CodesCracker { public static void main(String[] args) { String name; int n; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter Your Name: "); name = scan.nextLine(); System.out.print("Enter the Value of n: "); n = scan.nextInt(); System.out.println("\nPrinting \"" +name+ "\", " +n+ " times."); for(int i=0; i<n; i++) System.out.println(name); } }
The sample output produced by the above Java program with user input Mark as a name or string and 10 as the value of n is shown in the snapshot given below:
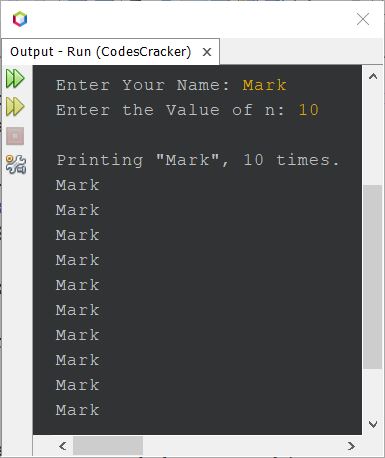
The above seven Java program examples are written to show you the demo of how the program can be written in Java. From now on, one by one, you'll get much more programs written in Java in different ways.
Other Language Examples
« Java Tutorial Next Program »