- Python Basic Programs
- Python Program Examples
- Python Print Hello World
- Python Get Input from User
- Python Add Two Numbers
- Add Subtract Multiply Divide
- Python Check Even or Odd
- Python Check Prime or Not
- Python Check Alphabet or Not
- Python Check Vowel or Not
- Python Check Leap Year or Not
- Check Reverse equal Original
- Check Positive Negative Zero
- Python Check Armstrong or Not
- Python Check Palindrome or Not
- Python Check Perfect Number
- Python Find Reverse of Number
- Python Count Digits in Number
- Python Add Digits of Number
- Sum of First and Last Digits
- Python Product of Mid Digits
- Sum of Squares of Digits
- Interchange Digits of Number
- Python Sum of n Numbers
- Python Print ASCII Values
- Python Swap Two Numbers
- Python Swap Two Variables
- Python Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Python Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Python Display Calendar
- Python Days into Years, Weeks
- Find Largest of Two Number
- Find Largest of Three Number
- Python Print Fibonacci Series
- Generate Armstrong Numbers
- Python Make Simple Calculator
- Python Add Binary Numbers
- Binary Number Multiplication
- Python Mathematical Programs
- Find Sum of Natural Numbers
- Find Average of n Numbers
- Python Print Multiplication Table
- Print Table using Recursion
- Python Find Average Percentage
- Python Find Grade of Student
- Find Square Root of Number
- Python Print Prime Numbers
- Find Numbers Divisible by
- Python Find Factors of Number
- Python Find Factorial of a Number
- Python Find HCF & LCM
- Python Kilometres to Miles
- Python Find Area of Square
- Python Find Area of Rectangle
- Python Find Area of Triangle
- Python Find Area of Circle
- Python Find Perimeter of Square
- Find Perimeter of Rectangle
- Python Find Perimeter of Triangle
- Find Circumference of Circle
- Python Simple Interest
- Python Solve Quadratic Equation
- Python Different Set of Operations
- Python Display Powers of 2
- Python Find nCr & nPr
- Python Pattern Programs
- Python Print Pattern Programs
- Python Print Diamond Pattern
- Python Print Floyd's Triangle
- Python Print Pascal's Triangle
- Python List Programs
- Python Count Even/Odd in List
- Python Positive/Negative in List
- Python Even Numbers in List
- Python Odd Numbers in List
- Python Sum of Elements in List
- Sum of Odd/Even Numbers
- Python Element at Even Position
- Python Element at Odd Position
- Python Search Element in List
- Python Largest Number in List
- Python Smallest Number in List
- Python Second Largest in List
- Python Second Smallest in List
- Python Insert Element in List
- Python Delete Element from List
- Python Multiply Numbers in List
- Swap Two Elements in List
- Python 1D Array Program
- Python Linear Search
- Python Binary Search
- Python Insertion Sort
- Python Bubble Sort
- Python Selection Sort
- Remove Duplicates from List
- Python Reverse a List
- Python Merge Two List
- Python Copy a List
- Python Conversion Programs
- Python Decimal to Binary
- Python Decimal to Octal
- Python Decimal to Hexadecimal
- Python Binary to Decimal
- Python Binary to Octal
- Python Binary to Hexadecimal
- Python Octal to Decimal
- Python Octal to Binary
- Python Octal to Hexadecimal
- Python Hexadecimal to Decimal
- Python Hexadecimal to Binary
- Python Hexadecimal to Octal
- Python Matrix Programs
- Python Add Two Matrices
- Python Subtract Two Matrices
- Python Transpose Matrix
- Python Multiply Matrices
- Python String Programs
- Python Print String
- Python Find Length of String
- Python Compare Two Strings
- Python Copy String
- Python Concatenate String
- Python Reverse a String
- Python Swap Two Strings
- Python Uppercase to Lowercase
- Python Lowercase to Uppercase
- Python Check Substring in String
- Python Count Character in String
- Count Repeated Characters
- Python Count Word in Sentence
- Python Count Each Vowels
- Python Capitalize Character
- Python Capitalize Word in String
- Python Smallest/Largest Word
- Remove Spaces from String
- Remove Duplicate Character
- Remove Vowels from String
- Remove Punctuation from String
- Python Remove Word in String
- Python Remove Duplicate Words
- WhiteSpace to Hyphens
- Replace Vowels with Character
- Replace Character in String
- Python Sort String in Alphabetical
- Sort Word in Alphabetical Order
- Extract Number from String
- Python Check Anagram Strings
- Python File Programs
- Python Read a File
- Python Write to File
- Python Append Text to File
- Python Copy Files
- Python Merge Two Files
- Python Counts Characters in File
- Python Count Words in File
- Python File Content in Reverse
- Python Lines Contains String
- Python Delete Line from File
- Python Capitalize Word in File
- Python Replace Text in File
- Replace Specific Line in File
- Python Find Size of File
- Python List Files in Directory
- Python Delete Files
- Python Misc Programs
- Python Reverse a Tuple
- Python Merge Two Dictionary
- Python bytes to String
- Python bytearray to String
- Generate Random Numbers
- Python Print Address of Variable
- Python Print Date and Time
- Python Get IP Address
- Python Shutdown/Restart PC
- Python Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
Python Program to Make Calculator
In this article, I've created some programs in Python, to make a simple calculator. Here are the list of calculator programs in Python:
- Calculator Program using while loop and if-else
- Using user-defined Function
- Using Class and Object
Calculator Program using while Loop and if-else
This program makes a simple calculator in Python that performs four basic mathematical operations such as add, subtract, multiply, and divide two numbers entered by user. Here I've provided 5 options to user, the fifth option is to exit.
while True: print("1. Addition") print("2. Subtraction") print("3. Multiplication") print("4. Division") print("5. Exit") print("Enter Your Choice (1-5): ", end="") ch = int(input()) if ch>=1 and ch<=4: print("\nEnter Two Numbers: ", end="") numOne = float(input()) numTwo = float(input()) if ch==1: res = numOne + numTwo print("\nResult =", res) elif ch==2: res = numOne - numTwo print("\nResult =", res) elif ch==3: res = numOne * numTwo print("\nResult =", res) elif ch==4: res = numOne / numTwo print("\nResult =", res) elif ch==5: break else: print("\nInvalid Input!..Try Again!") print("------------------------")
Here is the initial output produced by this Python program of simple calculator:
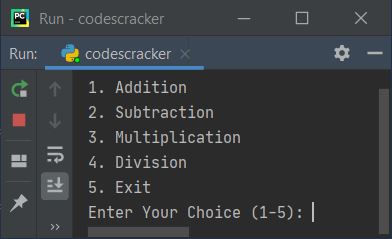
Now supply the input. For example type 1 as choice, and press ENTER key, here is the output you'll see:
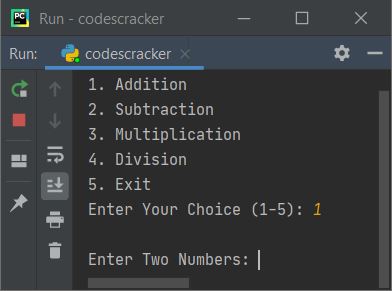
Now enter any two numbers say 32 as first, press ENTER and 44 as second number, again
press ENTER. Here is the output you'll see, that shows the result and again options gets displayed to operator further:
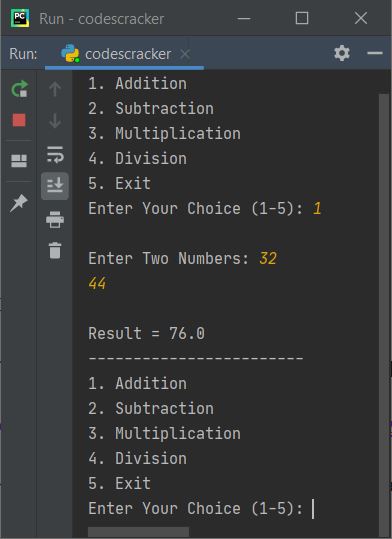
To exit, type 5 as choice and press ENTER. The program execution gets terminated like shown in the snapshot given below:
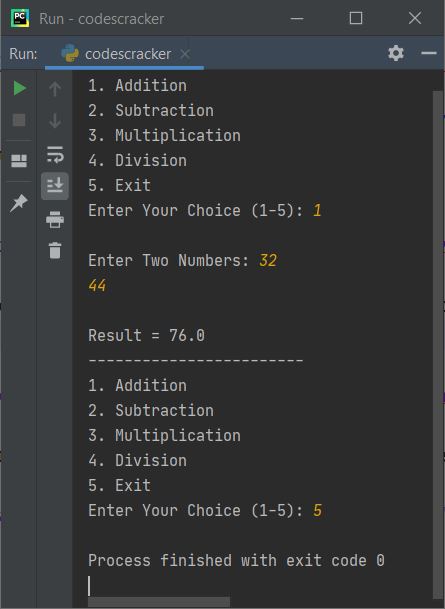
The dry run of above program goes like:
- Since I've given True (boolean) as a condition of while loop, therefore program flow directly goes inside the loop without evaluating anything (condition), because the condition already written as True
- Inside the loop, I've provided 5 options. The first four options is for mathematical operations, whereas the fifth option is to exit from the loop and terminate the program
- Now through input(), the option (1-5) entered by user gets received and initialized to ch variable. For example, if user enters 1 as option, then ch=1
- The condition (first condition of if) ch>=1 or 1>=1 evaluates to be true, therefore the second condition gets evaluated, that is the condition ch<=4 or ch<=4 also evaluates to be true, therefore program flow goes inside this if's body
- Inside if's body, I've received two numbers and initialized to two variables namely numOne and numTwo respectively. For example, if user enters 32 and 44 as first and second numbers. Then numOne=32 and numTwo=44
- Now the condition (of next if) ch==1 or 1==1 evaluates to be true, therefore program flow goes inside this if's body and numOne+numTwo or 32+44 or 76 gets initialized to res. So res=76
- And the value of res gets printed as output
- Since if's condition evaluates to be true, therefore no any upcoming elif or else's statement(s) gets executed
- So using the last statement, I've printed some dashes (-------)
- Now again 5 choices gets displayed, and user has to enter his/her choice again to operate further. This process continues, since I've used True as condition of while loop, that always evaluates to be true
- The only way to exit from the loop, is when user enters 5 as choice, so that the condition of last elif, that is ch==5 or 5==5 evaluates to be true, and using break keyword, the execution of while loop gets ended
Modified Version of Previous Program
This program is the modified version of previous program. This program uses try-except to handle invalid inputs. That is, when user enters any invalid input like c, # as number, then program raises (prints) error message and continue asking to enter the valid one. Let's have a look:
print("1. Addition") print("2. Subtraction") print("3. Multiplication") print("4. Division") print("5. Exit") while True: while True: print("Enter Your Choice (1-5): ", end="") try: ch = int(input()) if ch>=1 and ch<=4: print("\nEnter Two Numbers: ", end="") numOne = float(input()) numTwo = float(input()) if ch==1: print("\nResult =", numOne+numTwo) elif ch==2: print("\nResult =", numOne-numTwo) elif ch==3: print("\nResult =", numOne*numTwo) elif ch==4: print("\nResult =", numOne/numTwo) elif ch==5: break else: print("\nInvalid Input!..Try Again!") print("------------------------") except ValueError: print("\nInvalid Input!..Try Again!") print("------------------------") continue if ch==5: break
Here is its sample run with user input 3 as choice, then 2 and 5 as two numbers:
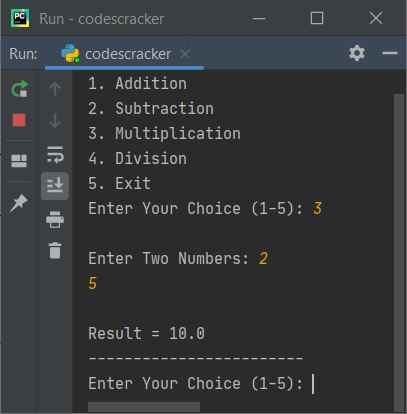
As you can see from above sample run, the menu is displayed only once. Later on, I've only displayed the message that asks to enter the choice to continue the operation. Here is continued sample run with invalid and valid inputs:
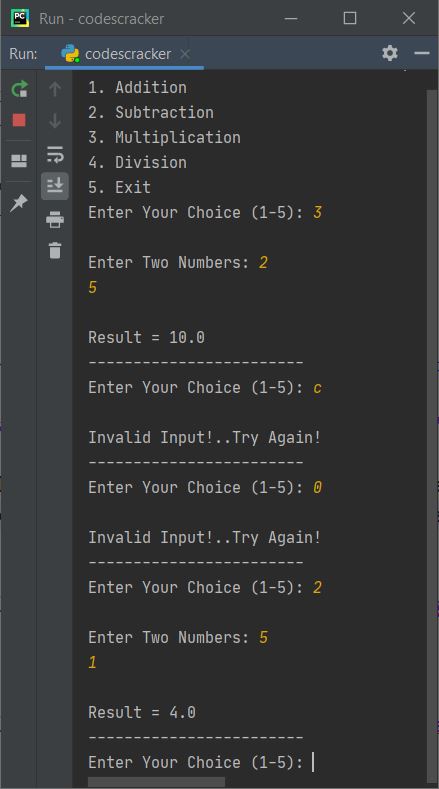
The only way to exit the program, is by using 5 as choice.
Note - In above program, when user enters invalid input, then program flow goes to except ValueError's body and prints an error message. Then using continue keyword, program flow goes to the initial (first) statement of while loop's body to receive the input again inside try
Calculator Program using Function
This program is created using four user-defined functions. All functions receives two arguments and returns the corresponding result.
def add(a, b): return a+b def sub(a, b): return a-b def mul(a, b): return a*b def div(a, b): return a/b print("1. Addition") print("2. Subtraction") print("3. Multiplication") print("4. Division") print("5. Exit") while True: while True: print("Enter Your Choice (1-5): ", end="") try: ch = int(input()) if ch>=1 and ch<=4: print("\nEnter Two Numbers: ", end="") nOne = float(input()) nTwo = float(input()) if ch==1: print("\nResult =", add(nOne, nTwo)) elif ch==2: print("\nResult =", sub(nOne, nTwo)) elif ch==3: print("\nResult =", mul(nOne, nTwo)) elif ch==4: print("\nResult =", div(nOne, nTwo)) elif ch==5: break else: print("\nInvalid Input!..Try Again!") print("------------------------") except ValueError: print("\nInvalid Input!..Try Again!") print("------------------------") continue if ch==5: break
This program produces same output as of previous program.
Calculator Program using Class
This is the last calculator program in Python, created using class. To access member function of a class, an object is required. Therefore an object ob is created of a class named CodesCracker, of which I've to access member functions using dot (.) operator.
class CodesCracker: def add(self, a, b): return a+b def sub(self, a, b): return a-b def mul(self, a, b): return a*b def div(self, a, b): return a/b print("1. Add") print("2. Subtract") print("3. Multiply") print("4. Divide") print("5. Exit") while True: while True: print("Enter Your Choice (1-5): ", end="") try: ch = int(input()) if ch>=1 and ch<=4: print("\nEnter Two Numbers: ", end="") nOne = float(input()) nTwo = float(input()) ob = CodesCracker() if ch==1: print("\n" +str(nOne)+ " + " +str(nTwo)+ " = " + str(ob.add(nOne, nTwo))) elif ch==2: print("\n" +str(nOne)+ " - " +str(nTwo)+ " = " + str(ob.sub(nOne, nTwo))) elif ch==3: print("\n" +str(nOne)+ " * " +str(nTwo)+ " = " + str(ob.mul(nOne, nTwo))) elif ch==4: print("\n" +str(nOne)+ " / " +str(nTwo)+ " = " + str(ob.div(nOne, nTwo))) elif ch==5: break else: print("\nInvalid Input!..Try Again!") print("------------------------") except ValueError: print("\nInvalid Input!..Try Again!") print("------------------------") continue if ch==5: break
Here is its sample run with some user inputs:
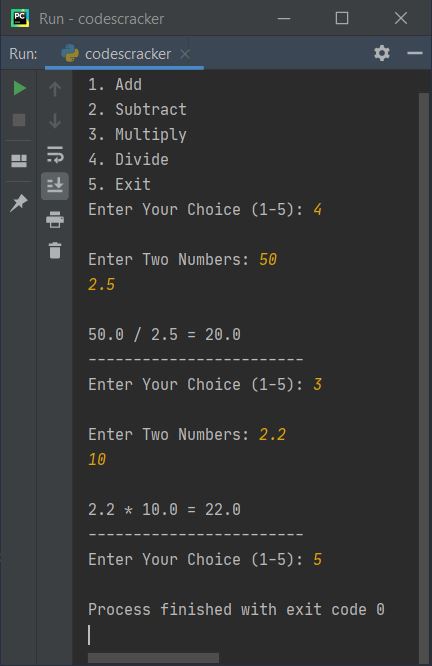
Same Program in Other Languages
« Previous Program Next Program »