- Python Basic Programs
- Python Program Examples
- Python Print Hello World
- Python Get Input from User
- Python Add Two Numbers
- Add Subtract Multiply Divide
- Python Check Even or Odd
- Python Check Prime or Not
- Python Check Alphabet or Not
- Python Check Vowel or Not
- Python Check Leap Year or Not
- Check Reverse equal Original
- Check Positive Negative Zero
- Python Check Armstrong or Not
- Python Check Palindrome or Not
- Python Check Perfect Number
- Python Find Reverse of Number
- Python Count Digits in Number
- Python Add Digits of Number
- Sum of First and Last Digits
- Python Product of Mid Digits
- Sum of Squares of Digits
- Interchange Digits of Number
- Python Sum of n Numbers
- Python Print ASCII Values
- Python Swap Two Numbers
- Python Swap Two Variables
- Python Fahrenheit to Celsius
- Python Celsius to Fahrenheit
- Python Display Calendar
- Python Days into Years, Weeks
- Find Largest of Two Number
- Find Largest of Three Number
- Python Print Fibonacci Series
- Generate Armstrong Numbers
- Python Make Simple Calculator
- Python Add Binary Numbers
- Binary Number Multiplication
- Python Mathematical Programs
- Find Sum of Natural Numbers
- Find Average of n Numbers
- Python Print Multiplication Table
- Print Table using Recursion
- Python Find Average Percentage
- Python Find Grade of Student
- Find Square Root of Number
- Python Print Prime Numbers
- Find Numbers Divisible by
- Python Find Factors of Number
- Python Find Factorial of a Number
- Python Find HCF & LCM
- Python Kilometres to Miles
- Python Find Area of Square
- Python Find Area of Rectangle
- Python Find Area of Triangle
- Python Find Area of Circle
- Python Find Perimeter of Square
- Find Perimeter of Rectangle
- Python Find Perimeter of Triangle
- Find Circumference of Circle
- Python Simple Interest
- Python Solve Quadratic Equation
- Python Different Set of Operations
- Python Display Powers of 2
- Python Find nCr & nPr
- Python Pattern Programs
- Python Print Pattern Programs
- Python Print Diamond Pattern
- Python Print Floyd's Triangle
- Python Print Pascal's Triangle
- Python List Programs
- Python Count Even/Odd in List
- Python Positive/Negative in List
- Python Even Numbers in List
- Python Odd Numbers in List
- Python Sum of Elements in List
- Sum of Odd/Even Numbers
- Python Element at Even Position
- Python Element at Odd Position
- Python Search Element in List
- Python Largest Number in List
- Python Smallest Number in List
- Python Second Largest in List
- Python Second Smallest in List
- Python Insert Element in List
- Python Delete Element from List
- Python Multiply Numbers in List
- Swap Two Elements in List
- Python 1D Array Program
- Python Linear Search
- Python Binary Search
- Python Insertion Sort
- Python Bubble Sort
- Python Selection Sort
- Remove Duplicates from List
- Python Reverse a List
- Python Merge Two List
- Python Copy a List
- Python Conversion Programs
- Python Decimal to Binary
- Python Decimal to Octal
- Python Decimal to Hexadecimal
- Python Binary to Decimal
- Python Binary to Octal
- Python Binary to Hexadecimal
- Python Octal to Decimal
- Python Octal to Binary
- Python Octal to Hexadecimal
- Python Hexadecimal to Decimal
- Python Hexadecimal to Binary
- Python Hexadecimal to Octal
- Python Matrix Programs
- Python Add Two Matrices
- Python Subtract Two Matrices
- Python Transpose Matrix
- Python Multiply Matrices
- Python String Programs
- Python Print String
- Python Find Length of String
- Python Compare Two Strings
- Python Copy String
- Python Concatenate String
- Python Reverse a String
- Python Swap Two Strings
- Python Uppercase to Lowercase
- Python Lowercase to Uppercase
- Python Check Substring in String
- Python Count Character in String
- Count Repeated Characters
- Python Count Word in Sentence
- Python Count Each Vowels
- Python Capitalize Character
- Python Capitalize Word in String
- Python Smallest/Largest Word
- Remove Spaces from String
- Remove Duplicate Character
- Remove Vowels from String
- Remove Punctuation from String
- Python Remove Word in String
- Python Remove Duplicate Words
- WhiteSpace to Hyphens
- Replace Vowels with Character
- Replace Character in String
- Python Sort String in Alphabetical
- Sort Word in Alphabetical Order
- Extract Number from String
- Python Check Anagram Strings
- Python File Programs
- Python Read a File
- Python Write to File
- Python Append Text to File
- Python Copy Files
- Python Merge Two Files
- Python Counts Characters in File
- Python Count Words in File
- Python File Content in Reverse
- Python Lines Contains String
- Python Delete Line from File
- Python Capitalize Word in File
- Python Replace Text in File
- Replace Specific Line in File
- Python Find Size of File
- Python List Files in Directory
- Python Delete Files
- Python Misc Programs
- Python Reverse a Tuple
- Python Merge Two Dictionary
- Python bytes to String
- Python bytearray to String
- Generate Random Numbers
- Python Print Address of Variable
- Python Print Date and Time
- Python Get IP Address
- Python Shutdown/Restart PC
- Python Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
Python Program to Check If Two Strings Are Anagrams or Not
This article is created to cover some programs in Python that receive two strings from the user at run-time and check whether the two strings are anagrams or not. Here is a list of programs:
- Check if two strings are anagrams or not using the for loop without sorting the string.
- Check if two strings are anagrams or not using the sorted() function.
- Check if two strings are anagrams or not using a user-defined function.
- Check if two strings are anagrams or not using Class.
Before creating these programs, let's first understand anagrams.
What are anagram strings?
Two strings can be called an anagram when:
- Both contain the same number of characters.
- The order of characters doesn't matter.
- One string can be rearranged to form the other one.
For example, abc and cba are two anagram strings. Similarly, creative and reactive are also anagrams. That is, characters from creative can be rearranged to form reactive, and vice versa.
Check Two strings are anagrams using a for loop
This program is created using a for loop to check whether the two strings entered by the user are anagrams or not. The question is: write a Python program to check if an anagram exists or not without sorting the string. Here is its answer:
print("Enter the First String:") textOne = str(input()) print("Enter the Second String:") textTwo = str(input()) found=0 notFound=0 lenOne = len(textOne) lenTwo = len(textTwo) if lenOne == lenTwo: for i in range(lenOne): found = 0 for j in range(lenOne): if textOne[i] == textTwo[j]: found = 1 break if found==0: notFound = 1 break if notFound==1: print("\nStrings are Not Anagram") else: print("\nStrings are Anagram") else: print("\nLength of Strings are not Equal")
Here is its sample run:
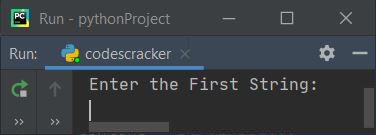
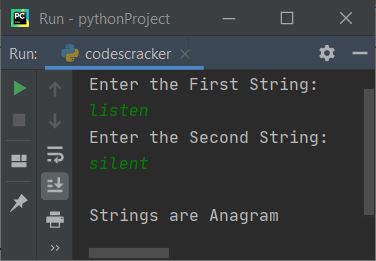
Now supply two strings input, say listen as the first string and silent as the second string, and press the ENTER key to check and print whether these two strings are anagrams or not, as shown in the snapshot given below:
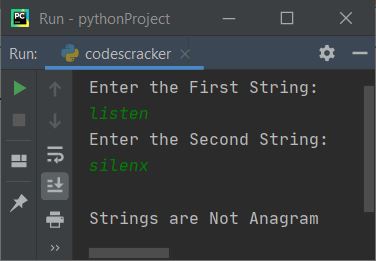
Here is another sample run with user input listen and silenx as the first and second strings:
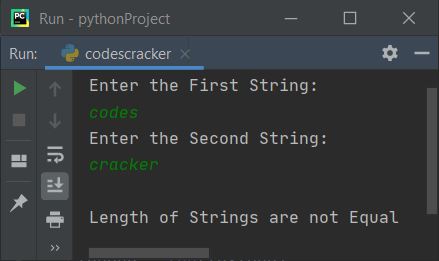
And here is the third sample run with user input codes and cracker as the first and second strings:
Note: The str() method is used to convert any type of value to a string type. And the len() method returns the length of the string passed as its argument.
The dry run of the above program with user input (listen and silent) goes like this:
- Initial values: textOne = listen (entered by the user), textTwo = silent (entered by the user), found = 0, notFound = 0.
- Now, using the len() method, the length of the first and second strings get initialized to the lenOne and lenTwo variables, respectively. So lenOne = 6 and lenTwo = 6.
- Since the condition (of if) lenOne == lenTwo or 6 == 6 evaluates to true, program flow goes inside this if's body.
- The range() function returns a sequence of values, starting with 0 and incrementing by 1 each time, by default. Continues until lenOne-1, since lenOne is provided as its argument.
- Therefore, at first execution, i's value is 0, so i<lenOne or 0<6 evaluates to true, and therefore program flow goes inside this for loop's body.
- And 0 gets initialized to found. Now there is another for loop that gets executed.
- So j=0 and since 0 is less than lenOne's value, the condition evaluates to true, and therefore program flow goes inside this for loop's body.
- Inside this loop, I've compared the character at the current index of the first string to all the characters of the second string. That is, if the character of the first string matches any character of the second string, then 1 gets stored to the found variable, and using the break keyword, the remaining execution of this for loop gets skipped.
- And using the found==0 condition, we've checked whether program flow goes inside the previous if's body or not. That is, if the previous if's condition evaluates to true, then we've got to continue; otherwise, initialize 1 to notFound and, using the break keyword, skip the remaining execution of the outer for loop.
- In this way, I've compared in a character-by-character manner and checked whether two strings entered by the user are anagrams or not.
- Since each and every character of the first string is available in the second string, therefore program flow never goes inside the body of if whose condition is found==0. So that 1 never gets initialized to the notFound variable. And the condition notFound==1 doesn't evaluate to true, so else's statement gets executed.
- That prints Strings are Anagram.
Modified version of the previous program
This program uses the sorted() method to sort the string and compares strings in a character-by-character manner to check whether two strings are anagrams or not. The end= is used to skip inserting an automatic newline using print().
print(end="Enter the First String: ") textOne = str(input()) print(end="Enter the Second String: ") textTwo = str(input()) lenOne = len(textOne) lenTwo = len(textTwo) notFound=0 if lenOne == lenTwo: textOne = sorted(textOne) textTwo = sorted(textTwo) for i in range(lenOne): if textOne[i] != textTwo[i]: notFound=1 break if notFound==0: print("\nStrings are Anagram") else: print("\nStrings are Not Anagram") else: print("\nLength of Strings are not Equal")
Here is its sample run with user input (creative and reactive) as two strings:
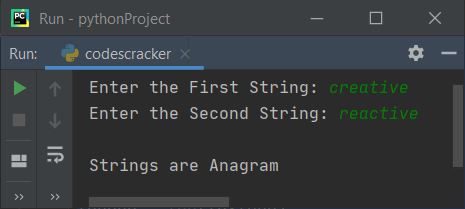
Check anagram strings using sorted()
This program uses the sorted() method to do the same job as the previous program did. The two strings entered by the user get compared directly using the == operator.
print("Enter First String: ", end="") textOne = str(input()) print("Enter Second String: ", end="") textTwo = str(input()) lenOne = len(textOne) lenTwo = len(textTwo) if lenOne == lenTwo: if sorted(textOne) == sorted(textTwo): print("\nStrings are Anagram") else: print("\nStrings are Not Anagram") else: print("\nLength of Strings are not Equal")
Here is its sample run with user input, sadder and dreads:
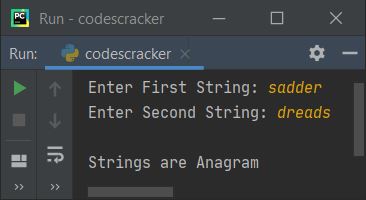
Check anagram strings using the function
This program is created using a user-defined function named CheckAnag(). The function receives two strings as its arguments and returns 1 if both strings are anagrams.
def CheckAnag(sOne, sTwo): if sorted(sOne) == sorted(sTwo): return 1 print("Enter First String: ", end="") textOne = str(input()) print("Enter Second String: ", end="") textTwo = str(input()) rVal = CheckAnag(textOne, textTwo) if rVal==1: print("\nStrings are Anagram") else: print("\nStrings are Not Anagram")
Check anagram strings using Class
This is the last program created using classes, an object-oriented feature of Python. To access the member functions of a class, an object is required. Therefore, an object named obj is created of class CodesCracker to access its member function named CheckAnag() using the dot (.) operator.
class CodesCracker: def CheckAnag(self, sOne, sTwo): if sorted(sOne) == sorted(sTwo): return 1 print("Enter First String: ", end="") textOne = str(input()) print("Enter Second String: ", end="") textTwo = str(input()) obj = CodesCracker() rVal = obj.CheckAnag(textOne, textTwo) if rVal==1: print("\nStrings are Anagram") else: print("\nStrings are Not Anagram")
« Previous Program Next Program »