- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
Variables in PHP with examples
Variables in PHP are basically a single or a combination of characters, followed by a $ sign, used to store information. Therefore, we can also say that variables are the containers used to store information. For example:
<?php $x = "codescracker.com"; echo "$x"; ?>
The output of the above PHP example is shown in the snapshot given below:
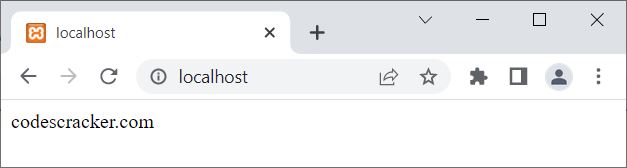
Note: The echo statement or keyword is used to output data.
In the above example, the variable $x stores codescracker.com. Therefore, using the statement:
echo "$x";
The value of $x was printed on the output.
Rules to Name a Variable in PHP
The first and most important rule to remember when creating/naming variables in PHP is that every variable must begin with a $ character.
The second rule is that every variable must start with either alphabetic characters (A-Z, a-z) or an underscore character (_).
The third rule is that every variable must be named using either alphanumeric characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9) or an underscore character (_).
The fourth rule is: do not forget that variables in PHP are case-sensitive. It means that $x and $X are two different variables. Similarly, $city, $City, and $CITY are all three different variables.
Here is a list of some valid variable names in PHP:
- $x
- $y
- $city
- $mycity
- $my_city
- $MyCity
- $myCity
- $_city
- $_city_
- $address
- $address23
- $address23albert
Let me create an example that uses all the above valid PHP variables:
<?php $x = 1; $y = 2; $city = "Vancouver"; $mycity = "Munich"; $my_city = "Munich, Germany"; $MyCity = "Nymphenburg Palace, Munich - Germany"; $myCity = "Munich, Germany, Europe"; $_city = "Frankfurt"; $_city_ = "Helsinki"; $address = "Wellington Street, Toronto, Ontario(ON)"; $address23 = "154 Wellington Street, Toronto, Ontario(ON)"; $address23albert = "100 Main St., Lucky Lake, Saskatchewan(SK)"; echo "<p>$x</p>"; echo "<p>$y</p>"; echo "<p>$city</p>"; echo "<p>$mycity</p>"; echo "<p>$my_city</p>"; echo "<p>$MyCity</p>"; echo "<p>$myCity</p>"; echo "<p>$_city</p>"; echo "<p>$_city_</p>"; echo "<p>$address</p>"; echo "<p>$address23</p>"; echo "<p>$address23albert</p>"; ?>
The output of this example is:
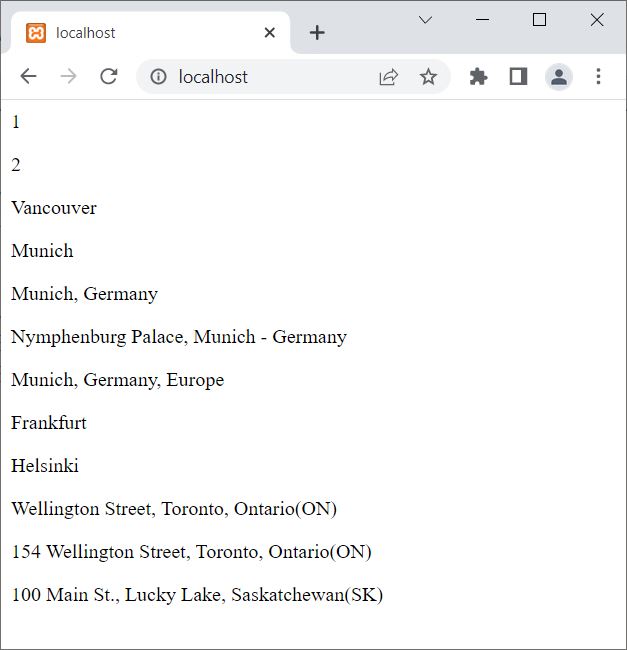
Note: Variables in PHP must not contain spaces. Also, when naming a variable in PHP, you cannot use a special character.
In PHP, a variable is created when a value is assigned to it.
Note: Since PHP is a loosely typed language, the type of the variable depends on the value assigned to it. For example:
<?php $x = 123; echo $x; $x = "codescracker.com"; echo $x; ?>
The output of the above PHP example should be 123codescracker.com. In the preceding example, the same variable, $x, first holds the value 123, which is an integer type value, and then I've assigned a string to it.
PHP Variable Scope
This article is created to cover the topic of the scope of a variable in PHP.
Variable scope in PHP is one of the important topics, as we must know whether:
- A variable defined outside a function can be accessed inside the function or not.
- A variable defined inside the function can be accessed from outside the function or not.
- What to do if we need to preserve the previous value of a variable defined inside a function?
- and so on.
There are the following three variable scopes available in PHP:
PHP Local Variable
Local variables in PHP are those variables that are defined within a function. And the scope of those variables is limited to that particular function where they are defined. For example:
<?php
function codescracker()
{
$x = 500;
echo $x;
}
codescracker();
?>
The output produced by the above PHP example is shown in the snapshot given below:
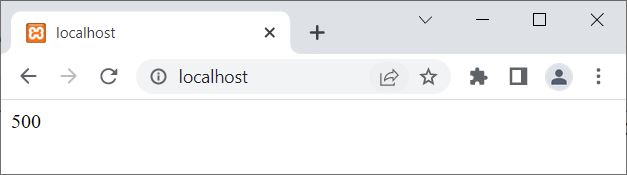
The variable $x defined inside the function named codescracker() is only accessible inside the function. Now the question is, what if we try to access a local variable from outside the function where it is defined? Let's find out, using the example given below:
<?php
function codescracker()
{
$x = 500;
}
echo $x;
?>
This time, the output produced by the above example is:
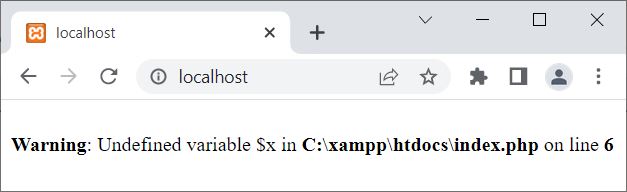
The same output you will get if you try to access a local variable from outside the scope where it is defined.
PHP Global Variable
Global variables in PHP are those variables that are defined outside a function. And the scope of those variables is everywhere except for the function(s). For example:
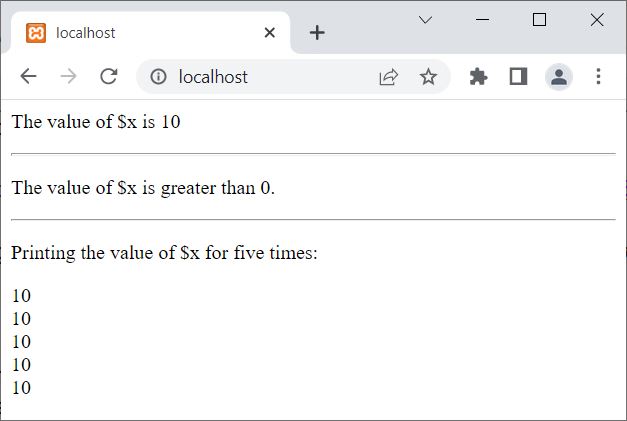
<?php
$x = 10;
echo "<p>The value of \$x is $x</p><hr>";
if($x>0)
echo "<p>The value of \$x is greater than 0.</p><hr>";
echo "<p>Printing the value of \$x for five times:</p>";
for($i=0; $i<5; $i++)
echo "$x<BR>";
?>
The output of the above PHP example is:
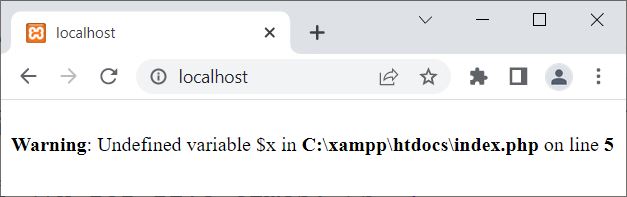
Now the question is, what if we try to access a variable declared outside a function from inside a function? Let's find out, using an example given below:
<?php
$x = 10;
function codescracker()
{
echo $x;
}
codescracker();
?>
Now the output produced by this example is:
You will get similar output every time you try to access a variable from inside a function that is defined outside the function. But PHP has a solution to use global variables from inside the function. The solution is the global keyword, which is defined right after this paragraph.
PHP global keyword
Use the "global" keyword to declare a global variable inside a function to be able to access that global variable in this way:
function functionName()
{
global variableName;
}
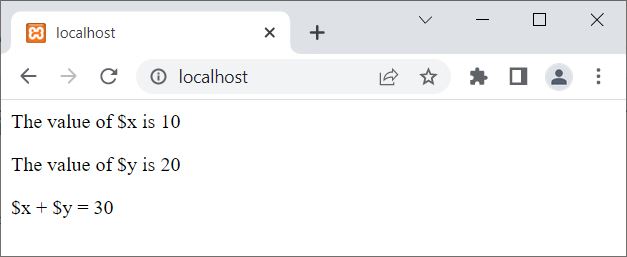
That is, use the global keyword to declare all the global variables inside the function where you want to use them. For example:
<?php
$x = 10;
$y = 20;
function codescracker()
{
global $x;
echo "<p>The value of \$x is $x</p>";
global $y;
echo "<p>The value of \$y is $y</p>";
$z = $x + $y;
echo "<p>\$x + \$y = $z</p>";
}
codescracker();
?>
The output of the above PHP example is:
However, PHP stores all variables that are declared globally in an array named $GLOBALS[variable]. Therefore, we can use this array to access and update a global variable from within a function. For example:
<?php
$x = 10;
$y = 20;
function codescracker()
{
echo "<p>The value of \$x is ", $GLOBALS['x'], "</p>";
echo "<p>The value of \$y is ", $GLOBALS['y'], "</p>";
$z = $GLOBALS['x'] + $GLOBALS['y'];
echo "<p>\$x + \$y = $z</p>";
}
codescracker();
?>
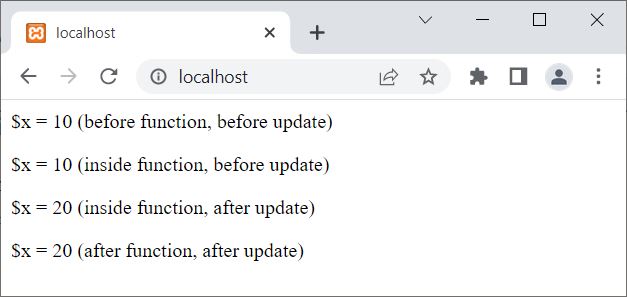
You will get the same output as in the previous example. Let me create another example, where I'm going to update the global variable from within the function:
<?php
$x = 10;
echo "<p>\$x = $x (before function, before update)</p>";
function codescracker()
{
echo "<p>\$x = ", $GLOBALS['x'], " (inside function, before update)</p>";
$GLOBALS['x'] = 20;
echo "<p>\$x = ", $GLOBALS['x'], " (inside function, after update)</p>";
}
codescracker();
echo "<p>\$x = $x (after function, after update)</p>";
?>
Now the output of this PHP example is:
PHP Static Variables
Static variables are those variables that preserve their previous value during the execution of a function. To create a static variable, we need to use the "static" keyword before the variable to make it static.
The PHP static keyword comes into play when we need to execute a function multiple times, preserving or using its previous values. As normally happens, variables get deleted after the execution of a function. For example:
<?php
function codes()
{
$x = 100;
echo "<p>$x</p>";
$x++;
}
codes();
codes();
codes();
codes();
echo "<hr>";
function cracker()
{
static $y = 200;
echo "<p>$y</p>";
$y++;
}
cracker();
cracker();
cracker();
cracker();
?>
The output of the above PHP example on a static variable is shown in the snapshot given below:
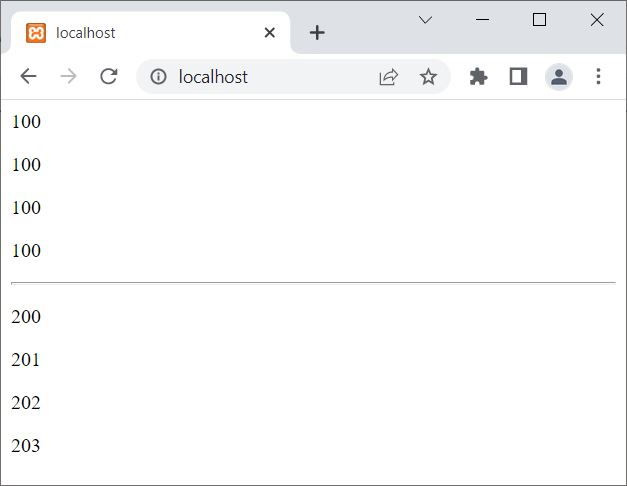
In the above example, the variable $x inside the first function, which is codes(), is defined as usual; therefore, every time after executing the function, its value gets printed, and the variable gets deleted. However, consider the variable $y defined in the second function with the static keyword, which makes the variable $y static. Therefore, it preserves its previous value, even after executing the function.
Here is another example of a static variable in PHP:
<?php
function codescracker()
{
static $num = 2;
echo "--Table of $num--<BR>";
for($i=1; $i<=10; $i++)
echo "$num * $i = ", $num*$i, "<BR>";
$num++;
}
codescracker();
echo "<HR>";
codescracker();
?>
The snapshot given below shows the sample output produced by the above PHP example:
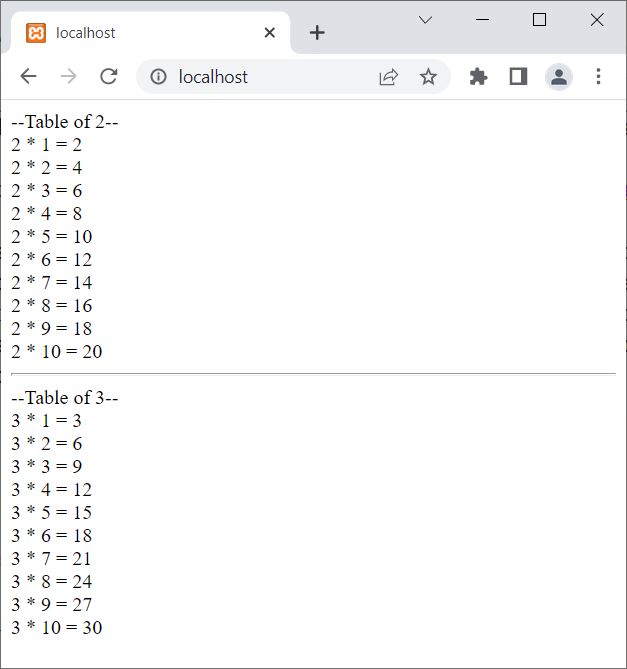
PHP gettype() | Find/Get Type of Variable
The PHP gettype() function is used when we need to find or get the type of a variable. For example:
<?php
$x = 10;
echo gettype($x), "<BR>";
$x = 10.23;
echo gettype($x), "<BR>";
$x = "Hi, there!";
echo gettype($x), "<BR>";
$x = array("Berlin", "Munich", "Frankfurt");
echo gettype($x), "<BR>";
$x = false;
echo gettype($x), "<BR>";
$x = NULL;
echo gettype($x), "<BR>";
class myClass{
}
$x = new myClass();
echo gettype($x), "<BR>";
?>
The output produced by the above PHP example of using the gettype() function to find and print the type of each variable one by one is shown in the snapshot given below:
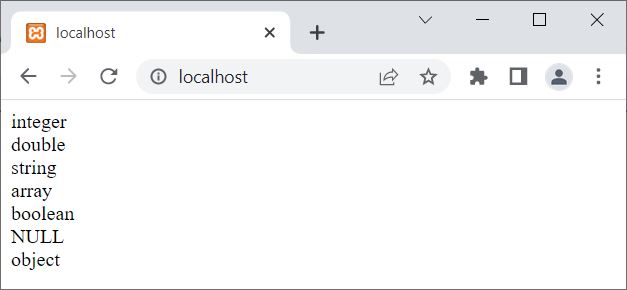
PHP gettype() Syntax
The syntax of the gettype() function in PHP is:
gettype(variable);
The required variable parameter refers to a variable whose type we need to find.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »