- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
break and continue Statement in PHP
This article is created to cover the two important statements or keywords in PHP, which are:
PHP break statement
The PHP break keyword or statement is used when we need to exit from the current loop or switch structure. For example:
<?php
for($i=1; $i<10; $i++)
{
if($i>5)
break;
echo $i;
echo "<BR>";
}
?>
The snapshot given below shows the output produced by this PHP example on the break statement:
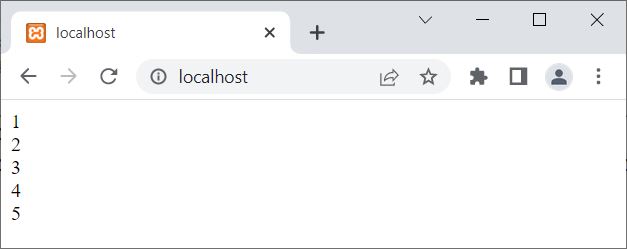
In the above example, when the value of $i becomes greater than 5, that is, when the value of $i becomes 6, then the condition $i>5 or 6>5 evaluates to be true, and therefore, the program flow goes inside the if block and the "break;" statement gets executed, which skips the remaining execution of the current for loop. Therefore, we only get the output from 1 to 5.
The break statement skips the execution of the remaining statement(s) (if any) along with all the remaining iterations of the current loop.
The break statement can also be used to stop the execution of an infinite loop (the loop whose condition always evaluates to true). For example:
<?php
$num = 10;
while(true)
{
echo $num, "<BR>";
if($num==12)
break;
$num++;
echo $num, "<BR>";
}
?>
The output of this PHP example should be:
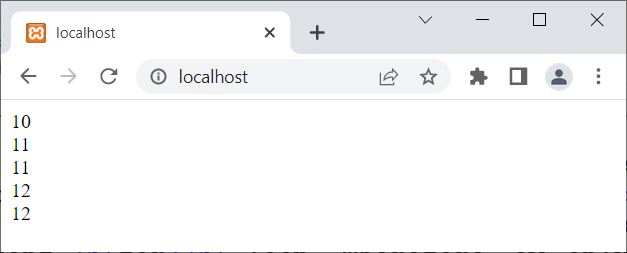
See the condition of the loop; it is true, which obviously evaluates to being true forever. Therefore, using the break statement, the execution of this loop ends.
The following is the dry run of the preceding example:
- The value 10 was initialized to the variable $num using the first statement.
- Now the execution of the while loop has started.
- Since the condition of the loop is true, therefore, the loop goes for its infinite execution.
- The value of $num is printed along with a line break using the BR tag in the first iteration using echo.
- Since the condition $num==12 or 10==12 evaluates to false, program flow will not go inside the if block to execute the break statement.
- The value of $num gets incremented by 1. Now $num=11.
- The value of $num again gets printed along with a line break.
- Now the second iteration of the loop starts.
- This process continues until the value of $num becomes 12.
- When the value of $num becomes 12, the condition $num==12 (of if) evaluates to true, and the break; statement gets executed, which forces the while loop to stop its execution.
PHP continue statement
The PHP continue statement or keyword is used when we need to skip the execution of remaining statement(s) for the current iteration of the current loop and continue for the next iteration of the current loop. For example:
<?php
for($i=1; $i<10; $i++)
{
if($i==5)
continue;
echo $i;
echo "<BR>";
}
?>
The output of the above PHP example on the continue statement is:
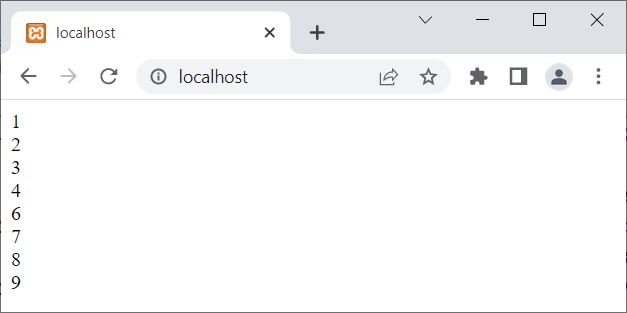
In the above example, when the value of $i becomes 5, the condition $i==5 evaluates to be true. Therefore, the continue statement gets executed, which forces the program to jump and continue the execution of the next iteration of the current loop. That is, the two echo statements get skipped for that iteration.
Difference between break and continue in PHP
The break is used to skip all the remaining executions and iterations of the current loop. where the continue keyword is used to skip the execution of the remaining statement(s) of the current iteration of the current loop. For example:
<?php
echo "<h2>Using the break Statement</h2>";
for($i=1; $i<=5; $i++)
{
if($i==3)
break;
echo $i, "<BR>";
}
echo "<h2>Using the continue Statement</h2>";
for($i=1; $i<=5; $i++)
{
if($i==3)
continue;
echo $i, "<BR>";
}
?>
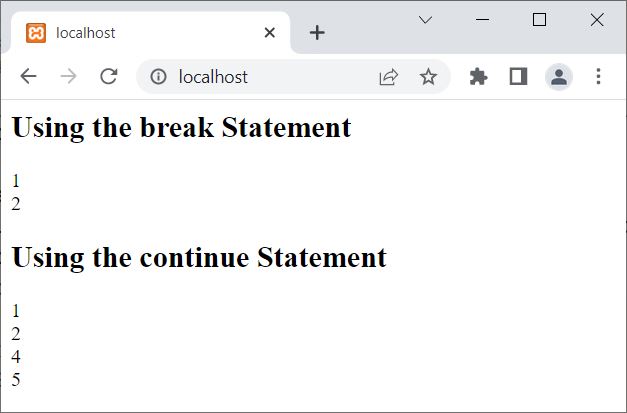
The output of the above PHP example is:
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »