- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
PHP code to create a file
This article is created to cover multiple scripts or programs in PHP to create a file. To create a file in PHP, use any of the following modes:
- w
- w+
- a
- a+
- x
- x+
- c
- c+
The last four modes, which are x, x+, c, and c+, only create a new file if the specified file does not exit.
PHP Create a File Example
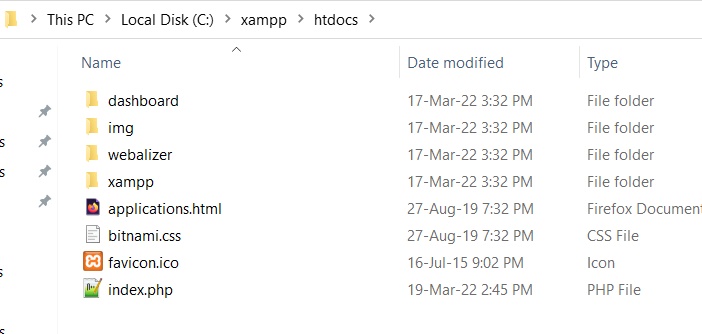
Here is a snapshot of the folder before executing the PHP script to create a file:
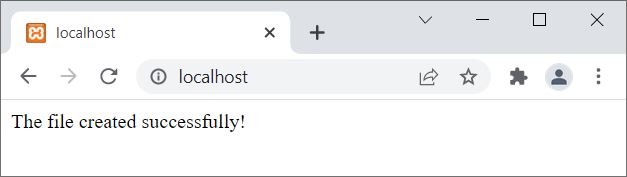
Now the PHP script to create a new file is:
<?php
if(fopen("codescracker.txt", "w"))
echo "The file created successfully!";
else
echo "The file already exists.";
?>
The output of the above PHP example is:
After running the above PHP script to make a new file, here is a snapshot of the same folder (the current directory):
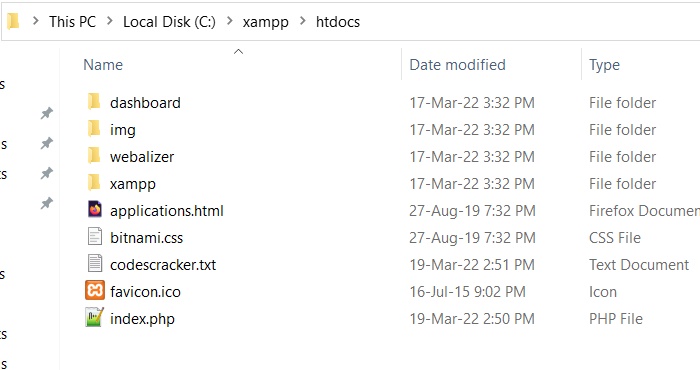
Note: The fopen() function opens a file. And with the "w" mode given to this function, it creates a new file and then opens that file.
Create a file if it doesn't exist in PHP
This section is created to cover a program in PHP that creates a new file only if the specified file does not exist.
The x mode is used when we need to create a file only if the specified file does not exist. For example:
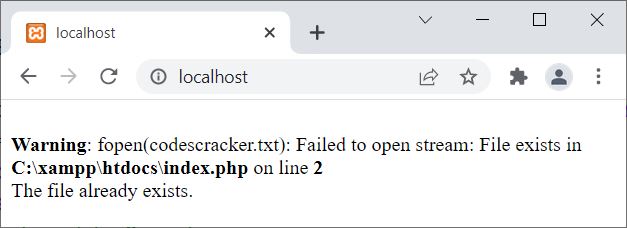
<?php
$fs = fopen("codescracker.txt", "x");
if($fs)
echo "The file created successfully!";
else
echo "The file already exists.";
?>
Since the file codescracker.txt already exists in the current directory. Therefore, the output produced by the above PHP example is:
The same program can also be created in this way:
<?php
if(fopen("codescracker.txt", "x"))
echo "The file created successfully!";
else
echo "The file already exists.";
?>
To hide the default error message, use the @ character before the fopen() function. For example:
<?php
if(@fopen("codescracker.txt", "x"))
echo "The file created successfully!";
else
echo "The file already exists.";
?>
Now the output produced by the above PHP example is:
Let me tell you again: if the specified file does not exist, a new one with the specified name will get created. For example, let me create another example in which I will provide the name of a file that does not exist in the current directory:
<?php
if(@fopen("temp.txt", "x"))
echo "The file created successfully!";
else
echo "The file already exists.";
?>
Since the file temp.txt is not available in the current directory, it will be created, and the output produced by the above PHP example should be "The file created successfully!"
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »