- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
PHP file(): Read a file into an array by lines
The PHP file() function is used when we need to get the whole content of a file as an array. For example:
<?php
$x = file("codescracker.txt");
print_r($x);
?>
The output of the above PHP example on the file() function is:
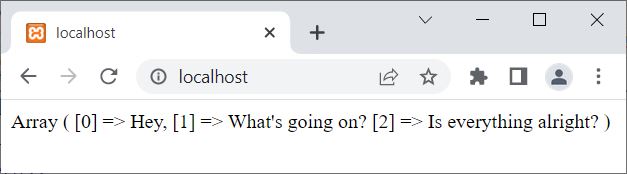
That is, the file() function reads a file into an array, where each line of the file becomes an element of the array. And since there are three lines, the file codescracker.txt contains them; therefore, we have seen the above output.
Also, if we write:
echo $x[0];
Or,
print_r($x[0]);
We will get the same output using both of the above statements; that will be the first line of the file. For example:
<?php
$x = file("codescracker.txt");
echo $x[0];
echo "<br>";
echo $x[1];
echo "<br>";
echo $x[2];
?>
Now the output of the above PHP example is:
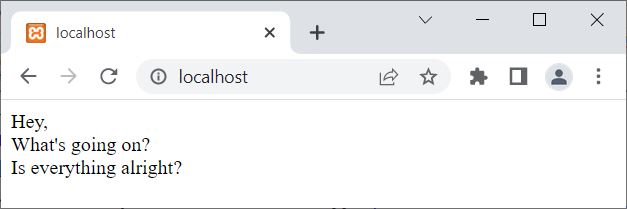
PHP file() Syntax
The syntax of the file() function in PHP is:
file(filename, flag, context)
The first parameter (filename) is required, whereas the last two (flag and context) parameters are optional.
Note: The filename parameter is used to specify the name of a file along with its extension, available in the current directory (the directory where the PHP code to read the file using file() is saved).
Note: The flag parameter is used to specify the flag value using:
- FILE_USE_INCLUDE_PATH: Used when we need to search the file in the include_path (in PHP.ini).
- FILE_IGNORE_NEW_LINES: Used when we need to omit the newline at the end of each element.
- FILE_SKIP_EMPTY_LINES: Used when we need to omit empty lines.
Note: The context is used when we need to specify the resource of the context stream.
Advantages of the file() function in PHP
- The file() function reads a file in one line of code.
- The file() function reads each file line without a loop.
- The file() function supports text, CSV, and XML files.
- PHP array functions make file manipulation easy since the function returns an array.
Disadvantages of the file() function in PHP
- For large files, the file() function reads the entire file into an array, which uses a lot of memory. This can slow or crash the script.
- If the user controls the file being read, the file() function can be dangerous. Malicious users can access sensitive server files.
- The file() function cannot skip lines or read specific file sections.
- The file() function does not provide detailed error messages if the file cannot be read, making file reading issues difficult to troubleshoot.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »