- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
PHP mysqli code to store form data in a database
This article is created to describe the way to store form data or the data entered by a user on the web, using PHP mysqli object-oriented and procedural scripts.
Store form data using PHP mysqli object-oriented script
I really do not know about your requirement for saving or storing user form data in the database. I mean, what type of data do you need to store? But here, I am going to create a form where users fill in their username along with a comment to store in the database.
Whatever the data you need to store, the process will be the same, as shown in the example given below:
<?php
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$server = "localhost";
$user = "root";
$pass = "";
$db = "codescracker";
$conn = new mysqli($server, $user, $pass, $db);
if($conn -> connect_errno)
{
echo "Database connection failed!<BR>";
echo "Reason: ", $conn -> connect_error;
exit();
}
else
{
$user = $_POST["user"];
$data = $_POST["data"];
$sql = "INSERT INTO comments(user, data)
VALUES('$user', '$data');";
$res = $conn -> query($sql);
if($res)
{
echo "Data inserted into the database successfully!";
// block of code to process further...
}
else
{
echo "Something went wrong!<BR>";
echo "Error description: ", $conn -> error;
exit();
}
}
$conn -> close();
}
?>
<HTML>
<BODY>
<FORM METHOD="POST">
Enter Data:<BR>
<INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="user" MAXLENGTH="40" PLACEHOLDER="Enter Username"><BR>
<TEXTAREA TYPE="text" STYLE="height:60px;" NAME="data" MAXLENGTH="240" PLACEHOLDER="Write Comment"></TEXTAREA><BR>
<INPUT TYPE="submit" NAME="comment" VALUE="Submit">
</FORM>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Before executing the above example of storing form data in a database, a database named codescracker must be available, in which a table named comments must have the following fields:
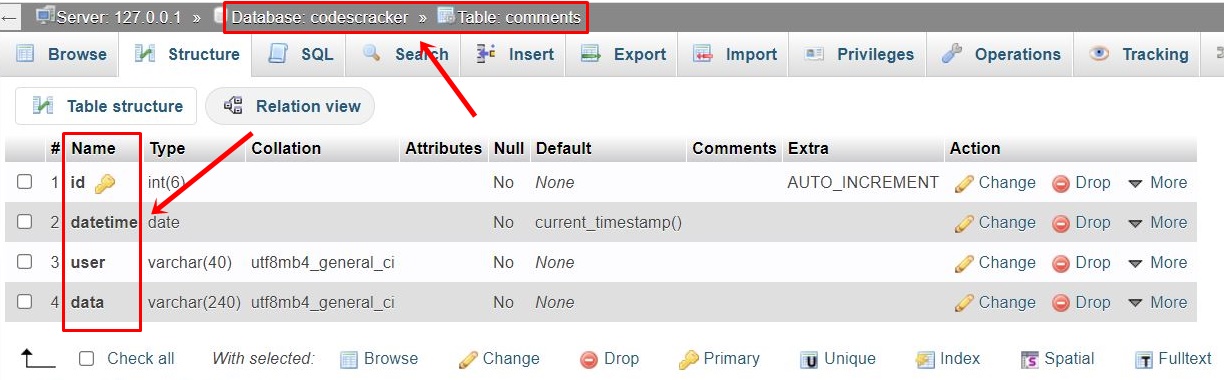
All the data, should be stored in this table. Now here is the sample initial output produced by above PHP mysqli object-oriented script to store user data in the database:
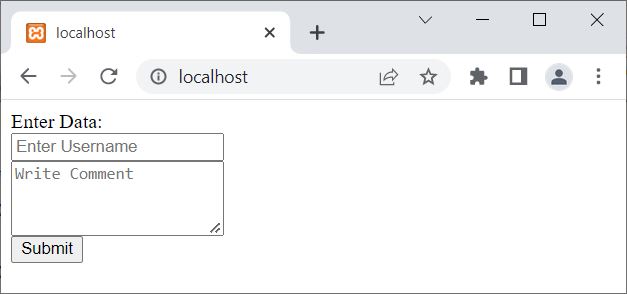
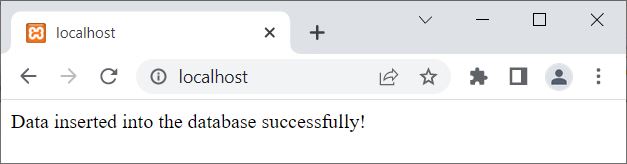
Now enter the data, say codescracker in the Username field, whereas
PHP is Fun?
Is not it?
in Comment field. And then hit Submit button. Here is the output, which you will see:
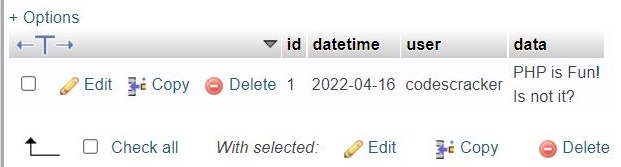
Here is the snapshot of the table, customer, after executing the above script:
Note: The mysqli() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in object-oriented style.
Note: The new keyword is used to create a new object.
Note: The connect_errno is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in object-oriented style.
Note: The connect_error is used to get the error description (if any) from the last connection in object-oriented style.
Note: The query() function is used to perform queries on the MySQL database in object-oriented style.
Note: The error is used to return the description of the error (if any) from the most recent function call in object-oriented style.
Note: The exit() function is used to terminate the execution of the current PHP script.
Note: The close() function is used to close an opened connection in object-oriented style.
The above example can also be created in this way:
<?php
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "codescracker");
if(!$conn -> connect_errno)
{
$user = $_POST["user"];
$data = $_POST["data"];
$sql = "INSERT INTO comments(user, data)
VALUES('$user', '$data');";
if($conn -> query($sql))
echo "Data inserted into the database successfully!";
}
$conn -> close();
}
?>
<HTML>
<BODY>
<FORM METHOD="POST">
Enter Data:<BR>
<INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="user" MAXLENGTH="40" PLACEHOLDER="Enter Username"><BR>
<TEXTAREA TYPE="text" STYLE="height:60px;" NAME="data" MAXLENGTH="240" PLACEHOLDER="Write Comment"></TEXTAREA><BR>
<INPUT TYPE="submit" NAME="comment" VALUE="Submit">
</FORM>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Store Form Data using PHP mysqli Procedural Script
To store form data using a PHP mysqli procedural script, follow the example given below:
<?php
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$conn = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "", "codescracker");
if(mysqli_connect_errno())
{
echo "Database connection failed!<BR>";
echo "Reason: ", mysqli_connect_error();
exit();
}
else
{
$user = $_POST["user"];
$data = $_POST["data"];
$sql = "INSERT INTO comments(user, data)
VALUES('$user', '$data');";
if(mysqli_query($conn, $sql))
echo "Data inserted into the database successfully!";
else
{
echo "Something went wrong!<BR>";
echo "Error description: ", $conn -> error;
exit();
}
}
mysqli_close($conn);
}
?>
<HTML>
<BODY>
<FORM METHOD="POST">
Enter Data:<BR>
<INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="user" MAXLENGTH="40" PLACEHOLDER="Enter Username"><BR>
<TEXTAREA TYPE="text" STYLE="height:60px;" NAME="data" MAXLENGTH="240" PLACEHOLDER="Write Comment"></TEXTAREA><BR>
<INPUT TYPE="submit" NAME="comment" VALUE="Submit">
</FORM>
</BODY>
</HTML>
Note: The mysqli_connect() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_connect_errno() is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_connect_error() function is used to return the error description (if any) from the last connection in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_query() function is used to perform queries on the MySQL database in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_error() function is used to return the description of the error (if any) from the most recent function call in object-oriented style.
Note: The mysqli_close() function is used to close an opened connection to the MySQL database in procedural style.
The examples given above look very simple and basic. Also, the data are getting saved in the database without even a basic filter, which may be sometimes malicious. Therefore, let me create another safe and secure PHP mysqli script that does the same job of storing form data in a database.
PHP mysqli Safe and Secure Script to Save Form Data in a Database
This example of storing user form data in a database was created using PHP mysqli safe and secure object-oriented script.
<?php
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "codescracker");
if($conn->connect_errno)
{
echo "Database connection failed!<BR>";
echo "Reason: ", $conn->connect_error;
exit();
}
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
function validate($x)
{
$x = trim($x);
$x = stripslashes($x);
$x = htmlspecialchars($x);
return $x;
}
$stmt = $conn->prepare("INSERT INTO comments(user, data) VALUES (?, ?)");
$stmt->bind_param("ss", $user, $data);
$user = validate($_POST["user"]);
$data = validate($_POST["data"]);
if($stmt->execute())
echo "Your comment posted successfully!";
}
?>
<HEAD>
<STYLE>
.myForm{width: 380px; margin: auto; padding: 12px;}
.myForm h2{text-align: center;}
.myForm input, textarea{width: 100%;}
.myForm input{padding: 8px; margin-bottom: 8px;}
.myForm textarea{height: 80px; padding: 8px; margin-bottom: 8px;}
button{width: 100%; background-color: #008080; color: white; font-size: 1em; padding: 12px;}
button:hover{cursor: pointer;}
.display{width: 380px; margin: auto; border-left: 2px solid #ccc; padding: 12px;}
.commentBox{margin-bottom: 12px;}
.right{text-align: right;}
</STYLE>
<HTML>
<BODY>
<DIV CLASS="myForm">
<FORM METHOD="POST">
<h2>Enter the Comment</h2>
<INPUT TYPE="text" NAME="user" MAXLENGTH="40" PLACEHOLDER="Enter Username"><BR>
<TEXTAREA TYPE="text" NAME="data" MAXLENGTH="240" PLACEHOLDER="Write Comment"></TEXTAREA><BR>
<BUTTON TYPE="submit">Post</BUTTON>
</FORM>
</DIV>
<DIV CLASS="display">
<h2>Latest Comments</h2>
<?php
$sql = "SELECT * FROM comments ORDER BY id DESC LIMIT 10";
if($result = $conn->query($sql))
{
while($row = $result->fetch_row())
{
echo "<div class=\"commentBox\">";
echo "By <B>", $row[2], "</B><BR>";
echo $row[3];
echo "<div class=\"right\">", $row[1], "</div>";
echo "</div>";
}
}
$conn->close();
?>
</DIV>
</BODY>
</HTML>
The output produced by the above PHP example is:
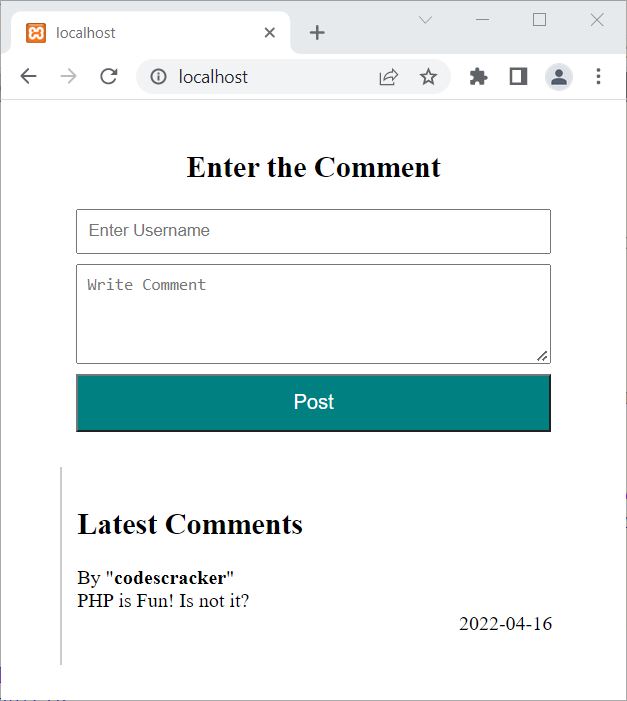
Now enter your username along with your comment, then hit the Post button to post your comment on the website. For example, let me type some random anonymous username along with a comment:
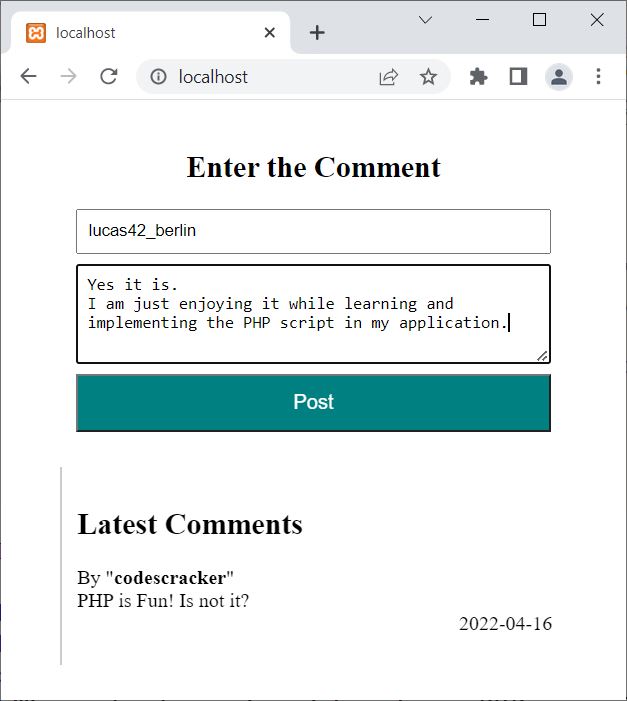
Now click on the Post button, and here is the new output:
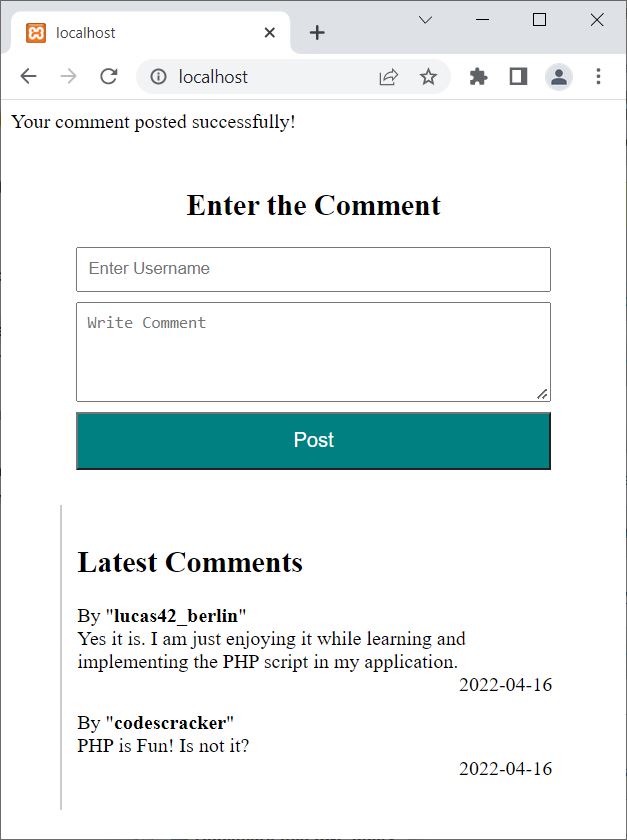
Notice your latest comment, which is now on the website.
Note: The prepare() function is used to prepare an SQL statement before its execution on the MySQL database in object-oriented style, to avoid SQL injection.
Note: The bind_param() function is used to bind variables to a prepared statement as parameters in object-oriented style.
Note: The execute() function is used to execute a prepared statement on the MySQL database in object-oriented style.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »