- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
PHP MySQL Create Database
A database consists of tables. A table stores information in the form of rows and columns. Therefore, to store information in your database, you need to create a database first.
We can follow any of the following approaches to create a database on our MySQL database server:
- Using manually
- Using PHP mysqli script
Note: A database consists of one or more tables. A table consists of one or more rows (records), where each row consists of one or more columns (fields).
PHP MySQL Create Database - Manually
In the previous post, I've already mentioned that I'm going to use XAMPP, which provides a MySQL database to work with. Therefore, to create a MySQL database manually, follow these steps:
Step No. 1: Open the XAMPP Control Panel.
Step No. 2: Click on Start, next to Apache.
Step No. 3: Click on Start, next to MySQL.
Step No. 4: Now click on Admin, next to MySQL, as shown in the snapshot of the XAMPP Control Panel window given below:
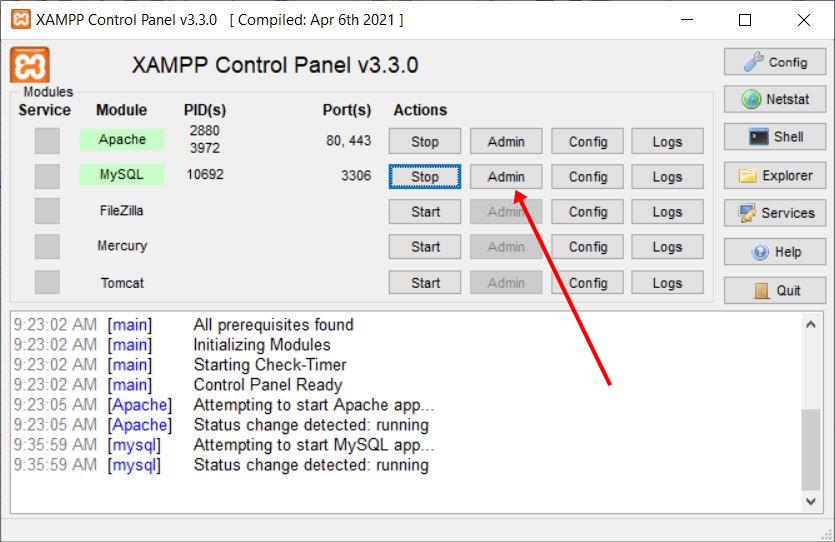
Step No.5: The window opened after clicking on the Admin, as directed above, looks like this:
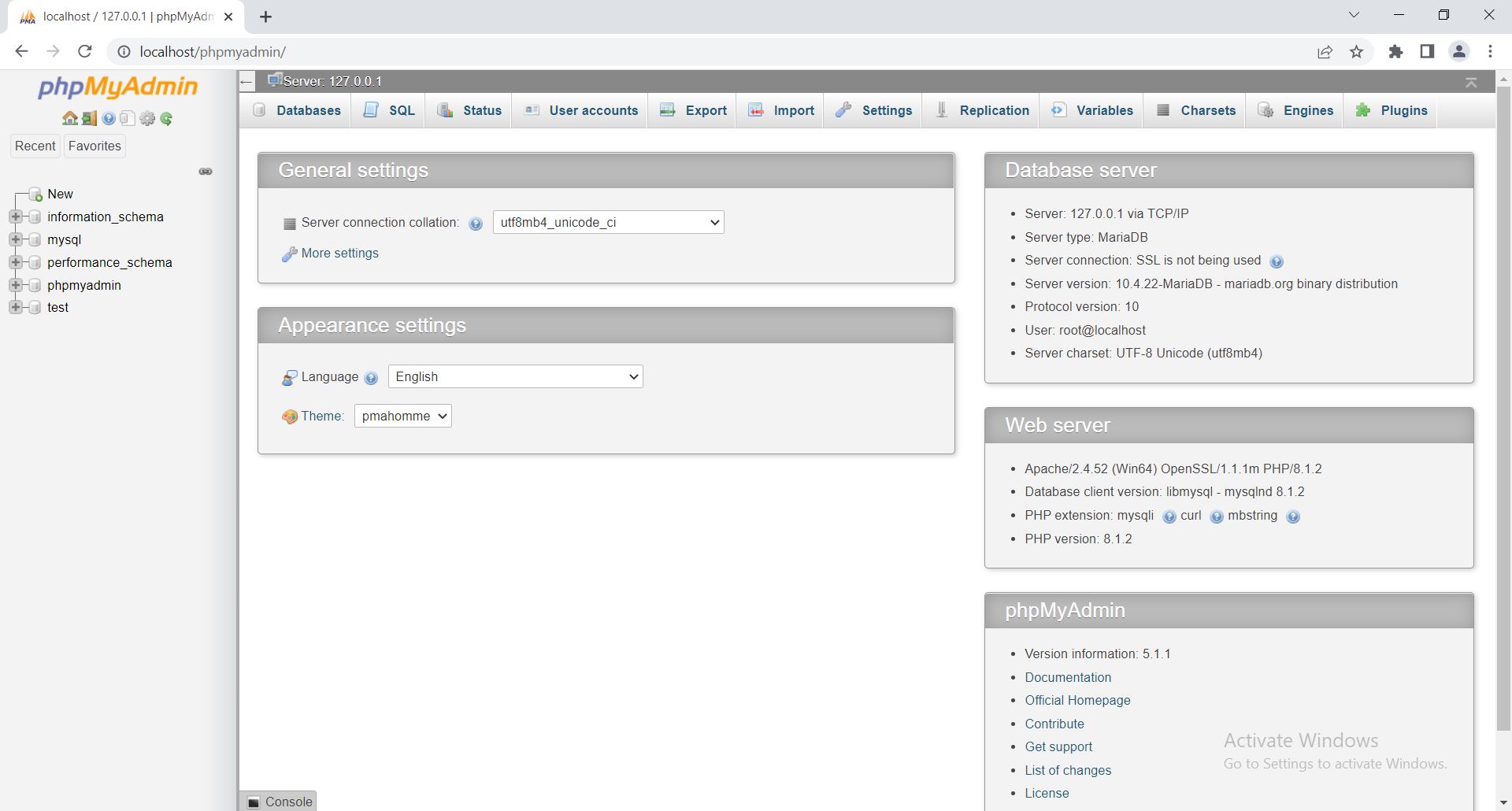
Step No.6: Click on the Databases available at the top left of the top menus, as shown in the snapshot given below:
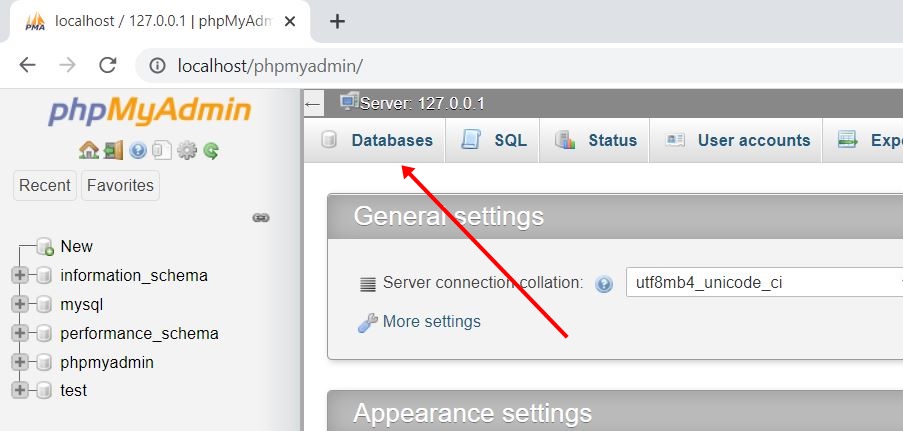
Step No.7: Enter the name of the database, say, codescracker, and click on the Create button, as shown in the snapshot given below:
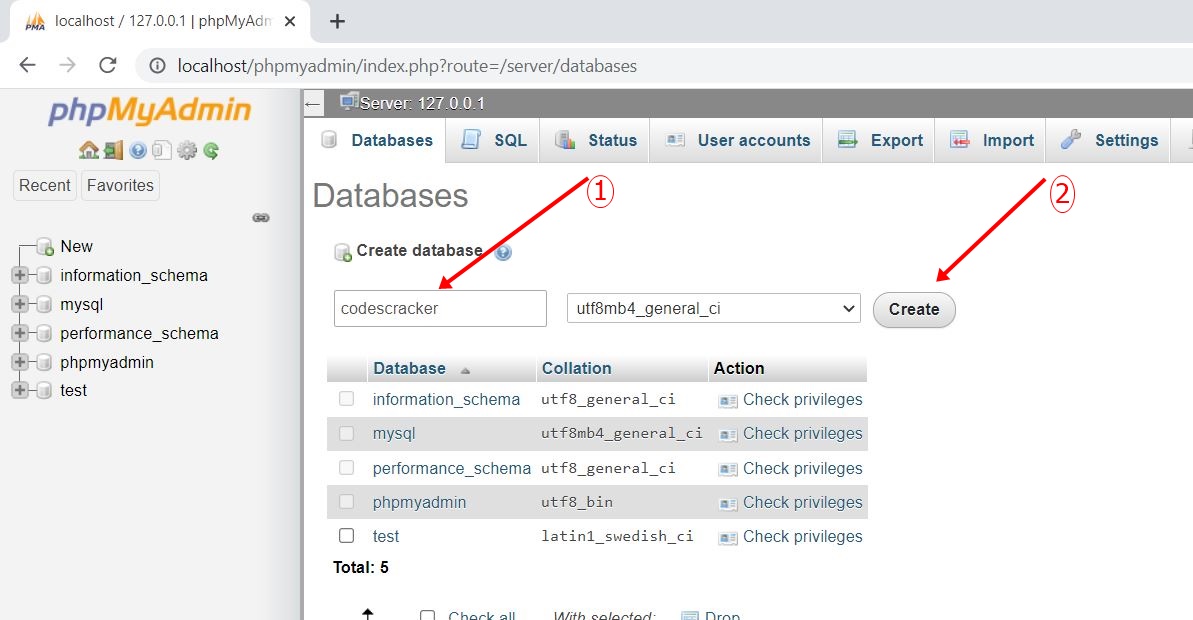
The database named codescracker is created successfully. If you see on the left menu, codescracker can be seen every time you open the MySQL Databases.
Create a MySQL database using PHP and the mysqli object-oriented script
To create a MySQL database using a PHP mysqli object-oriented script, follow the example given below:
<?php $servername = "localhost"; $username = "root"; $password = ""; // Opens a connection to the MySQL server $conn = new mysqli($servername, $username, $password); // Checks the connection if($conn->connect_errno) { echo "Database connection failed!<BR>"; echo "Reason: ", $conn->connect_error; exit(); } // Creates a database named "student" $sql = "CREATE DATABASE student"; $qry = $conn->query($sql); if($qry) { echo "Database created successfully."; // block of code to process further... } else { echo "Database has not been created!!<BR>"; echo "Reason: ", $conn->error; } $conn->close(); ?>
The output produced by the above PHP example of creating a database using the PHP mysqli script is shown in the snapshot given below:
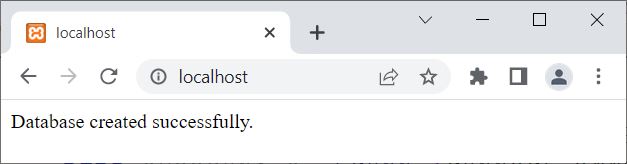
Now if you open the database server, a new database named student, will be available there.
Now let me re-execute the above PHP script again. Okay, here is the output I have:
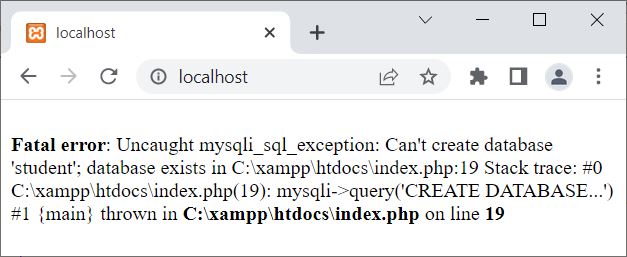
Since the database named student was already created, we are seeing this output. But the problem is, the error message displayed is not as I have written it in script. That is because of the default error reporting mode.
To get the manually written error message to be displayed instead of the default one, we need to change the error reporting mode, using either mysqli_report() (for procedural) or mysqli_driver() (for object-oriented). For example:
<?php
$driver = new mysqli_driver();
$driver -> report_mode = MYSQLI_REPORT_OFF;
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "");
if(!$conn->connect_errno)
{
if($conn->query("CREATE DATABASE student"))
echo "Database created successfully.";
else
echo "Error Occurred<BR>Reason: ", $conn->error;
}
$conn->close();
?>
Now the output should be:
Error Occurred Reason: Can't create database 'student'; database exists
ImportantSince we only need to provide the first three arguments to the mysqli() function to connect to the database server, therefore, if you want to use a specific port, connect through it. Then let me tell you, you always need to add or specify that port number on the fifth parameter. Therefore, just give an empty string, that is, "" as the fourth parameter (used for the database name), then use the fifth parameter to specify the port number. For example:
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "", 67);
to connect to the database server at port number 67.
Note: The mysqli() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in object-oriented style.
Note: The new keyword is used to create a new object.
Note: The connect_errno is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in object-oriented style.
Note: The connect_error is used to get the error description (if any) from the last connection in object-oriented style.
Note: The query() function is used to perform queries on the MySQL database in object-oriented style.
Note: The error is used to return the description of the error (if any) by the most recent function call in object-oriented style.
Note: The close() function is used to close an opened connection in object-oriented style.
Note: The mysqli_driver() is used to modify the error reporting mode in object-oriented style.
Create MySQL database using PHP mysqli procedural script
To create a MySQL database using PHP mysqli procedural script, here is an example you need to follow:
<?php
mysqli_report(MYSQLI_REPORT_OFF);
$conn = mysqli_connect("localhost", "root", "");
if($conn)
{
if(mysqli_query($conn, "CREATE DATABASE student"))
echo "Database created successfully.";
else
echo "Error Occurred<BR>Reason: ", mysqli_error($conn);
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
This script does the same job as the previous one.
Note: The mysqli_report() function is used to modify the error reporting mode in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_connect() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_connect_errno() function is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_error() function is used to return the description of the error (if any) from the most recent function call in object-oriented style.
Note: The mysqli_close() function is used to close an opened connection to the MySQL database in procedural style.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »