- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
PHP mysqli code to create a signup or registration page or form
This article is created to describe how a registration form or page can be created using PHP mysqli object-oriented and procedural scripts.
But before creating a registration form to allow users to register, store their data in the database. We need to create a database and then create a table inside it to store the user registration data.
Note: A database consists of one or multiple tables. A table consists of information in the form of rows (records) and columns (fields).
Note: I have created a database named codescracker. In this database, a table named users is created with the following columns:
- ID
- FirstName
- LastName
- Username
- Password
Here is a snapshot of the table available in my database:
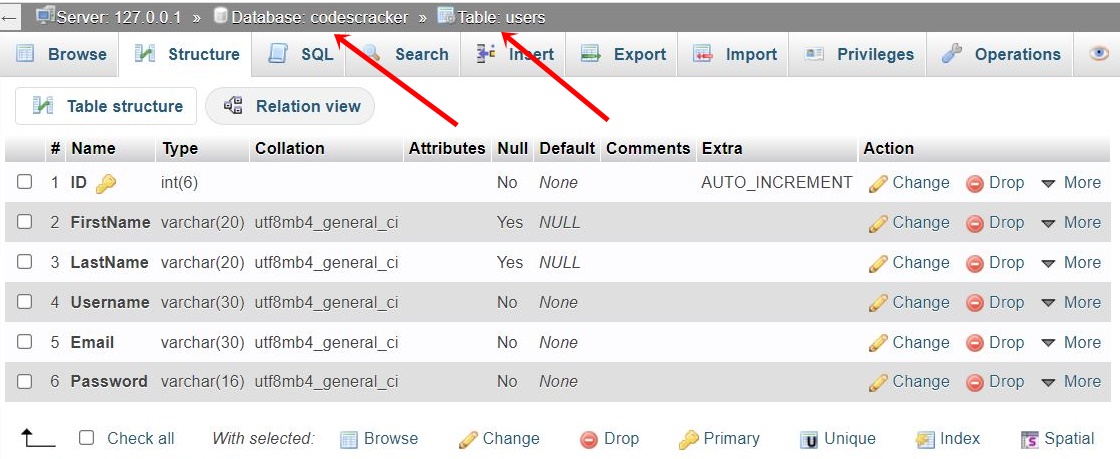
You can either follow the manual way to create this table or use the following SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE users (
ID INT(6) UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
FirstName VARCHAR(20),
LastName VARCHAR(20),
Username VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
Email VARCHAR(30) NOT NULL,
Password VARCHAR(16) NOT NULL )
You can also use your own custom table with custom fields (columns). But I recommend going with the same, to make understanding the things provided here much easier. After learning all the things given here, you can proceed to modify and implement them further to meet your own requirements.
PHP mysqli: Simple registration form
Before creating a complete version of the registration form or page, use the PHP mysqli script. Let's first create a simple and basic one. To create a simple and basic registration form, we need to take the following two steps:
- Step No. 1: Create a user registration form using simple HTML code.
- Step No. 2: Create a PHP mysqli script to get the form data and send or insert the data into the database.
PHP mysqli Registration Form, Step No. 1
Now let's create an HTML form to allow users to enter their data to register on the website. Here I am going to create a simple and basic HTML form to get the data from the user. Later, I will create the impressive one.
<H2>User Registration Form</H2> <FORM action="register.php" METHOD="post"> First Name: <INPUT type="text" name="firstname"><BR> Last Name: <INPUT type="text" name="lastname"><BR> Username: <INPUT type="text" name="username" required><BR> Email: <INPUT type="text" name="email" required><BR> Password: <INPUT type="text" name="password" required><BR> <BUTTON type="submit">Register</BUTTON><HR> <P>Already registered ? <a href="login.php">Login</a></P> </FORM>
The output produced by the above user registration form code is shown in the snapshot given below:
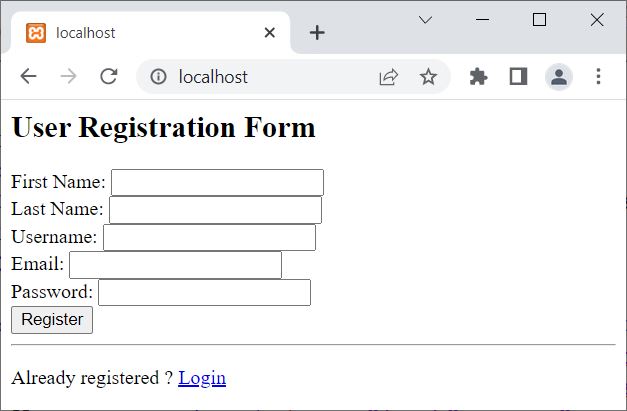
Notice the register.php page, assigned to the FORM action. That is, whatever the user enters into the form, the form data will be sent to the register.php page after the form is submitted by clicking on the Register button.
Now fill in the data in this user registration form, and hit the Register button to register. Here is the new snapshot of the same registration form after filling out the data:
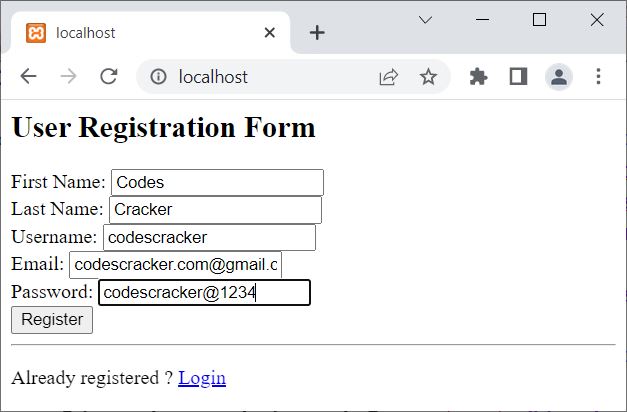
But before clicking on the Register button, I have to create a register.php page that will handle the form data and send the data into the database. Let me create the register.php page.
PHP mysqli Registration Form, Step No. 2
I am going to create the register.php page using both PHP mysqli procedural and object-oriented scripts. Let's start with object-oriented first.
PHP mysqli object-oriented script: register.php
This is the register.php page, created using PHP mysqli object-oriented script or code.
<?php
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$server = "localhost";
$user = "root";
$pass = "";
$db = "codescracker";
$conn = new mysqli($server, $user, $pass, $db);
if($conn -> connect_errno)
{
echo "Database connection failed!<BR>";
echo "Reason: ", $conn->connect_error;
exit();
}
else
{
$fname = $_POST["firstname"];
$lname = $_POST["lastname"];
$uname = $_POST["username"];
$email = $_POST["email"];
$pass = $_POST["password"];
$sql = "INSERT INTO `users`(`FirstName`, `LastName`, `Username`, `Email`, `Password`)
VALUES ('$fname', '$lname', '$uname', '$email', '$pass')";
$qry = $conn -> query($sql);
if($qry)
{
echo "Registration done successfully!";
// block of code to process further...
}
else
{
echo "Something went wrong while registration!<BR>";
echo "Error Description: ", $conn -> error;
}
}
}
$conn -> close();
?>
Note: The mysqli() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in object-oriented style.
Note: The new keyword is used to create a new object.
Note: The connect_errno is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in object-oriented style.
Note: The connect_error is used to get the error description (if any) from the last connection in object-oriented style.
Note: The exit() function is used to terminate the execution of the current PHP script.
Note: The query() function is used to perform queries on the MySQL database in object-oriented style.
Note: The error is used to return the description of the error (if any) from the most recent function call in object-oriented style.
Note: The close() function is used to close an opened connection in object-oriented style.
The above PHP mysqli object-oriented script to handle user registration form data can also be created in this way:
<?php
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$conn = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "codescracker");
if(!$conn->connect_errno)
{
$fname = $_POST["firstname"];
$lname = $_POST["lastname"];
$uname = $_POST["username"];
$email = $_POST["email"];
$pass = $_POST["password"];
$sql = "INSERT INTO `users`(`FirstName`, `LastName`, `Username`, `Email`, `Password`)
VALUES ('$fname', '$lname', '$uname', '$email', '$pass')";
if($conn->query($sql))
echo "Registration done successfully!";
}
}
$conn->close();
?>
PHP mysqli procedural script: register.php
Here is the register.php page, created using PHP mysqli procedural script:
<?php
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
$server = "localhost";
$user = "root";
$pass = "";
$db = "codescracker";
$conn = mysqli_connect($server, $user, $pass, $db);
if(mysqli_connect_errno())
{
echo "Database connection failed!<BR>";
echo "Reason: ", mysqli_connect_error();
exit();
}
else
{
$fname = $_POST["firstname"];
$lname = $_POST["lastname"];
$uname = $_POST["username"];
$email = $_POST["email"];
$pass = $_POST["password"];
$sql = "INSERT INTO `users`(`FirstName`, `LastName`, `Username`, `Email`, `Password`)
VALUES ('$fname', '$lname', '$uname', '$email', '$pass')";
$qry = mysqli_query($conn, $sql);
if($qry)
{
echo "Registration done successfully!";
// block of code to process further
}
else
{
echo "Something went wrong while registration!<BR>";
echo "Error Description: ", mysqli_error($conn);
}
}
}
mysqli_close($conn);
?>
Now fill in the data and click on the Register button. Here is the output you will get:
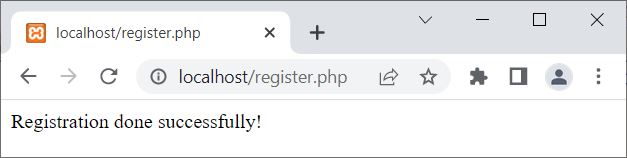
Now if you open the table named users available in the database codescracker, a record has been inserted. Here is the new snapshot of the table:
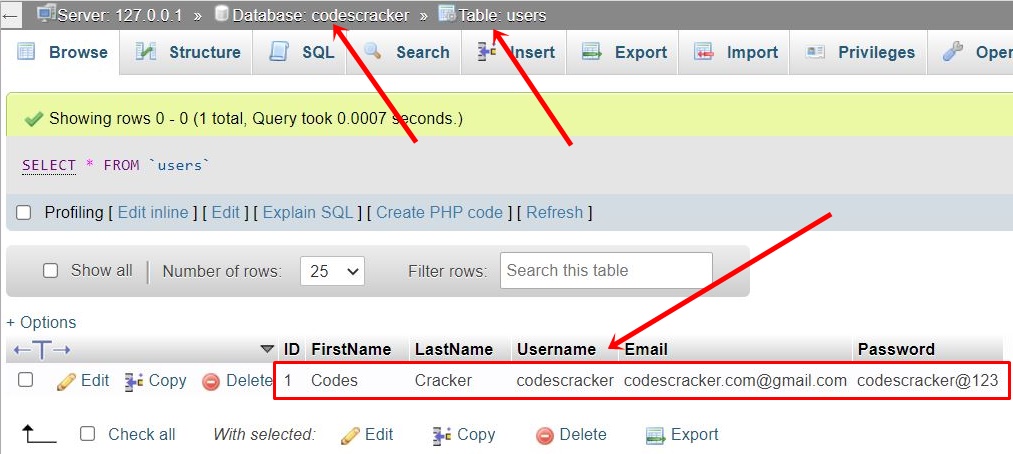
Note: The mysqli_connect() function is used to open a connection to the MySQL database server in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_connect_errno() is used to get or return the error code (if any) from the last connect call in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_connect_error() function is used to return the error description (if any) from the last connection in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_query() function is used to perform queries on the MySQL database in procedural style.
Note: The mysqli_error() function is used to return the description of the error (if any) from the most recent function call in object-oriented style.
Note: The mysqli_close() function is used to close an opened connection to the MySQL database in procedural style.
PHP mysqli security issue with the registration form
While creating a web application where users are allowed to enter their information, we need to take care about the steps to make our application more secure.
Over the internet or on your application, many suspicious users may try to exploit your application, hack your application, or do whatever they can to take steps against your application or for their own benefit.
Therefore, we need to take some steps to avoid a suspicious attack on our database:
- Use prepared statements instead of the normal ones. Because when using a prepared statement, the parameters are always considered to be parameters, not commands.
- Filter the data before sending it into the database.
I really do not know what type of application you are building or plan to build. But what I wanted to say is, just take all necessary steps to protect your database from attackers. Now let me create the complete registration form on a single page. This time, I have taken some necessary steps to secure the registration form.
Complete PHP mysqli Registration Form and Script in One Page
It is very subjective what a developer wants to implement in the registration form. For example, some developers want to allow users to enter a username and/or password whose length should be between 8 and 16 or whatever, and some developers do not. It is up to you. Therefore, I am going to create a normal, in-depth PHP mysqli script for the user registration page.
This PHP mysqli script uses prepared statements to register the users data in the database. Also, I have created the form and the form handler script on a single page to display the error regarding the form (if any) on the same page.
<?php
$driver = new mysqli_driver();
$driver -> report_mode = MYSQLI_REPORT_OFF;
if(isset($_SESSION['log']))
{
header('Location: welcome.php');
exit();
}
else
{
if($_SERVER["REQUEST_METHOD"] == "POST")
{
function validData($x)
{
$x = trim($x);
$x = stripslashes($x);
$x = htmlspecialchars($x);
return $x;
}
$server = "localhost";
$user = "root";
$pass = "";
$db = "codescracker";
$conn = @new mysqli($server, $user, $pass, $db);
if($conn->connect_errno)
{
echo "Database connection failed!<BR>";
echo "Reason: ", $conn->connect_error;
exit();
}
$fname = $lname = $uname = $email = $pass = "";
$unameE = $emailE = $passE = "";
$fname = validData($_POST["firstname"]);
$lname = validData($_POST["lastname"]);
$uname = validData($_POST["username"]);
$email = validData($_POST["email"]);
$pass = validData($_POST["password"]);
if(empty($uname))
$unameE = "Username field was empty!<BR>";
if(empty($email))
$emailE = "Email Id field was empty!<BR>";
if(empty($pass))
$passE = "Password field was empty!<BR>";
if(strlen($uname)<6)
$unameE .= "Username must be of 6 or more characters!<BR>";
if(strlen($pass)<6)
$passE .= "Password must be of 6 or more characters!<BR>";
if(!filter_var($email, FILTER_VALIDATE_EMAIL))
$emailE .= "Enter a valid Email ID!<BR>";
if(!empty($unameE) || !empty($emailE) || !empty($passE))
$err = "Try again";
else
{
$sql = "INSERT INTO `users`(`FirstName`, `LastName`, `Username`, `Email`, `Password`)
VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
$stmt = $conn->prepare($sql);
$stmt->bind_param("sssss", $fname, $lname, $uname, $email, $pass);
if($stmt->execute())
{
$_SESSION['log'] = $uname;
header('Location: welcome.php');
exit();
}
else
$execE = "Something went wrong<BR>Please try again!";
}
$conn->close();
}
}
?>
<HTML>
<HEAD>
<STYLE>
.form{width: 400px; margin: auto; padding: 12px; border-left: 2px solid #ccc; border-radius: 18px;}
h2{color: purple; text-align: center;}
input{padding: 12px; width: 100%; margin-bottom: 12px; border: 0px; border-radius: 6px;
background-color: #ccc;}
button{margin: 20px 0px; width: 100%; background-color: #008080; color: white; padding: 12px;
font-size: 1rem; border-radius: 6px;}
p{text-align: center;}
button:hover{cursor: pointer;}
.red{color: red;}
</STYLE>
</HEAD>
<BODY>
<DIV class="form">
<H2>User Registration Form</H2>
<FORM name="register" method="post" action="<?php echo htmlspecialchars($_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]);?>">
<LABEL>First Name</LABEL><BR>
<INPUT type="text" name="firstname" placeholder="First Name"><BR>
<LABEL>Last Name</LABEL><BR>
<input type="text" name="lastname" placeholder="Last Name"><BR>
<LABEL>Username
<?php
if(!empty($unameE))
echo "<SPAN class=\"red\">*</SPAN>";
else
echo "*";
?>
</LABEL><BR>
<INPUT type="text" name="username" placeholder="Create Username" required><BR>
<LABEL>Email
<?php
if(!empty($emailE))
echo "<SPAN class=\"red\">*</SPAN>";
else
echo "*";
?>
</LABEL><BR>
<INPUT type="text" name="email" placeholder="Email ID" required><BR>
<LABEL>Password
<?php
if(!empty($passE))
echo "<SPAN class=\"red\">*</SPAN>";
else
echo "*";
?>
</LABEL><BR>
<INPUT type="text" name="password" placeholder="Create Password" required><BR>
<BUTTON type="submit">Register</BUTTON>
</FORM>
<?php
if(isset($err))
{
echo "<DIV class=\"red\">";
if(!empty($unameE))
echo $unameE;
if(!empty($emailE))
echo $emailE;
if(!empty($passE))
echo $passE;
echo "</DIV>";
}
elseif(isset($execE))
echo $execE;
else
{
echo "<P><B>Direction: </B> Username and Password must be of 6 or more characters.<BR>";
echo "Star (*) Fields must not be empty.<BR>";
echo "Special characters are not allowed.</P>";
}
?>
<P>Already registered ? <a href="login.php">Login</a></P>
</DIV>
</BODY>
</HTML>
The output produced by the above PHP mysqli user registration form is shown in the snapshot given below:
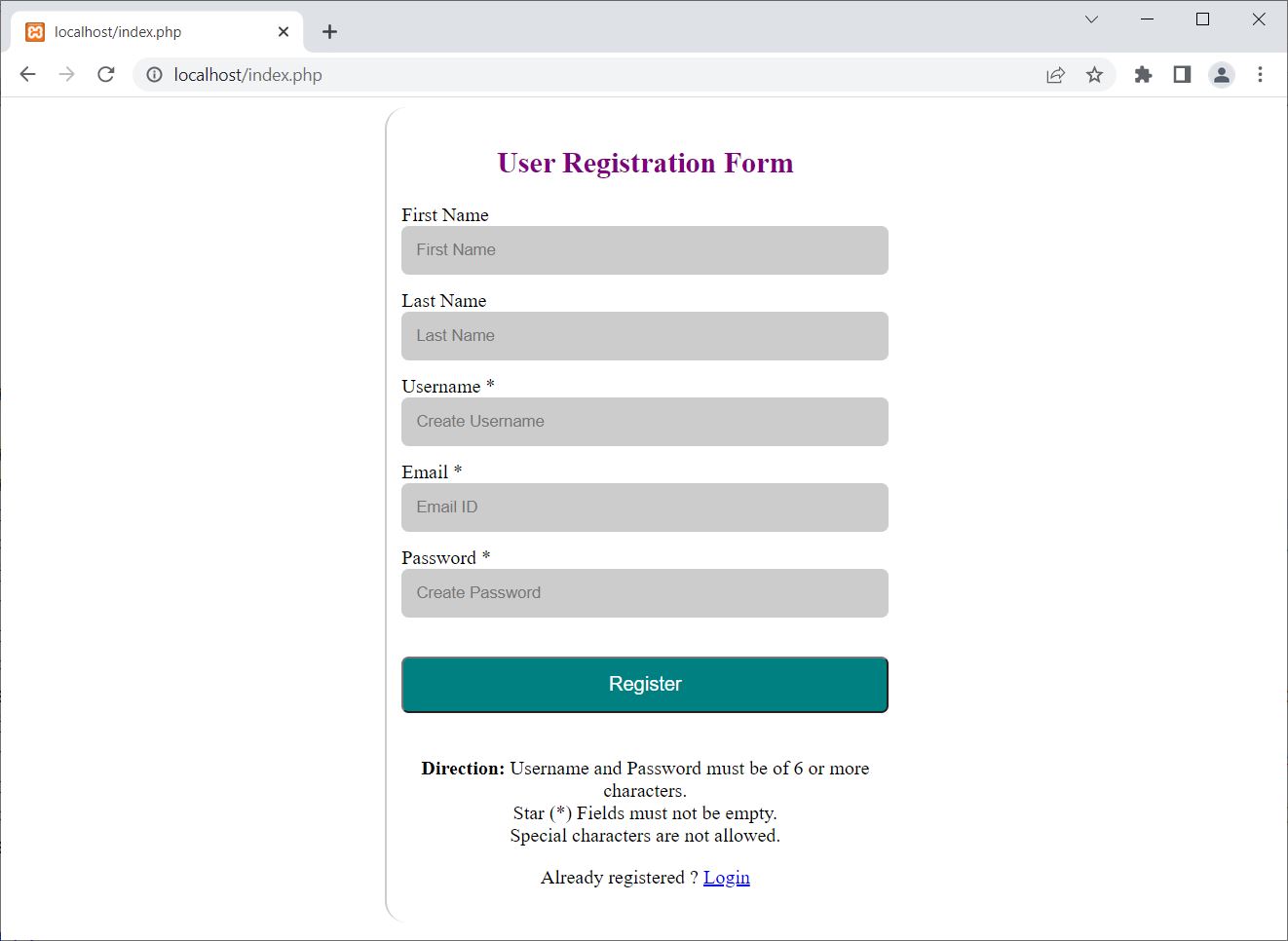
Now if you enter invalid or wrong input, then you will get the error message on the same page. Here is the snapshot after providing codes#xyz.com as Email ID and leaving other fields empty:
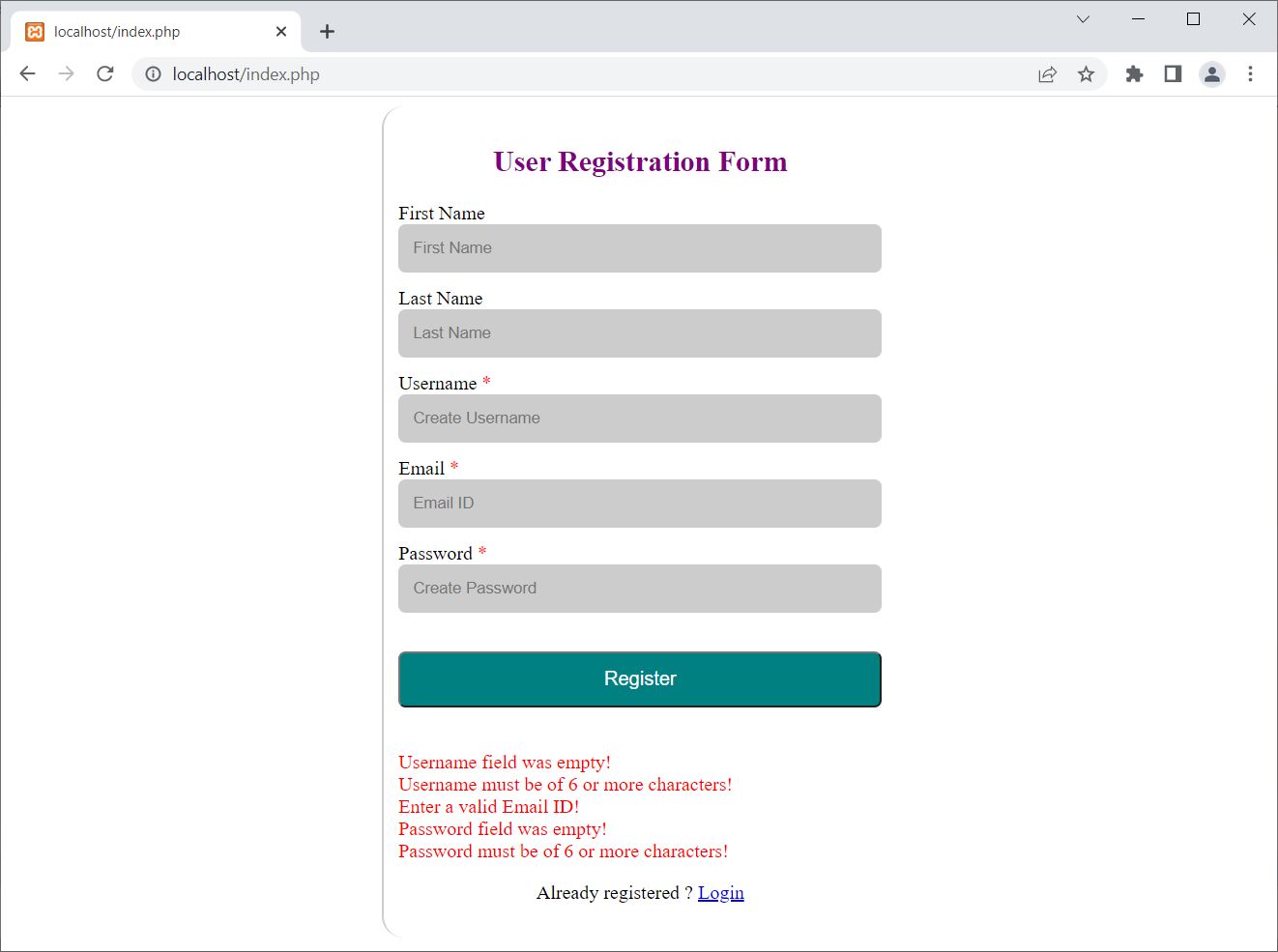
I removed the required attribute before hitting the Register button, leaving the fields Username and Password empty and the Email ID field with codes#xyz.com.
After providing valid data, the user gets registered on the website, and the page will be redirected to the welcome.php page.
Note: The mysqli_driver() function is used to modify the error reporting mode in object-oriented style.
Note: The header() function function is used to send raw HTTP headers. The majority of the time, it is used for redirection.
Note: The prepare() function is used to prepare an SQL statement before its execution on the MySQL database in object-oriented style to avoid SQL injection.
Note: The bind_param() function is used to bind variables to a prepared statement as parameters in object-oriented style.
Note: The execute() function is used to execute a prepared statement on the MySQL database in object-oriented style.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »