- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
PHP include() | Call Another PHP File to Execute
The PHP include() function is used when we need to include an external PHP file in a PHP script to execute the script available in that external file in the current PHP file. For example:
<?php
include("header.php");
echo "Hey, PHP is Fun!<BR>";
echo "Is not it?";
?>
The file header.php is available in the current directory and contains the following script:
<?php echo "-------Welcome to Company.com---------<HR>"; ?>
Therefore, the output of the above example on the include() function in PHP is shown in the snapshot given below:
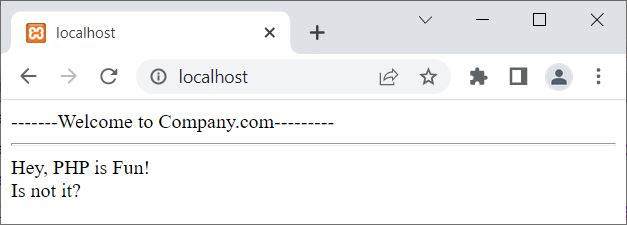
Now the question is, what if the included file does not exist? Let us find out the answer using the example given below:
<?php
include("unknown.php");
echo "Hey, PHP is Fun!<BR>";
echo "Is not it?";
?>
Now the output is:
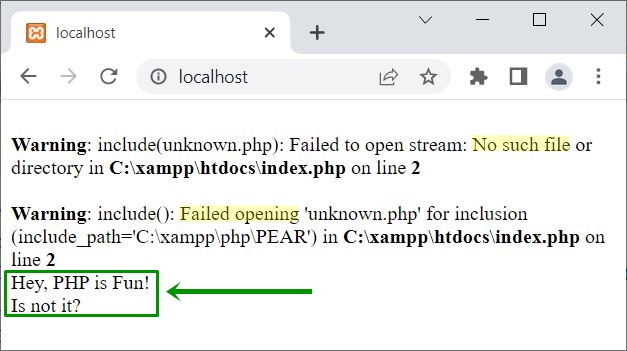
That is, since the file unknown.php does not exist, you are seeing the error. But the current script after the include() function has still been executed. Use error_reporting(0) to turn off error reporting.
PHP include() Syntax
The syntax of the include() function in PHP is:
include "file";
Or
include 'file';
Or
include("file");
Or
include('file');
Note: The include() function produces a warning (E_WARNING) message if the specified file does not exist, and the script continues its execution.
Why use include() in PHP?
I do not know what your purpose is for using the function include(). But, with the use of the include() function, the same script need not be written for every file. That is, if some PHP scripts like header and footer content are available in multiple files of your web application. Then it is better to go with the include() function to write the header and footer content at once, in two PHP files. And include these two files in each to avoid writing them multiple times.
Another benefit is that if you want to change the content of the footer and/or header, then just change the content of those two files. It reflects the change in the whole application or all files, where these files are included. For example:
<?php error_reporting(0); ?>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
* {box-sizing: border-box;}
body {margin: 0;}
.head {padding: 22px 0; font-size: 1.4em; text-align: center; background: maroon; color: white;}
.navigation {display: flex; background-color: peru;}
.navigation a {color: white; padding: 12px 16px; text-decoration: none; text-align: center;}
.cont {display: flex; flex-wrap: wrap; min-height: 540px;}
.menu {flex: 20%; background-color: #ccc; padding: 16px;}
.content {flex: 60%; padding: 16px;}
.right {flex: 20%; background-color: grey; color: white; padding: 16px;}
.foot {padding: 22px 0; text-align: center; background: maroon; color: white;}
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {.cont, .navigation {flex-direction: column;}}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<?php include 'header.php'; ?>
<div class="cont">
<div class="menu">
<p>----Some Menu----</p>
</div>
<div class="content">
<p>Content of the Page...</p>
</div>
<div class="right">
<p>----Right Side----</p>
</div>
</div>
<?php include 'footer.php'; ?>
</body>
</html>
The content of the header.php file is:
<div class="head">CodesCracker</div>
<div class="navigation">
<a href="#">MenuOne</a>
<a href="#">MenuTwo</a>
<a href="#">MenuThree</a>
<a href="#">MenuFour</a>
<a href="#">MenuFive</a>
</div>
And the content of the footer.php file is:
<div class="foot"> <p>Some texts/links...</p> </div>
Now the output should be:
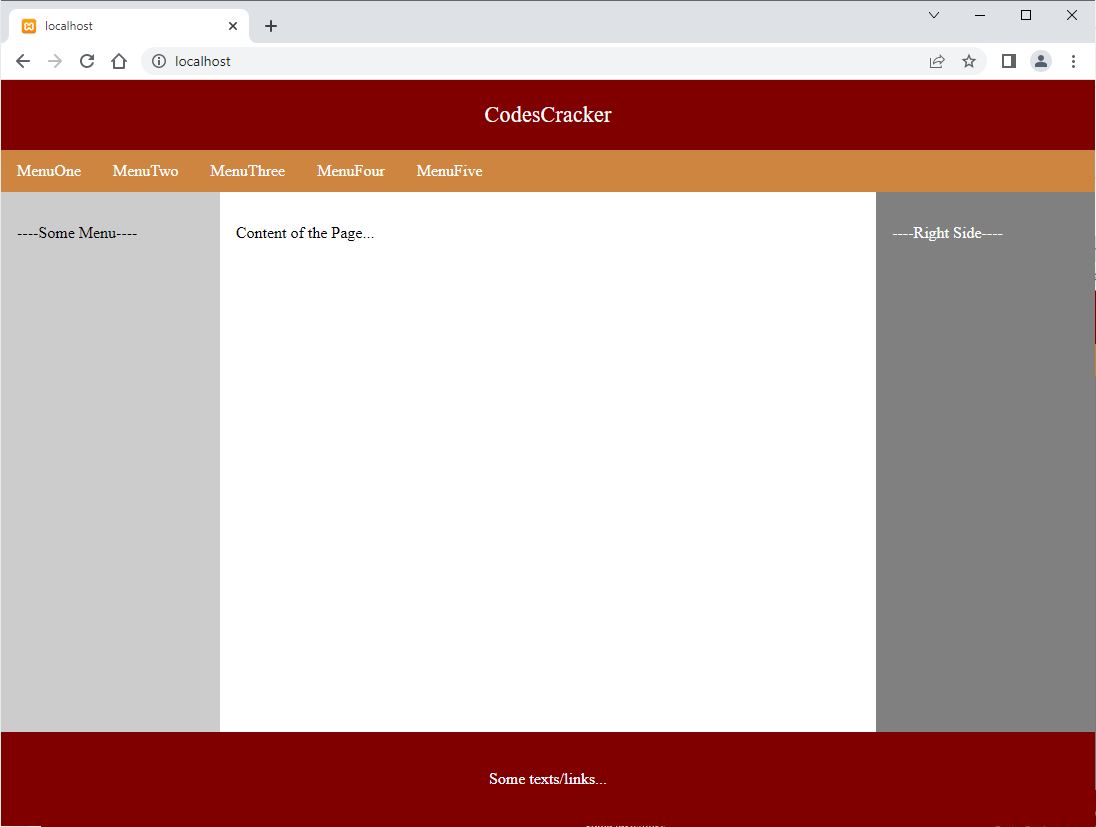
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »