- PHP Basics
- Learn PHP
- PHP Comments
- PHP Data Types
- PHP Variables
- PHP Operators
- PHP echo
- PHP print
- PHP echo vs. print
- PHP if else
- PHP switch
- PHP for Loop
- PHP while Loop
- PHP do...while Loop
- PHP foreach Loop
- PHP break and continue
- PHP exit()
- PHP exit() vs. break
- PHP isset()
- PHP Arrays
- PHP print_r()
- PHP unset()
- PHP Strings
- PHP Functions
- PHP File Handling
- PHP File Handling
- PHP Open File
- PHP Create a File
- PHP Write to File
- PHP Read File
- PHP feof()
- PHP fgetc()
- PHP fgets()
- PHP Close File
- PHP Delete File
- PHP Append to File
- PHP Copy File
- PHP file_get_contents()
- PHP file_put_contents()
- PHP file_exists()
- PHP filesize()
- PHP Rename File
- PHP fseek()
- PHP ftell()
- PHP rewind()
- PHP disk_free_space()
- PHP disk_total_space()
- PHP Create Directory
- PHP Remove Directory
- PHP Get Files/Directories
- PHP Get filename
- PHP Get Path
- PHP filemtime()
- PHP file()
- PHP include()
- PHP require()
- PHP include() vs. require()
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP mysqli Tutorial
- PHP and MySQL Setup
- PHP mysqli: Create Database
- PHP mysqli: Create Table
- PHP mysqli: Insert Record
- PHP mysqli: Update Record
- PHP mysqli: Fetch Record
- PHP mysqli: Delete Record
- PHP mysqli: SignUp Page
- PHP mysqli: LogIn Page
- PHP mysqli: Store User Data
- PHP mysqli Functions
- PHP mysqli_connect()
- PHP mysqli_close()
- PHP mysqli_connect_errno()
- PHP mysqli_connect_error()
- PHP mysqli_query()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_row()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_assoc()
- PHP mysqli_fetch_array()
- PHP mysqli_free_result()
- PHP mysqli_error()
- PHP mysqli_prepare()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_param()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_execute()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_fetch()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_store_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_num_rows()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_bind_result()
- PHP mysqli_stmt_get_result()
- PHP mysqli_result class
- PHP mysqli_report()
- PHP error_reporting()
- PHP mysqli_real_escape_string()
- PHP htmlspecialchars()
- PHP Misc Topics
- PHP Object Oriented
- PHP new Keyword
- PHP header()
- PHP getallheaders()
- PHP Cookies
- PHP Sessions
- PHP Date and Time
- PHP GET vs. POST
- PHP File Upload
- PHP Image Processing
PHP exit(): Stop execution of the current PHP script
The PHP exit() function is used to stop running a PHP script or file that is already running. For example:
<?php
if(isset($_SESSION['user']))
{
// block of code to process user
}
else
{
header('Location: login.htm');
exit();
// some block of code
}
// other block of code
?>
Since the session variable user is not set, the program flow goes to the "else" block, and the following two statements get executed:
header('Location: login.htm');
exit();
The header() function redirects the page to the login.htm page, whereas the exit() function skips the execution of any remaining PHP script. That is, the execution of current PHP scripts stops when an exit() function is encountered.
The output of the above PHP example is shown in the snapshot given below:
Since the header() function redirects to another page, that is the login.htm page. Therefore, I think I have to create another example of the exit() function that shows how it terminates the execution of a current PHP script:
<?php
$x = 10;
for($i=1; $i<$x; $i++)
{
if($i==4)
exit();
echo "The value of \$i is $i <br>";
}
echo "The value of \$i is $i <br>";
echo "Some other text...";
// some other block of code...
?>
The output of the above PHP example is shown in the snapshot given below:
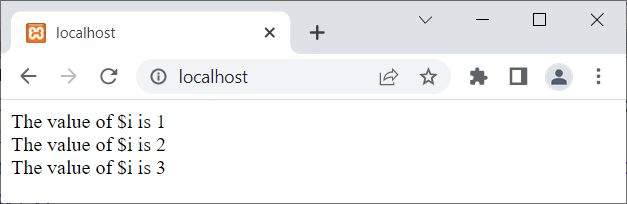
That is, when the value of $i becomes equal to 4, the exit() function is encountered, which terminates the execution of the current PHP scripts. Therefore, in the above example, including the remaining values of $i, the statements available right after the loop have also not been executed.
PHP exit() Syntax
The syntax of the exit() function in PHP is:
exit(message|status);
That is, either we can display some message before stopping the execution of the current PHP script or we can provide some status code. The status code or number will not be displayed on the output; rather, it is used for exit status.
But let me tell you one thing: when an exit(); statement is encountered, the execution of current PHP scripts halts or stops, but shutdown functions and object destructors will complete its execution.
Note: If you are not passing any status code or message to the exit() function, then you can write simply exit; to exit the program normally. That is:
- exit;
- exit();
- exit(0);
All three statements do the same thing: exit the program normally.
To print some messages before exiting the program, follow the example given below:
<?php
$x = 10;
for($i=1; $i<$x; $i++)
{
if($i==4)
exit("Exiting...");
echo "The value of \$i is $i <br>";
}
echo "The value of \$i is $i <br>";
?>
The output should be:
The value of $i is 1 The value of $i is 2 The value of $i is 3 Exiting...
Advantages of the exit() function in PHP
- The script can be easily terminated by using the easy-to-use function exit(). It doesn't need any extra parameters or difficult syntax.
- Using the exit() function can assist in preventing a script from using excessive server resources if it is running for an excessively long time or is caught in an infinite loop.
- A value can also be returned to the calling process using the exit() function. In some circumstances, like when a script must convey a status code or error message, this can be helpful.
Disadvantages of the exit() function in PHP
- Use of exit() within a loop or function may result in an early termination of the script, which might result in some tasks being left unfinished.
- Can make debugging challenging: If a script uses exit() to end when an error occurs, it may be more challenging to find and fix the issue. Utilizing PHP's built-in error reporting functions will allow you to handle errors in a more controlled manner.
- exit() has the potential to behave unexpectedly or lead to script errors if it is used incorrectly or in the wrong situation.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »