- CSS Basics
- CSS Tutorial
- CSS Where to Write
- CSS Syntax
- CSS Selectors
- CSS Combinators
- CSS Attribute Selectors
- CSS Pseudo Classes
- CSS Pseudo-Classes
- CSS :link :hover :active
- CSS :first-child
- CSS :first-of-type
- CSS :last-child
- CSS :last-of-type
- CSS :only-child
- CSS :only-of-type
- CSS :nth-child()
- CSS :nth-of-type()
- CSS :nth-last-child()
- CSS :nth-last-of-type()
- CSS :focus
- CSS :not()
- CSS :root
- CSS :empty
- CSS :target
- CSS :lang()
- CSS :valid
- CSS :invalid
- CSS :optional
- CSS :required
- CSS :in-range
- CSS :out-of-range
- CSS :enabled :disabled
- CSS :read-only
- CSS :read-write
- CSS Pseudo Elements
- CSS Pseudo-Elements
- CSS ::before
- CSS ::after
- CSS ::first-letter
- CSS ::first-line
- CSS ::marker
- CSS ::selection
- CSS Colors
- CSS Colors
- CSS rgb() and rgba()
- CSS hsl() and hsla()
- CSS Background
- CSS background
- CSS background-color
- CSS background-image
- CSS linear-gradient()
- CSS radial-gradient()
- CSS conic-gradient()
- CSS repeating-linear-gradient()
- CSS repeating-radial-gradient()
- CSS repeating-conic-gradient()
- CSS background-position
- CSS background-size
- CSS background-repeat
- CSS background-origin
- CSS background-clip
- CSS background-attachment
- CSS background-blend-mode
- CSS Border
- CSS border
- CSS border-style
- CSS border-style Values
- CSS border-width
- CSS border-color
- CSS border-top
- CSS border-top-style
- CSS border-top-width
- CSS border-top-color
- CSS border-bottom
- CSS border-bottom-style
- CSS border-bottom-width
- CSS border-bottom-color
- CSS border-left
- CSS border-left-style
- CSS border-left-width
- CSS border-left-color
- CSS border-right
- CSS border-right-style
- CSS border-right-width
- CSS border-right-color
- CSS border-top-left-radius
- CSS border-top-right-radius
- CSS border-bottom-left-radius
- CSS border-bottom-right-radius
- CSS border-radius
- CSS border-collapse
- CSS empty-cells
- CSS border-spacing
- CSS border-image
- CSS border-image-source
- CSS border-image-slice
- CSS border-image-width
- CSS border-image-outset
- CSS border-image-repeat
- CSS Fonts
- CSS font
- CSS font-style
- CSS font-variant
- CSS font-variant-caps
- CSS font-weight
- CSS font-size
- CSS line-height
- CSS font-family
- CSS font-stretch
- CSS font-kerning
- CSS font-face
- CSS font-feature-settings
- CSS Text
- CSS Text
- CSS color
- CSS text-decoration
- CSS text-decoration-line
- CSS text-decoration-color
- CSS text-decoration-style
- CSS text-underline-position
- CSS text-align
- CSS text-align-last
- CSS text-justify
- CSS letter-spacing
- CSS word-spacing
- CSS text-shadow
- CSS text-transform
- CSS white-space
- CSS text-indent
- CSS word-wrap
- CSS overflow-wrap
- CSS word-break
- CSS text-overflow
- CSS hyphens
- CSS direction
- CSS unicode-bidi
- CSS writing-mode
- CSS Padding & Margin
- CSS Box Model
- CSS padding
- CSS padding-top
- CSS padding-right
- CSS padding-bottom
- CSS padding-left
- CSS margin
- CSS margin-top
- CSS margin-right
- CSS margin-bottom
- CSS margin-left
- CSS Padding Vs Margin
- CSS Dimensions
- CSS Dimensions
- CSS height
- CSS max-height
- CSS min-height
- CSS width
- CSS max-width
- CSS min-width
- CSS overflow
- CSS overflow-x
- CSS overflow-y
- CSS Multi-Column Layout
- CSS Multi-Column Layout
- CSS columns
- CSS column-width
- CSS column-count
- CSS column-rule
- CSS column-rule-width
- CSS column-rule-style
- CSS column-rule-color
- CSS column-span
- CSS column-fill
- CSS Display
- CSS display
- CSS inline Vs block
- CSS inline Vs inline-block
- CSS flex Vs inline-flex
- CSS inline-flex Vs inline-block
- CSS flex Vs grid
- CSS grid Vs inline-grid
- CSS Float and Position
- CSS float
- CSS clear
- CSS Align
- CSS position
- CSS left
- CSS right
- CSS top
- CSS bottom
- CSS Style List Marker
- CSS Style List Marker
- CSS list-style
- CSS list-style-type
- CSS list-style-position
- CSS list-style-image
- CSS Outline
- CSS outline
- CSS outline-width
- CSS outline-style
- CSS outline-color
- CSS outline-offset
- CSS Effects
- CSS Effects
- CSS Gradients
- CSS Shadows
- CSS box-shadow
- CSS opacity
- CSS Transforms
- CSS transform
- CSS translateX()
- CSS translateY()
- CSS translateZ()
- CSS translate()
- CSS translate3d()
- CSS scaleX()
- CSS scaleY()
- CSS scaleZ()
- CSS scale()
- CSS scale3d()
- CSS rotateX()
- CSS rotateY()
- CSS rotateZ()
- CSS rotate()
- CSS rotate3d()
- CSS skewX()
- CSS skewY()
- CSS skew()
- CSS matrix()
- CSS matrix3d()
- CSS perspective() Function
- CSS perspective Property
- CSS perspective-origin
- CSS transform-style
- CSS transform-origin
- CSS 2D Transform
- CSS 3D Transform
- CSS Transition
- CSS transition
- CSS transition-property
- CSS transition-duration
- CSS transition-timing-function
- CSS transition-delay
- CSS Animation
- CSS animation
- CSS @keyframes
- CSS animation-name
- CSS animation-duration
- CSS animation-timing-function
- CSS animation-delay
- CSS animation-iteration-count
- CSS animation-direction
- CSS animation-fill-mode
- CSS animation-play-state
- CSS Grid Layout
- CSS Grid Layout
- CSS gap
- CSS column-gap
- CSS row-gap
- CSS grid-area
- CSS grid-column-start
- CSS grid-column-end
- CSS grid-row-start
- CSS grid-row-end
- CSS grid-template
- CSS grid-template-columns
- CSS grid-template-rows
- CSS grid-template-areas
- CSS grid-auto-columns
- CSS grid-auto-rows
- CSS grid-auto-flow
- CSS grid-column
- CSS grid-row
- CSS Template Layout
- CSS Flex Layout
- CSS FlexBox
- CSS flex-direction
- CSS flex-wrap
- CSS flex-flow
- CSS justify-content
- CSS align-content
- CSS align-items
- CSS flex-grow
- CSS flex-shrink
- CSS flex-basis
- CSS flex
- CSS align-self
- CSS order
- CSS Misc
- CSS Length Units
- CSS Style Link
- CSS Navigation Bar
- CSS Style Image
- CSS Style Tables
- CSS table-layout
- CSS caption-side
- CSS Create Frames
CSS Syntax: How is CSS Code Written?
The syntax to write CSS code consists of:
- selector
- declaration
For example:
p {color: brown;}
In the above code:
- p is a selector. Selects the paragraph (P) tag.
- color: brown; is a declaration. Declares brown color to text inside the P tag.
- color is a property.
- brown is a value.
Note: The declaration block consists of property and value in the form property: value;.
Note: We can have multiple declarations for a selector (an HTML element). For example:
p {color: brown; text-align: center;}
Note - All the declarations must be enclosed within a {} (an opening and a closing curly brace).
Now let's take a complete example that shows how the CSS code can be implemented to style HTML elements.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> p {color: brown;} span {background-color: tomato; color: white;} </style> </head> <body> <p>This is <span>Para</span> one.</p> <p>This is Para two.</p> </body> </html>
This is Para one.
This is Para two.
In the above example, the CSS code inside the "style" tags has two selectors.
The first selector p matches all p elements and gives their text a "brown" color. As a result, the text color for both p elements in the HTML will be "brown".
The second selector span matches all span elements and gives their content a "tomato" background color and a "white" text color. Only the span element within the first p element will be affected in this case. The span element's content, the word "Para," will have a background color of "tomato" and a text color of "white." The second p element is unaffected because it lacks a span element.
As a result, the first p element will have brown text, with the word "Para" inside it having a tomato background color and white text. Only brown text will appear on the second p element.
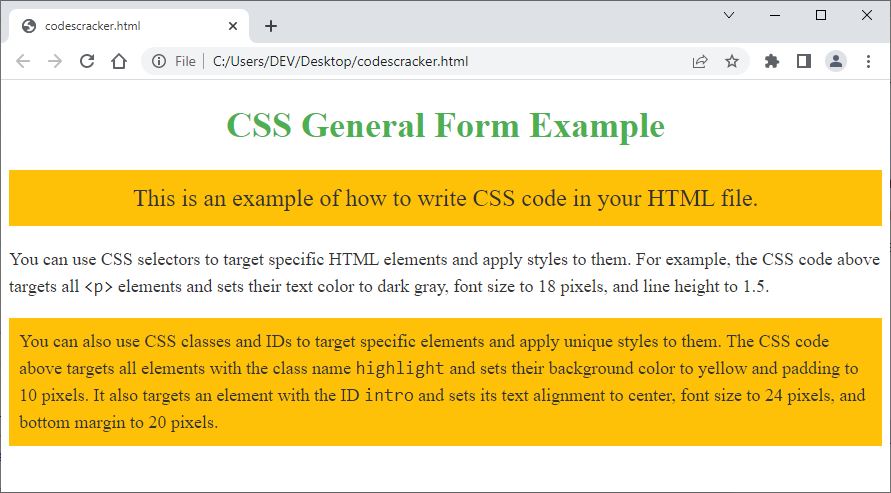
Before concluding the discussion on the general format of CSS code, I'd like to provide one more example. So here's an example to show the syntax of CSS codes. To explain the main portion of the CSS codes, I used comments.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
/* This is a CSS comment */
/* CSS selectors */
h1 {
/* CSS properties */
color: #4CAF50; /* green */
font-size: 36px;
font-weight: bold;
text-align: center;
}
p {
color: #333; /* dark gray */
font-size: 18px;
line-height: 1.5;
}
/* CSS class selector */
.highlight {
background-color: #FFC107; /* yellow */
padding: 10px;
}
/* CSS ID selector */
#intro {
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>CSS General Form Example</h1>
<p id="intro" class="highlight">This is an example of how to write CSS code in your HTML file.</p>
<p>You can use CSS selectors to target specific HTML elements and apply styles to them. For example,
the CSS code above targets all <code><p></code> elements and sets their text color to dark gray,
font size to 18 pixels, and line height to 1.5.</p>
<p class="highlight">You can also use CSS classes and IDs to target specific elements and apply unique
styles to them. The CSS code above targets all elements with the class name <code>highlight</code> and
sets their background color to yellow and padding to 10 pixels. It also targets an element with the ID
<code>intro</code> and sets its text alignment to center, font size to 24 pixels, and bottom margin to
20 pixels.</p>
</body>
</html>
The sample output produced by this HTML and CSS example code should look exactly like the screenshot below:
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »