- Python Basics
- Python Tutorial
- Python Applications
- Python Versions
- Python environment setup
- Python Basic Syntax
- Python end (end=)
- Python sep (sep=)
- Python Comments
- Python Identifiers
- Python Variables
- Python Operators
- Python Ternary Operator
- Python Operator Precedence
- Python Control and Decision
- Python Decision Making
- Python if elif else
- Python Loops
- Python for Loop
- Python while Loop
- Python break Statement
- Python continue Statement
- Python pass Statement
- Python break vs. continue
- Python pass vs. continue
- Python Built-in Types
- Python Data Types
- Python Lists
- Python Tuples
- Python Sets
- Python frozenset
- Python Dictionary
- List vs. Tuple vs. Dict vs. Set
- Python Numbers
- Python Strings
- Python bytes
- Python bytearray
- Python memoryview
- Python Misc Topics
- Python Functions
- Python Variable Scope
- Python Enumeration
- Python import Statement
- Python Modules
- Python operator Module
- Python os Module
- Python Date and Time
- Python Exception Handling
- Python File Handling
- Python Advanced
- Python Classes and Objects
- Python @classmethod Decorator
- Python @staticmethod Decorator
- Python Class vs. Static Method
- Python @property Decorator
- Python Keywords
- Python Keywords
- Python and
- Python or
- Python not
- Python True
- Python False
- Python None
- Python in
- Python is
- Python as
- Python with
- Python yield
- Python return
- Python del
- Python from
- Python lambda
- Python assert
- Python Built-in Functions
- Python All Built-in Functions
- Python print() Function
- Python input() Function
- Python int() Function
- Python len() Function
- Python range() Function
- Python str() Function
- Python ord() Function
- Python chr() Function
- Python read()
- Python write()
- Python open()
- Python Examples
- Python Examples
String in Python with Examples
Strings are used to represent text, which is a combination of characters, regardless of the type of characters. Therefore, strings can also store a value that contains numbers.
But the question is, how can we identify whether the value is of the string (str) type or not? The answer is: anything enclosed within a single or double quote is a string. For example:
x = 'codescracker' print(type(x)) x = 'Python is Fun' print(type(x)) x = "134" print(type(x)) x = '243.554' print(type(x)) x = 'Python@134' print(type(x))
The output is:
<class 'str'> <class 'str'> <class 'str'> <class 'str'> <class 'str'>
Note: The type() function is used to find the type of a value or variable.
Strings are a contiguous set of characters enclosed within a single or double quotation mark.
In this post, I have covered the following topics regarding the string in Python:
- Assign a string in Python
- Access the elements of a string in Python
- Python string length
- String splitting in Python
- Python escape sequence characters
- Python string methods
- Python string programs
Assign a string in Python
To assign a string in Python, follow the program given below:
a = 'Welcome to codescracker.com' b = "Python is Fun!"
How to Assign a Multiline String in Python
We need to use a large string value that expands into multiple lines on occasion. Therefore, to assign a multiline string, we need to enclose the string in three single or double quotes. For example:
a = '''This is Lukas. I'm from Berlin. I studied at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. I am a data science enthusiast.''' print(a)
The output should be:
This is Lukas. I'm from Berlin. I studied at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. I am a data science enthusiast.
If you place some space before the string, other than the variable's line, Then the space will be considered part of the string. For example:
a = """Hey, Python is fun. Is not it?""" print(a)
The output should be:
Hey,
Python is fun.
Is not it?
Access the elements (characters) of a string in Python
Characters in a string can be accessed using their index numbers. Therefore, just like a list, a string is also an iterable object. The syntax to access an element or character of a string in Python is:
x[index]
where "x" refers to the string, and "index" refers to the index number of the character or element that needs to be accessed. For example:
x = "Python is easy to learn" print(x[0]) print(x[1]) print(x[2])
The output is:
P y t
Access String Elements from the End
An element of a string can also be accessed using, of course, negative indexing. The "x[-1]" refers to the last character of string "x." For example:
x = "Python is easy to learn" print(x[-1]) print(x[-2]) print(x[-3])
The output is:
n r a
The last element can also be accessed using:
print(x[len(x)-1])
The len() function returns the length of x. But it is not recommended to use the above code to access the last character of a string. It is preferable to use print(x[-1]).
Iterate over a string using the Python for loop
A for loop can also be used to iterate over the string. For example:
mystr = "Python Robust" for c in mystr: print(c)
The output is:
P y t h o n R o b u s t
To print all the characters of a string on a single line while iterating using the for loop, replace the following statement from the above program:
print(c)
with the statement given below:
print(c, end="")
Now the output is:
Python Robust
Note: The end= parameter skips the insertion of an automatic newline after each print().
Python string length
The len() function is used to get the length of a string. For example:
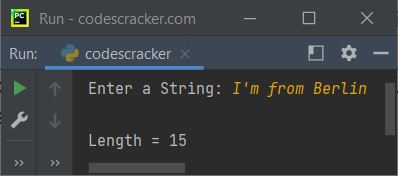
print("Enter a String: ", end="") x = input() print("\nLength =", len(x))
The snapshot given below shows the sample run of the above program, with user input "I'm from Berlin" as a string:
String splitting (slicing) in Python
The following program and its output demonstrate how the string gets split in Python:
x = "Python is Awesome!" print(x[0]) print(x[1:5]) print(x[1:6]) print(x[0:6]) print(x[7:])
The output is:
P ytho ython Python is Awesome!
While splitting the string in Python, using:
string[indexStart:indexStop]
The indexStart is included, whereas the indexStop is excluded.
Python escape sequence characters
The following table briefly describes the escape sequence characters used in Python:
| Escape Character Code | Used to/for |
|---|---|
| \\ | Print one backslash |
| \' | Print a single quote |
| \" | Print a double quote |
| \b | Move the cursor one space back |
| \a | Alert the Bell |
| \cx | Control-x |
| \b | Backspace |
| \C-x | Control-x |
| \f | Form feed |
| \e | Escape |
| \M-\C-x | Meta-Control-x |
| \r | Carriage return |
| \n | Newline |
| \nnn | Octal notation |
| \s | Space |
| \x | x |
| \t | Tab |
| \v | Vertical tab |
| \xnn | Hexadecimal notation |
Example of Python Escape Sequence Characters
Here is an example program that uses some of the escape sequence characters in Python.
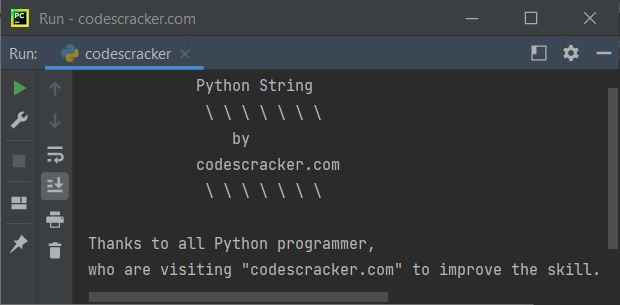
print("\t\t\tPython String") print("\t\t\t \\ \\ \\ \\ \\ \\ \\") print("\t\t\t\tby") print("\t\t\tcodescracker.com") print("\t\t\t \\ \\ \\ \\ \\ \\ \\") print("\nThanks to all Python programmer,") print("who are visiting \"codescracker.com\" to improve the skill.")
The snapshot given below shows the sample output produced by the above program, demonstrating the use of escape sequence characters in Python:
In Python, repeat a string for n times
To repeat a string n times, simply multiply it by the value of n, for example, multiply by 2 to repeat the string twice, and multiply by 3 to repeat the string three times. For example:
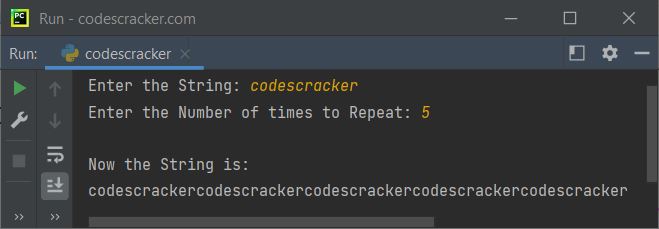
print("Enter the String: ", end="") x = input() print("Enter the Number of times to Repeat: ", end="") t = int(input()) x = x*t print("\nNow the String is:") print(x)
The sample run with user input "codescracker" as a string and 5 as the number of times to repeat "codescracker" is shown in the snapshot given below:
Python string methods
The pre-defined or built-in methods used to handle the string in Python are:
- str(): This function converts a value to a string.
- join(): joins all iterable items into a string.
- format() is used to format a string.
- split() converts a string to a list.
- replace(): replaces an old phrase with a new one.
- index() returns the first occurrence of a specified value in a string.
- count() returns the number of occurrences of a specified phrase in a string.
- reversed() returns the reversed string object of the given string.
Python string programs
Here is a list of some recommended programs related to string handling in Python.
- Compare two strings in Python
- Copy a string in Python
- String concatenation in Python
- Find the reverse of a string in Python
- Swap two strings in Python
- Uppercase string to lowercase in Python
- Lowercase string to uppercase in Python
- Count the number of characters in a given string
- Count the number of words in a given string
- Find the smallest and largest word in a given string
- Sort the string in alphabetical order
- Sort words from a string in alphabetical order
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »