- Python Basics
- Python Tutorial
- Python Applications
- Python Versions
- Python environment setup
- Python Basic Syntax
- Python end (end=)
- Python sep (sep=)
- Python Comments
- Python Identifiers
- Python Variables
- Python Operators
- Python Ternary Operator
- Python Operator Precedence
- Python Control and Decision
- Python Decision Making
- Python if elif else
- Python Loops
- Python for Loop
- Python while Loop
- Python break Statement
- Python continue Statement
- Python pass Statement
- Python break vs. continue
- Python pass vs. continue
- Python Built-in Types
- Python Data Types
- Python Lists
- Python Tuples
- Python Sets
- Python frozenset
- Python Dictionary
- List vs. Tuple vs. Dict vs. Set
- Python Numbers
- Python Strings
- Python bytes
- Python bytearray
- Python memoryview
- Python Misc Topics
- Python Functions
- Python Variable Scope
- Python Enumeration
- Python import Statement
- Python Modules
- Python operator Module
- Python os Module
- Python Date and Time
- Python Exception Handling
- Python File Handling
- Python Advanced
- Python Classes and Objects
- Python @classmethod Decorator
- Python @staticmethod Decorator
- Python Class vs. Static Method
- Python @property Decorator
- Python Keywords
- Python Keywords
- Python and
- Python or
- Python not
- Python True
- Python False
- Python None
- Python in
- Python is
- Python as
- Python with
- Python yield
- Python return
- Python del
- Python from
- Python lambda
- Python assert
- Python Built-in Functions
- Python All Built-in Functions
- Python print() Function
- Python input() Function
- Python int() Function
- Python len() Function
- Python range() Function
- Python str() Function
- Python ord() Function
- Python chr() Function
- Python read()
- Python write()
- Python open()
- Python Examples
- Python Examples
Python not Keyword
In Python, we use the "not" keyword when we want to change the boolean value of an expression that has already been evaluated. That is, the "not" keyword returns "True", if the expression evaluates to be "False", otherwise returns "False", if the expression evaluates to be "True". For example:
print(not True) print(not False)
The output is:
False True
Python not Keyword Truth Table
The truth table of the "not" keyword in Python is:
| X | not X |
|---|---|
| True | False |
| False | True |
To reverse the truth value of a boolean expression, use the "not" keyword. For example, if x is True, then "not x" is False; conversely, if x is False, then "not x" is True.
Python not Keyword Example
Here is an example of the "not" keyword in Python:
print("Enter the Two Number: ", end="") numOne = int(input()) numTwo = int(input()) x = numOne>numTwo if not x: print("\nThe value", numOne, "is greater than", numTwo) else: print("\nThe value", numTwo, "is greater than", numOne) print("\n\n\n@April Fool")
The snapshot given below shows the sample run of the above program, with user input of 10 and 30 as the first and second numbers:
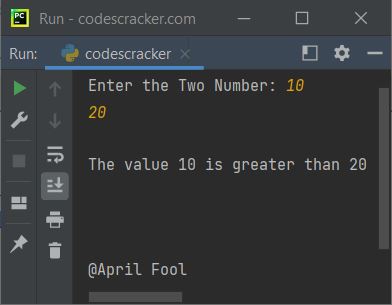
The "not" keyword in the above program reversed the result or output.
Advantages of the not keyword in Python
- Boolean expressions can be easily negated using the "not" keyword, which can make code simpler to read and comprehend.
- When writing conditional statements and loops, it can be helpful when a boolean expression's negation is required.
Disadvantages of the not keyword in Python
- The "not" keyword should not be overused as it can make code more difficult to read and comprehend, especially when there are several negations present.
- Sometimes using the positive form of an expression rather than negating it with "not" can make it clearer.
- It can be simple to inadvertently use the "not" keyword incorrectly, which can result in logical mistakes in the code.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »