- Python Basics
- Python Tutorial
- Python Applications
- Python Versions
- Python environment setup
- Python Basic Syntax
- Python end (end=)
- Python sep (sep=)
- Python Comments
- Python Identifiers
- Python Variables
- Python Operators
- Python Ternary Operator
- Python Operator Precedence
- Python Control and Decision
- Python Decision Making
- Python if elif else
- Python Loops
- Python for Loop
- Python while Loop
- Python break Statement
- Python continue Statement
- Python pass Statement
- Python break vs. continue
- Python pass vs. continue
- Python Built-in Types
- Python Data Types
- Python Lists
- Python Tuples
- Python Sets
- Python frozenset
- Python Dictionary
- List vs. Tuple vs. Dict vs. Set
- Python Numbers
- Python Strings
- Python bytes
- Python bytearray
- Python memoryview
- Python Misc Topics
- Python Functions
- Python Variable Scope
- Python Enumeration
- Python import Statement
- Python Modules
- Python operator Module
- Python os Module
- Python Date and Time
- Python Exception Handling
- Python File Handling
- Python Advanced
- Python Classes and Objects
- Python @classmethod Decorator
- Python @staticmethod Decorator
- Python Class vs. Static Method
- Python @property Decorator
- Python Keywords
- Python Keywords
- Python and
- Python or
- Python not
- Python True
- Python False
- Python None
- Python in
- Python is
- Python as
- Python with
- Python yield
- Python return
- Python del
- Python from
- Python lambda
- Python assert
- Python Built-in Functions
- Python All Built-in Functions
- Python print() Function
- Python input() Function
- Python int() Function
- Python len() Function
- Python range() Function
- Python str() Function
- Python ord() Function
- Python chr() Function
- Python read()
- Python write()
- Python open()
- Python Examples
- Python Examples
Difference between pass and continue in Python
This article is created to clear all your doubts on the two conditional statements of the Python language, which are pass and continue.
The table given below differentiates "pass" and "continue" statements in the Python programming language.
| pass | continue |
|---|---|
| does nothing | jumps for the next iteration |
| required when syntactically necessary but practically not | required when you want to skip the execution of the remaining statement(s) inside the loop for the current iteration |
| can be used as a placeholder for future code | can not be used as a placeholder for future code |
pass vs. continue example in Python
Examples are extremely useful in understanding the topic of any computer programming language, such as Python. Therefore, here also, I've created an example that easily shows you the difference between these two statements:
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] print("----Using \"pass\"-------") for n in nums: if n == 3: pass print(n) print("----Using \"continue\"-------") for n in nums: if n == 3: continue print(n)
This program produces the following output:
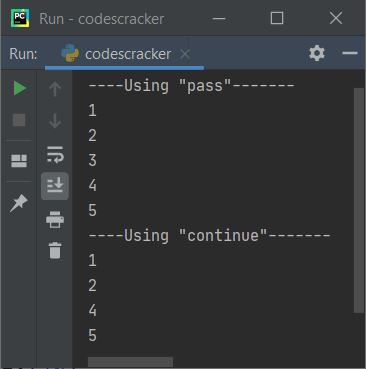
As you can see from the above output, the pass statement does nothing, whereas the continue statement skips the execution of the remaining statements; that is, "continue" jumps for the next iteration, whereas "pass" does not.
Advantages of the pass statement in Python
- When you need to define a function, class, or other code block that does not yet have functionality, the "pass" statement is useful as a placeholder. It enables you to write code that compiles without providing an actual implementation at this time.
- The "pass" statement is a valid Python statement that can be used to fulfill Python's syntax requirements. When creating a new class, for instance, you must include at least one method; the "pass" statement allows you to create an empty method without triggering a syntax error.
- Readability: The "pass" statement can be used to improve the readability of your code by indicating that a particular block of code is intentionally left blank.
Disadvantages of the pass statement in Python
- Using the pass statement excessively can make your code appear sloppy and unprofessional. It can also indicate that you are uncertain about the purpose of a particular block of code, which is an indication of poor planning.
- Maintenance: The "pass" statement can complicate code maintenance because it can be difficult to determine whether a block of empty code is intentional or accidental. This can make it more difficult for other developers to comprehend and modify your code.
Advantages of the continue statement in Python
- The "continue" statement allows you to control the flow of a loop by skipping iterations based on specific conditions. This can make your code more readable and efficient.
- The "continue" statement can be used in for, while, and nested loops, making it a versatile tool for controlling the flow of your code.
- Customization: The "continue" statement permits you to tailor the behavior of your loops by specifying precisely which iterations should be skipped. Complex programs that require a great deal of conditional logic may benefit from this.
Disadvantages of the continue statement in Python
- Complex logic: Using the "continue" statement can add another layer of conditional logic to your code, making it more complex. This can make your code more difficult to read and understand, particularly if you have many nested loops and conditions.
- Debugging: The "continue" statement can make debugging your code more difficult because it skips over certain iterations of a loop that may be causing errors. This can make determining the source of the problem more difficult.
- Performance: Using the "continue" statement can have a negative impact on the performance of your code in some cases, especially if you are skipping a large number of iterations. This is due to the fact that each iteration of a loop requires a certain amount of overhead, and skipping too many iterations can cause your program to slow down.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »