- Python Built-in Functions
- Python All Built-in Functions
- Python print() Function
- Python input() Function
- Python int() Function
- Python float() Function
- Python len() Function
- Python range() Function
- Python str() Function
- Python ord() Function
- Python chr() Function
- Python ascii() Function
- Python pow() Function
- Python type() Function
- Python List Functions
- Python list() Function
- Python insert() Function
- Python append() Function
- Python extend() Function
- Python pop() Function
- Python remove() Function
- Python reverse() Function
- Python sort() Function
- Python sorted() Function
- Python Dictionary Functions
- Python dict() Function
- Python update() Function
- Python get() Function
- Python keys() Function
- Python setdefault() Function
- Python fromkeys() Function
- Python items() Function
- Python popitem() Function
- Python Tuple Function
- Python tuple() Function
- Python Set Functions
- Python set() Function
- Python frozenset() Function
- Python String Functions
- Python split() Function
- Python join() Function
- Python format() Function
- Python replace() Function
- Python Iterator Functions
- Python iter() Function
- Python min() Function
- Python max() Function
- Python sum() Function
- Python count() Function
- Python index() Function
- Python copy() Function
- Python clear() Function
- Python next() Function
- Python filter() Function
- Python enumerate() Function
- Python zip() Function
- Python reversed() Function
- Python Number Functions
- Python abs() Function
- Python bin() Function
- Python oct() Function
- Python hex() Function
- Python round() Function
- Python divmod() Function
- Python complex() Function
- Python File Handling Functions
- Python open() Function
- Python read() Function
- Python readable() Function
- Python readline() Function
- Python readlines() Function
- Python write() Function
- Python writable() Function
- Python writelines() Function
- Python close() Function
- Python seek() Function
- Python tell() Function
- Python flush() Function
- Python fileno() Function
- Python truncate() Function
- Python Class Functions
- Python object() Function
- Python property() Function
- Python getattr() Function
- Python setattr() Function
- Python hasattr() Function
- Python delattr() Function
- Python classmethod() Function
- Python staticmethod() Function
- Python issubclass() Function
- Python super() Function
- Python Misc Functions
- Python all() Function
- Python any() Function
- Python isatty() Function
- Python bool() Function
- Python callable() Function
- Python globals() Function
- Python locals() Function
- Python dir() Function
- Python id() Function
- Python isinstance() Function
- Python map() Function
- Python repr() Function
- Python slice() Function
- Python vars() Function
- Python Advance Functions
- Python help() Function
- Python hash() Function
- Python breakpoint() Function
- Python bytes() Function
- Python bytearray() Function
- Python memoryview() Function
- Python compile() Function
- Python eval() Function
- Python exec() Function
- Python Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- Python Examples
- Python Examples
Python bytes() Function
The bytes() function in Python returns a bytes object, or converts an object into a bytes type object. For example:
x = bytes() print(type(x)) print(bytes(5)) a = "codescracker" x = bytes(a, "utf-8") print(x) b = "python" b = bytes(b, "utf-16") print(b)
The snapshot given below shows the sample run of above program, demonstrating the bytes() function in Python:
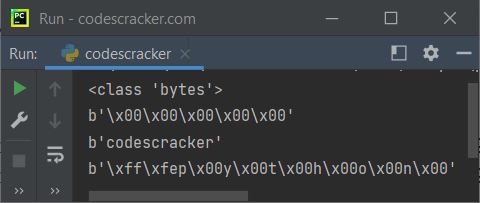
Note: Unlike bytearray(), bytes() returns an object that cannot be modified.
Note: Everything like syntax and example is similar to bytearray() function, except bytes() returns bytes type object, and can be modified.
Python bytes() Function Syntax
The syntax of bytes() function in Python is:
bytes(x, encoding, error)
where x refers to the source. The source may be of string, integer, iterable, or object type. If the source is an integer type, then an empty bytes object with specified size will get created. The encoding is needed when x is of string type. The error is used when the encoding fails or mismatched. All the three parameters are optional.
Python bytes() Function Example
Here is an example of bytes() function in Python:
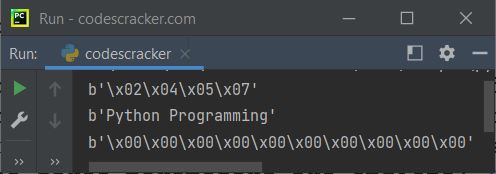
x = [2, 4, 5, 7] ba = bytes(x) print(ba) x = "Python Programming" ba = bytes(x, "utf-8") print(ba) x = 10 ba = bytes(x) print(ba)
Here is its sample output:
« Previous Function Next Function »