- Python Built-in Functions
- Python All Built-in Functions
- Python print() Function
- Python input() Function
- Python int() Function
- Python float() Function
- Python len() Function
- Python range() Function
- Python str() Function
- Python ord() Function
- Python chr() Function
- Python ascii() Function
- Python pow() Function
- Python type() Function
- Python List Functions
- Python list() Function
- Python insert() Function
- Python append() Function
- Python extend() Function
- Python pop() Function
- Python remove() Function
- Python reverse() Function
- Python sort() Function
- Python sorted() Function
- Python Dictionary Functions
- Python dict() Function
- Python update() Function
- Python get() Function
- Python keys() Function
- Python setdefault() Function
- Python fromkeys() Function
- Python items() Function
- Python popitem() Function
- Python Tuple Function
- Python tuple() Function
- Python Set Functions
- Python set() Function
- Python frozenset() Function
- Python String Functions
- Python split() Function
- Python join() Function
- Python format() Function
- Python replace() Function
- Python Iterator Functions
- Python iter() Function
- Python min() Function
- Python max() Function
- Python sum() Function
- Python count() Function
- Python index() Function
- Python copy() Function
- Python clear() Function
- Python next() Function
- Python filter() Function
- Python enumerate() Function
- Python zip() Function
- Python reversed() Function
- Python Number Functions
- Python abs() Function
- Python bin() Function
- Python oct() Function
- Python hex() Function
- Python round() Function
- Python divmod() Function
- Python complex() Function
- Python File Handling Functions
- Python open() Function
- Python read() Function
- Python readable() Function
- Python readline() Function
- Python readlines() Function
- Python write() Function
- Python writable() Function
- Python writelines() Function
- Python close() Function
- Python seek() Function
- Python tell() Function
- Python flush() Function
- Python fileno() Function
- Python truncate() Function
- Python Class Functions
- Python object() Function
- Python property() Function
- Python getattr() Function
- Python setattr() Function
- Python hasattr() Function
- Python delattr() Function
- Python classmethod() Function
- Python staticmethod() Function
- Python issubclass() Function
- Python super() Function
- Python Misc Functions
- Python all() Function
- Python any() Function
- Python isatty() Function
- Python bool() Function
- Python callable() Function
- Python globals() Function
- Python locals() Function
- Python dir() Function
- Python id() Function
- Python isinstance() Function
- Python map() Function
- Python repr() Function
- Python slice() Function
- Python vars() Function
- Python Advance Functions
- Python help() Function
- Python hash() Function
- Python breakpoint() Function
- Python bytes() Function
- Python bytearray() Function
- Python memoryview() Function
- Python compile() Function
- Python eval() Function
- Python exec() Function
- Python Tutorial
- Python Tutorial
- Python Examples
- Python Examples
Python classsmethod() Function
The classmethod() function in Python returns a class method of specified function. For example:
class CodesCracker: def welcome(self): print("Welcome to CodesCracker") CodesCracker.welcome = classmethod(CodesCracker.welcome) CodesCracker.welcome()
The output produced by this program is:
Welcome to CodesCracker
Note: A class method can be called by an object or by a class, both.
Note: A class method is a method, bound to the class, rather than the object of the class.
Recommend - Use @classmethod decorator to define class methods, instead of using classmethod() function to get/convert to a class method.
Python classmethod() Function Syntax
The syntax of classmethod() function is:
classsmethod(x)
where x is a function. The classmethod() converts the function x into a class method.
Python classmethod() Function Example
Here is an example of classmethod() function in Python:
class CodesCracker: def myfun(self, x): print("Value of x:", x) print(CodesCracker.myfun) CodesCracker.myfun = classmethod(CodesCracker.myfun) CodesCracker.myfun(100) print(CodesCracker.myfun)
The snapshot given below shows the sample output produced by above Python program, demonstrating the classmethod() function:
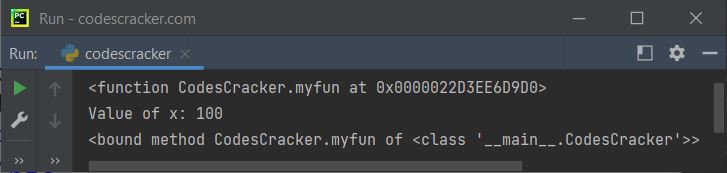
As you can see from the above output, before converting the method named myfun() to a class method using classmethod() function. The statement:
print(CodesCracker.myfun)
prints:
<function CodesCracker.myfun at 0x0000022D3EE6D9D0>
indicates that the function myfun of the class CodesCracker is like a normal function. But after using the following statement:
CodesCracker.myfun = classmethod(CodesCracker.myfun)
The same function gets converted into class method. Therefore now the following statement:
print(CodesCracker.myfun)
prints:
<bound method CodesCracker.myfun of <class '__main__.CodesCracker'>>
indicates that the function myfun becomes a method that is now bounded to the class CodesCracker, and myfun() is now a class method.
Related Article - Python class method Vs static method.
« Previous Function Next Function »