- JavaScript Basics
- JavaScript Tutorial
- JavaScript: where to write
- JavaScript: how to display
- JavaScript: keywords
- JavaScript: comments
- JavaScript: variables
- JavaScript: operators
- JavaScript: data types
- JavaScript Conditional Statements
- JavaScript: if-else
- JavaScript: switch
- JavaScript: for loop
- JavaScript: while loop
- JavaScript: do-while loop
- JavaScript: break and continue
- JavaScript Popup Boxes
- JavaScript: alert box
- JavaScript: confirm box
- JavaScript: prompt box
- JavaScript Popular Topics
- JavaScript: functions
- JavaScript: innerHTML
- JavaScript: getElementById()
- JavaScript: getElementsByClassName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByTagName()
- JavaScript: querySelector()
- JavaScript: querySelectorAll()
- JavaScript: document.write()
- JavaScript: console.log()
- JavaScript: boolean
- JavaScript: events
- JavaScript: Math object
- JavaScript: Math.random()
- JavaScript: Number()
- JavaScript: parseInt()
- JavaScript: parseFloat()
- JavaScript Arrays
- JavaScript: array
- JavaScript: find length of array
- JavaScript: add element at beginning
- JavaScript: add element at end
- JavaScript: remove first element
- JavaScript: remove last element
- JavaScript: get first index
- JavaScript: get last index
- JavaScript: reverse an array
- JavaScript: sort an array
- JavaScript: concatenate arrays
- JavaScript: join()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: from()
- JavaScript: check if value exists
- JavaScript: check if array
- JavaScript: slice an array
- JavaScript: splice()
- JavaScript: find()
- JavaScript: findIndex()
- JavaScript: entries()
- JavaScript: every()
- JavaScript: fill()
- JavaScript: filter()
- JavaScript: forEach()
- JavaScript: map()
- JavaScript Strings
- JavaScript: string
- JavaScript: length of string
- JavaScript: convert to lowercase
- JavaScript: convert to uppercase
- JavaScript: string concatenation
- JavaScript: search()
- JavaScript: indexOf()
- JavaScript: search() vs. indexOf()
- JavaScript: match()
- JavaScript: match() vs. search()
- JavaScript: replace()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: String()
- JavaScript: includes()
- JavaScript: substr()
- JavaScript: slice string
- JavaScript: charAt()
- JavaScript: repeat()
- JavaScript: split()
- JavaScript: charCodeAt()
- JavaScript: fromCharCode()
- JavaScript: startsWith()
- JavaScript: endsWith()
- JavaScript: trim()
- JavaScript: lastIndexOf()
- JavaScript Date and Time
- JavaScript: date and time
- JavaScript: Date()
- JavaScript: getFullYear()
- JavaScript: getMonth()
- JavaScript: getDate()
- JavaScript: getDay()
- JavaScript: getHours()
- JavaScript: getMinutes()
- JavaScript: getSeconds()
- JavaScript: getMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: getTime()
- JavaScript: getUTCFullYear()
- JavaScript: getUTCMonth()
- JavaScript: getUTCDate()
- JavaScript: getUTCDay()
- JavaScript: getUTCHours()
- JavaScript: getUTCMinutes()
- JavaScript: getUTCSeconds()
- JavaScript: getUTCMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: toDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleTimeString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleString()
- JavaScript: toUTCString()
- JavaScript: getTimezoneOffset()
- JavaScript: toISOString()
- JavaScript Regular Expression
- JavaScript: regular expression
- JavaScript: RegEx . (dot)
- JavaScript: RegEx \w and \W
- JavaScript: RegEx \d and \D
- JavaScript: RegEx \s and \S
- JavaScript: RegEx \b and \B
- JavaScript: RegEx \0
- JavaScript: RegEx \n
- JavaScript: RegEx \xxx
- JavaScript: RegEx \xdd
- JavaScript: RegEx quantifiers
- JavaScript: RegEx test()
- JavaScript: RegEx lastIndex
- JavaScript: RegEx source
- JavaScript Programs
- JavaScript Programs
JavaScript operators: definition, types, and examples
The utilization of operators is one of the fundamental building blocks that JavaScript consists of. Operators are used to perform a wide range of operations in JavaScript, including arithmetic, logical, assignment, and comparison. Operators are crucial to the operation of any JavaScript program because they carry out tasks that can range from as simple as adding numbers together to as complex as performing intricate logical operations.
In this article, we'll go in-depth on the various JavaScript operators and show you how you can use them to manipulate data and carry out intricate operations. So fasten your seatbelts and get ready to explore JavaScript's operator world!
Types of operators in JavaScript
These are the following types of operators available in JavaScript:
- Arithmetic operators are used when we need to perform arithmetical tasks.
- Assignment operators are used to assign values.
- Comparison operators are used to compare between two variables or values.
- Logical (relational) operators are used to connect multiple expressions to evaluate and return a boolean value (true or false).
- Bitwise operators are used to perform bitwise (or bit-wise or bit-by-bit) operations.
- The ?: (ternary or conditional operator) is used as an alternative to if-else.
Arithmetic operators in JavaScript
Arithmetic operators in JavaScript are used when we need to perform arithmetical tasks. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>10 + 20 = <span id="mySpan"></span></p>
<script>
let x = 10, y = 20;
document.getElementById("mySpan").innerHTML = x+y;
</script>
</body>
</html>10 + 20 =
List of all arithmetic operators in JavaScript
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (-)
- Multiplication (*)
- Exponentiation (**)
- Division (/)
- Modulus (%)
- Increment (++)
- Decrement (--)
JavaScript arithmetic operators example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="1"></p>
<p id="2"></p>
<p id="3"></p>
<p id="4"></p>
<p id="5"></p>
<p id="6"></p>
<p id="7"></p>
<p id="8"></p>
<script>
let a = 20, b = 10, c = 3, d = 4;
res = a+b;
document.getElementById("1").innerHTML = res;
res = a-b;
document.getElementById("2").innerHTML = res;
res = a*b;
document.getElementById("3").innerHTML = res;
res = c**d;
document.getElementById("4").innerHTML = res;
res = a/b;
document.getElementById("5").innerHTML = res;
res = a%c;
document.getElementById("6").innerHTML = res;
res = a++;
document.getElementById("7").innerHTML = res;
res = a--;
document.getElementById("8").innerHTML = res;
</script>
</body>
</html>The increment (++) and decrement (--) operators in JavaScript
Both increment and decrement operators in JavaScript are of two types, namely:
- Pre-increment operator (++x)
- Post-increment operator (x++)
- Pre-decrement operator (--x)
- Post-decrement operator (x--)
The pre-increment or pre-decrement is used to increment or decrement the value before use. where the post-increment or post-decrement is used to use the value before the increment or decrement. The value will be incremented or decremented by 1 each time. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="a"></p>
<p id="b"></p>
<p id="c"></p>
<p id="d"></p>
<p id="e"></p>
<p id="f"></p>
<p id="g"></p>
<p id="h"></p>
<script>
let m = 10, n = 20;
document.getElementById("a").innerHTML = m++;
document.getElementById("b").innerHTML = m;
document.getElementById("c").innerHTML = ++m;
document.getElementById("d").innerHTML = m;
document.getElementById("e").innerHTML = n--;
document.getElementById("f").innerHTML = n;
document.getElementById("g").innerHTML = --n;
document.getElementById("h").innerHTML = n;
</script>
</body>
</html>Assignment operators in JavaScript
Assignment operators in JavaScript are used to assign values. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="abc"></p>
<p id="xyz"></p>
<script>
let x;
x = 20;
document.getElementById("abc").innerHTML = x;
x += 5;
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = x;
</script>
</body>
</html>List of all assignment operators in JavaScript
- Simple assign (=)
- Add, then assign (+=)
- Subtract, then assign (-=)
- Multiply, then assign (*=)
- Divide, then assign (/=)
- Modulus, then assign (%=)
- Exponent, then assign (**=)
JavaScript assignment operators example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="para1"></p>
<p id="para2"></p>
<p id="para3"></p>
<p id="para4"></p>
<p id="para5"></p>
<p id="para6"></p>
<p id="para7"></p>
<script>
let a = 20, b = 3, res;
res = b;
document.getElementById("para1").innerHTML = res;
res += 5;
document.getElementById("para2").innerHTML = res;
res -= 5;
document.getElementById("para3").innerHTML = res;
res *= 5;
document.getElementById("para4").innerHTML = res;
res /= 10;
document.getElementById("para5").innerHTML = res;
a %= 3;
document.getElementById("para6").innerHTML = a;
b **= 4;
document.getElementById("para7").innerHTML = b;
</script>
</body>
</html>Note: The expression x += 10 is the same as x = x + 10. Alternatively, x += y is equivalent to x = x + y.
Comparison operators in JavaScript
Comparison operators in JavaScript are used to compare between two variables or values. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="xyz"></p>
<script>
let x = 20;
let y = 20;
if(x==y) {
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = "The value of 'x' is equal to the value of 'y'";
} else {
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = "The value of 'x' is not equal to the value of 'y'";
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Note: Comparison operators in JavaScript returns boolean values (true or false). Therefore, x==y or 20==20 returns true because both numbers are obviously equal to each other.
List of all comparison operators in JavaScript
| Operator | Name |
|---|---|
| == | equal to |
| === | equal value and equal type |
| != | not equal |
| !== | not equal value or not equal type |
| < | less than |
| > | greater than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
JavaScript comparison operators example
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="para1"></p>
<p id="para2"></p>
<p id="para3"></p>
<p id="para4"></p>
<p id="para5"></p>
<p id="para6"></p>
<p id="para7"></p>
<p id="para8"></p>
<p id="para9"></p>
<p id="para10"></p>
<p id="para11"></p>
<p id="para12"></p>
<p id="para13"></p>
<p id="para14"></p>
<p id="para15"></p>
<p id="para16"></p>
<p id="para17"></p>
<p id="para18"></p>
<script>
let a = 10, b = 10, c = 20, d = "10";
document.getElementById("para1").innerHTML = a==b;
document.getElementById("para2").innerHTML = a==c;
document.getElementById("para3").innerHTML = a===b;
document.getElementById("para4").innerHTML = a===c;
document.getElementById("para5").innerHTML = a===d;
document.getElementById("para6").innerHTML = a!=b;
document.getElementById("para7").innerHTML = a!=c;
document.getElementById("para8").innerHTML = a!==b;
document.getElementById("para9").innerHTML = a!==c;
document.getElementById("para10").innerHTML = a!==d;
document.getElementById("para11").innerHTML = a>b;
document.getElementById("para12").innerHTML = a>c;
document.getElementById("para13").innerHTML = a<b;
document.getElementById("para14").innerHTML = a<c;
document.getElementById("para15").innerHTML = a>=b;
document.getElementById("para16").innerHTML = a>=c;
document.getElementById("para17").innerHTML = a<=b;
document.getElementById("para18").innerHTML = a<=c;
</script>
</body>
</html>Logical operators in JavaScript
Logical operators in JavaScript are used to connect multiple expressions to evaluate and return a boolean value (true or false). For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Largest = <span id="xyz"></span></p>
<script>
var a = 10, b = 20, c = 30, large;
if(a>b && a>c) {
large = a;
}
else if(b>a && b>c) {
large = b;
}
else {
large = c;
}
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = large;
</script>
</body>
</html>Largest = 30
List of all logical operators in JavaScript
JavaScript logical OR (||) operator
The || operator returns true if any of the expressions evaluate to be true. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="abc"></p>
<script>
var x = 10, y = 12, z = 11, res;
res = x>y || y>z;
document.getElementById("abc").innerHTML = res;
</script>
</body>
</html>In the above example, since the first expression, which is x>y or 10>12, evaluates to be false but the second expression, which is y>z or 12>11, evaluates to be true, therefore true will be initialized to the res variable.
JavaScript logical AND (&&) operator
The && operator returns true if all the expressions evaluate to be true. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="myPara"></p>
<script>
var x = 10, y = 12, z = 11, res;
res = z>x && y>z;
document.getElementById("myPara").innerHTML = res;
</script>
</body>
</html>JavaScript logical NOT (!) operator
The ! operator reverses the boolean value. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="mp"></p>
<script>
var x = 10, y = 12, z = 11, res;
res = !(z>x && y>z);
document.getElementById("mp").innerHTML = res;
</script>
</body>
</html>Bitwise operators in JavaScript
Bitwise operators in JavaScript are used to perform bitwise (bit-wise or bit-by-bit) operations. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="xyz"></p>
<script>
let x = 6, y = 3;
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = x & y;
</script>
</body>
</html>Note: Bit operators work on 32-bit numbers. Bitwise operations go on bit patterns (binary numerals) and involve individual bit manipulation.
In the above example, the binary equivalent of 6 is 110 (or 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0110 in a 32-bit number). Whereas the binary equivalent of 3 is 11 (or 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0011 in a 32-bit number). Therefore:
1 1 0
& 0 1 1
----------
0 1 0
The 010 or 10 is equal to 2 in decimal. That is, in 32-bit numbers:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 (6)
& 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 (3)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 (2)
List of all Bitwise operators in JavaScript
- Bitwise AND (&)
- Bitwise OR (|)
- Bitwise XOR (^)
- Bitwise NOT (˜)
- Bitwise Right Shift (>>)
- Bitwise Left Shift (<<)
- Bitwise Unsigned Right Shift (>>>)
To learn about Bitwise operators with examples in detail, refer to its separate tutorial.
?: (conditional or ternary) operator in JavaScript
The ?: (conditional or ternary) operator in JavaScript takes three operands and is used as an alternative to if-else. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
let x = 10, y = 20;
x>y ? console.log(x) : console.log(y);
</script>
</body>
</html>The snapshot given below shows the sample output produced by the above JavaScript example:
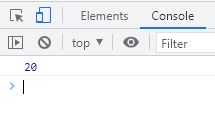
The same JavaScript code can also be written as:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Largest = <span id="xyz"></span></p>
<script>
let x = 10, y = 20, large;
large = x>y ? x : y;
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = large;
</script>
</body>
</html>Largest = 20
JavaScript Ternary Operator (?:) Syntax
The syntax of the ternary operator in JavaScript is:
condition ? evaluateIfTrue : evaluateIfFalse
That is, if the condition evaluates to be true, then the whole expression is replaced with evaluateIfTrue, otherwise with evaluateIfFalse. For example:
20==20 ? document.write("Both numbers are equal") : document.write("Both numbers are not equal")
Since the condition 20==20 evaluates to be true, therefore the first expression gets executed, that is:
document.write("Both numbers are equal")
will be executed, and Both numbers are equal will be displayed on the output.
Nested ternary operator in JavaScript
To understand the nested ternary operator in JavaScript, the best and most simple example that I can give you is finding the largest of three numbers using the ternary operator:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Largest = <span id="abc"></span></p>
<script>
let a = 10, b = 20, c = 30, large;
large = (a>b) ? ((b>c) ? (a) : (c>a ? c : a)) : (b>c ? b : c);
document.getElementById("abc").innerHTML = large;
</script>
</body>
</html>Largest =
In above example, the following expression:
(a>b) ? ((b>c) ? (a) : (c>a ? c : a)) : (b>c ? b : c);
will be evaluated in a way that:
- First, the condition (a>b) gets evaluated.
- Since the condition (a>b) or (10>20) evaluates to be false.
- Therefore, (b>c ? b : c) replaced the whole expression.
- Now the condition b>c gets evaluated.
- Since the condition b>c or 20>30 evaluates to be false.
- Therefore, c replaced the whole expression.
- Since the value of c is 30, 30 gets initialized as a large variable.
The operators not covered in this post are "typeof" and "instanceof." The "typeof" operator is used to determine the type of a variable, while the "instanceof" operator is used to determine whether the prototype property of a constructor appears in an object's prototype chain.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »