- JavaScript Basics
- JavaScript Tutorial
- JavaScript: where to write
- JavaScript: how to display
- JavaScript: keywords
- JavaScript: comments
- JavaScript: variables
- JavaScript: operators
- JavaScript: data types
- JavaScript Conditional Statements
- JavaScript: if-else
- JavaScript: switch
- JavaScript: for loop
- JavaScript: while loop
- JavaScript: do-while loop
- JavaScript: break and continue
- JavaScript Popup Boxes
- JavaScript: alert box
- JavaScript: confirm box
- JavaScript: prompt box
- JavaScript Popular Topics
- JavaScript: functions
- JavaScript: innerHTML
- JavaScript: getElementById()
- JavaScript: getElementsByClassName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByTagName()
- JavaScript: querySelector()
- JavaScript: querySelectorAll()
- JavaScript: document.write()
- JavaScript: console.log()
- JavaScript: boolean
- JavaScript: events
- JavaScript: Math object
- JavaScript: Math.random()
- JavaScript: Number()
- JavaScript: parseInt()
- JavaScript: parseFloat()
- JavaScript Arrays
- JavaScript: array
- JavaScript: find length of array
- JavaScript: add element at beginning
- JavaScript: add element at end
- JavaScript: remove first element
- JavaScript: remove last element
- JavaScript: get first index
- JavaScript: get last index
- JavaScript: reverse an array
- JavaScript: sort an array
- JavaScript: concatenate arrays
- JavaScript: join()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: from()
- JavaScript: check if value exists
- JavaScript: check if array
- JavaScript: slice an array
- JavaScript: splice()
- JavaScript: find()
- JavaScript: findIndex()
- JavaScript: entries()
- JavaScript: every()
- JavaScript: fill()
- JavaScript: filter()
- JavaScript: forEach()
- JavaScript: map()
- JavaScript Strings
- JavaScript: string
- JavaScript: length of string
- JavaScript: convert to lowercase
- JavaScript: convert to uppercase
- JavaScript: string concatenation
- JavaScript: search()
- JavaScript: indexOf()
- JavaScript: search() vs. indexOf()
- JavaScript: match()
- JavaScript: match() vs. search()
- JavaScript: replace()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: String()
- JavaScript: includes()
- JavaScript: substr()
- JavaScript: slice string
- JavaScript: charAt()
- JavaScript: repeat()
- JavaScript: split()
- JavaScript: charCodeAt()
- JavaScript: fromCharCode()
- JavaScript: startsWith()
- JavaScript: endsWith()
- JavaScript: trim()
- JavaScript: lastIndexOf()
- JavaScript Date and Time
- JavaScript: date and time
- JavaScript: Date()
- JavaScript: getFullYear()
- JavaScript: getMonth()
- JavaScript: getDate()
- JavaScript: getDay()
- JavaScript: getHours()
- JavaScript: getMinutes()
- JavaScript: getSeconds()
- JavaScript: getMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: getTime()
- JavaScript: getUTCFullYear()
- JavaScript: getUTCMonth()
- JavaScript: getUTCDate()
- JavaScript: getUTCDay()
- JavaScript: getUTCHours()
- JavaScript: getUTCMinutes()
- JavaScript: getUTCSeconds()
- JavaScript: getUTCMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: toDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleTimeString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleString()
- JavaScript: toUTCString()
- JavaScript: getTimezoneOffset()
- JavaScript: toISOString()
- JavaScript Regular Expression
- JavaScript: regular expression
- JavaScript: RegEx . (dot)
- JavaScript: RegEx \w and \W
- JavaScript: RegEx \d and \D
- JavaScript: RegEx \s and \S
- JavaScript: RegEx \b and \B
- JavaScript: RegEx \0
- JavaScript: RegEx \n
- JavaScript: RegEx \xxx
- JavaScript: RegEx \xdd
- JavaScript: RegEx quantifiers
- JavaScript: RegEx test()
- JavaScript: RegEx lastIndex
- JavaScript: RegEx source
- JavaScript Programs
- JavaScript Programs
Where to Write JavaScript Code in HTML
The list of places in HTML where we can write our JavaScript code is as follows:
- <HEAD>
- <BODY>
That is, either we can write our JavaScript code anywhere between <HEAD> and </HEAD> or anywhere between <BODY> and </BODY>.
Note: We can also write our JavaScript code in both the HEAD and BODY section of an HTML document.
Write JavaScript in the HEAD Section of an HTML Document
Before writing JavaScript code inside an HTML document, open a <SCRIPT> tag, and after the JavaScript code is complete, close the </SCRIPT> tag.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function codescracker() {
alert("Hello there!");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<input type="button" onclick="codescracker()" value="Click Me">
</body>
</html>When you click on the Click Me button, a function named codescracker is called that displays Hello there! as an alert box.
In the above example, the following JavaScript code:
function codescracker() {
...
}
is the declaration of the JavaScript function codescracker(). It defines a function that, upon execution, will show an alert box with the text "Hello there!"
Now the following JavaScript statement:
alert("Hello there!");
is a JavaScript function that creates an alert box with the specified message using built-in technology. Finally, the following code:
onclick="codescracker()
is used to call the function "codescracker()" when the button associated with this "onclick" event is clicked.
Note: The <script> tag is used to include JavaScript code in the HTML document.
You will learn both the function, alert box, and the onclick event later in this JavaScript tutorial series.
Write JavaScript in the BODY Section of an HTML Document
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<input type="button" onclick="codescracker()" value="Click Me">
<script>
function codescracker() {
alert("Hello there!");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Write JavaScript in the HEAD and BODY Sections of an HTML Document
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function codes() {
alert("Hello there!");
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<script>
function cracker() {
alert("JavaScript is Fun!");
}
</script>
<input type="button" onclick="codes()" value="Button 1"><br><br>
<input type="button" onclick="cracker()" value="Button 2">
</body>
</html>Note: To include external JavaScript in an HTML document, use the src attribute of the SCRIPT tag.
Include an external JavaScript file in HTML
We can also write our JavaScript code in an external file and then include or link that file into an HTML document anywhere in the HEAD or BODY section.
For example, write the following JavaScript code in any text editor, say NotePad:
function codescracker() {
alert("Hello there!");
}
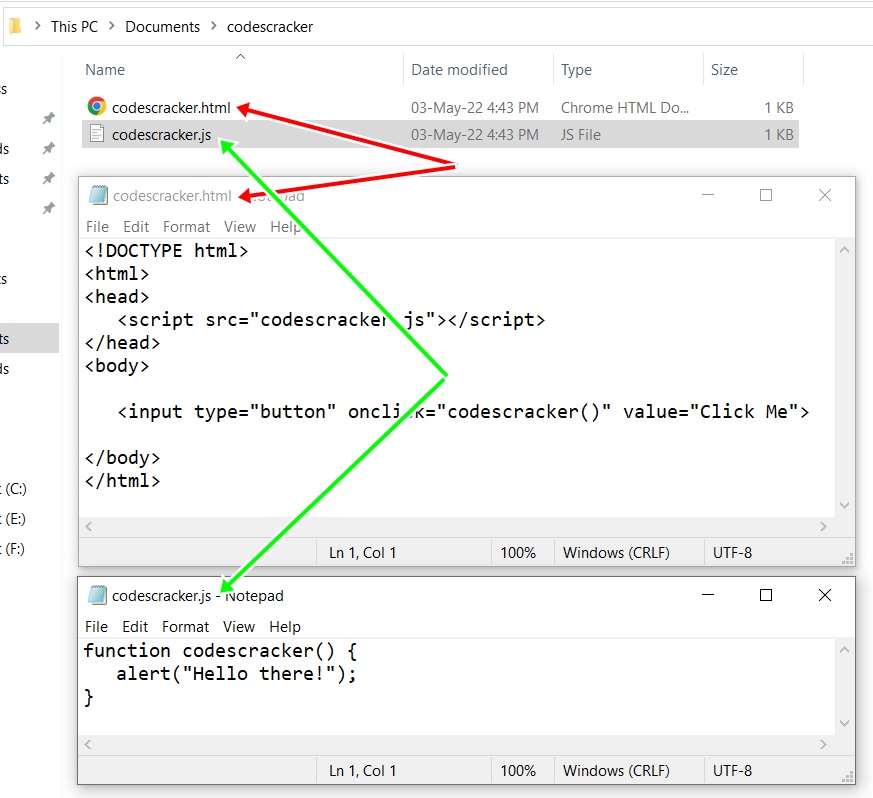
Save this file with any name ending with .js extension, say codescracker.js, inside the same directory (the directory where the .html file is saved). Now, here is the code for the codescracker.html file:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <script src="codescracker.js"></script> </head> <body> <input type="button" onclick="codescracker()" value="Click Me"> </body> </html>
You will get the same output as the first example available at the top of this article.
Here is a snapshot of both files, that is, codescracker.html and codescracker.js, available in the same folder:
You can also include an external JavaScript file from another directory or folder. For that, provide the full path to the src attribute. For example:
<script src="file:///C:/javascript/files/codescracker.js"></script>
Here are the ways to access and include an external JavaScript file in an HTML document from different directories.
- <script src="codescracker.js"> - Indicates the file codescracker.js available in the same folder.
- <script src="myjs/codescracker.js"> - Indicates the file codescracker.js available in the myjs folder of the current folder.
- <script src="/myjs/codescracker.js"> - Indicates to the file codescracker.js available in the myjs folder from the root.
- <script src="../codescracker.js"> - Indicates the file codescracker.js available in the one level up folder from the current folder.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »