- JavaScript Basics
- JavaScript Tutorial
- JavaScript: where to write
- JavaScript: how to display
- JavaScript: keywords
- JavaScript: comments
- JavaScript: variables
- JavaScript: operators
- JavaScript: data types
- JavaScript Conditional Statements
- JavaScript: if-else
- JavaScript: switch
- JavaScript: for loop
- JavaScript: while loop
- JavaScript: do-while loop
- JavaScript: break and continue
- JavaScript Popup Boxes
- JavaScript: alert box
- JavaScript: confirm box
- JavaScript: prompt box
- JavaScript Popular Topics
- JavaScript: functions
- JavaScript: innerHTML
- JavaScript: getElementById()
- JavaScript: getElementsByClassName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByTagName()
- JavaScript: querySelector()
- JavaScript: querySelectorAll()
- JavaScript: document.write()
- JavaScript: console.log()
- JavaScript: boolean
- JavaScript: events
- JavaScript: Math object
- JavaScript: Math.random()
- JavaScript: Number()
- JavaScript: parseInt()
- JavaScript: parseFloat()
- JavaScript Arrays
- JavaScript: array
- JavaScript: find length of array
- JavaScript: add element at beginning
- JavaScript: add element at end
- JavaScript: remove first element
- JavaScript: remove last element
- JavaScript: get first index
- JavaScript: get last index
- JavaScript: reverse an array
- JavaScript: sort an array
- JavaScript: concatenate arrays
- JavaScript: join()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: from()
- JavaScript: check if value exists
- JavaScript: check if array
- JavaScript: slice an array
- JavaScript: splice()
- JavaScript: find()
- JavaScript: findIndex()
- JavaScript: entries()
- JavaScript: every()
- JavaScript: fill()
- JavaScript: filter()
- JavaScript: forEach()
- JavaScript: map()
- JavaScript Strings
- JavaScript: string
- JavaScript: length of string
- JavaScript: convert to lowercase
- JavaScript: convert to uppercase
- JavaScript: string concatenation
- JavaScript: search()
- JavaScript: indexOf()
- JavaScript: search() vs. indexOf()
- JavaScript: match()
- JavaScript: match() vs. search()
- JavaScript: replace()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: String()
- JavaScript: includes()
- JavaScript: substr()
- JavaScript: slice string
- JavaScript: charAt()
- JavaScript: repeat()
- JavaScript: split()
- JavaScript: charCodeAt()
- JavaScript: fromCharCode()
- JavaScript: startsWith()
- JavaScript: endsWith()
- JavaScript: trim()
- JavaScript: lastIndexOf()
- JavaScript Date and Time
- JavaScript: date and time
- JavaScript: Date()
- JavaScript: getFullYear()
- JavaScript: getMonth()
- JavaScript: getDate()
- JavaScript: getDay()
- JavaScript: getHours()
- JavaScript: getMinutes()
- JavaScript: getSeconds()
- JavaScript: getMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: getTime()
- JavaScript: getUTCFullYear()
- JavaScript: getUTCMonth()
- JavaScript: getUTCDate()
- JavaScript: getUTCDay()
- JavaScript: getUTCHours()
- JavaScript: getUTCMinutes()
- JavaScript: getUTCSeconds()
- JavaScript: getUTCMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: toDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleTimeString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleString()
- JavaScript: toUTCString()
- JavaScript: getTimezoneOffset()
- JavaScript: toISOString()
- JavaScript Regular Expression
- JavaScript: regular expression
- JavaScript: RegEx . (dot)
- JavaScript: RegEx \w and \W
- JavaScript: RegEx \d and \D
- JavaScript: RegEx \s and \S
- JavaScript: RegEx \b and \B
- JavaScript: RegEx \0
- JavaScript: RegEx \n
- JavaScript: RegEx \xxx
- JavaScript: RegEx \xdd
- JavaScript: RegEx quantifiers
- JavaScript: RegEx test()
- JavaScript: RegEx lastIndex
- JavaScript: RegEx source
- JavaScript Programs
- JavaScript Programs
JavaScript comments: definitions, types, and examples
If you're a developer or want to be one, you already know how important clean, readable, and well-organized code is. But did you know that your comments can help you achieve your goals? In JavaScript, comments are notes you leave behind to assist yourself and other developers in understanding the purpose and functionality of your code.
In this post, we'll look at the various types of JavaScript comments and when and where to use them. Prepare to take your programming skills to the next level with JavaScript comments!
What are comments in JavaScript?
Comments in JavaScript are lines of code that the interpreter or compiler ignore and are used to provide explanatory or descriptive text about the code. They are a way for developers to document the code and make it easier to understand, especially when working in a team environment.
The word comment refers to a written remark or opinion about anything. And in the world of computer programming, a comment is a piece of text placed within a program that helps other programmers understand the program.
The comments are ignored while executing the program. Therefore, comments are often helpful while debugging the code.
You can use comments for multiple purposes. For example, use comments to:
- explain some blocks of code
- explain a particular statement
- avoid executing some statement or block of code
- debug the code
- etc.
Types of Comments in JavaScript
There are two types of comments that JavaScript allows. That are:
Single Line Comment in JavaScript
A single-line comment in JavaScript starts with //. That is, anything written after the // on the same line will be treated as a comment. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
console.log("One");
// console.log("Two");
console.log("Three"); // console.log("Four");
console.log("Five");
</script>
</body>
</html>The snapshot given below shows the sample output produced by the above JavaScript example.
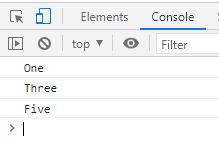
Multi-line comment in JavaScript
A multi-line comment in JavaScript starts with /* and ends with */. That is, anything between /* and */ will be treated as a comment. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
console.log("One");
/*
console.log("Two");
console.log("Three");
*/
console.log("Four"); /* console.log("Five"); */
console.log("Six"); /* console.log("Seven");
console.log("Eight"); */
console.log("Nine");
</script>
</body>
</html>The output produced by this example is:
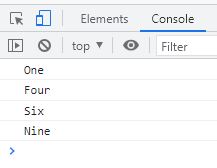
Comments can be used to explain complex code, describe the purpose of the code, and provide context for future developers who may be working on the same code. They can also be used to disable code temporarily without deleting it, which is useful during testing or debugging.
It is best practice to include comments in code to make it more readable and maintainable. However, it is also critical not to overdo it and clutter the code with unnecessary comments.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »