- JavaScript Basics
- JavaScript Tutorial
- JavaScript: where to write
- JavaScript: how to display
- JavaScript: keywords
- JavaScript: comments
- JavaScript: variables
- JavaScript: operators
- JavaScript: data types
- JavaScript Conditional Statements
- JavaScript: if-else
- JavaScript: switch
- JavaScript: for loop
- JavaScript: while loop
- JavaScript: do-while loop
- JavaScript: break and continue
- JavaScript Popup Boxes
- JavaScript: alert box
- JavaScript: confirm box
- JavaScript: prompt box
- JavaScript Popular Topics
- JavaScript: functions
- JavaScript: innerHTML
- JavaScript: getElementById()
- JavaScript: getElementsByClassName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByTagName()
- JavaScript: querySelector()
- JavaScript: querySelectorAll()
- JavaScript: document.write()
- JavaScript: console.log()
- JavaScript: boolean
- JavaScript: events
- JavaScript: Math object
- JavaScript: Math.random()
- JavaScript: Number()
- JavaScript: parseInt()
- JavaScript: parseFloat()
- JavaScript Arrays
- JavaScript: array
- JavaScript: find length of array
- JavaScript: add element at beginning
- JavaScript: add element at end
- JavaScript: remove first element
- JavaScript: remove last element
- JavaScript: get first index
- JavaScript: get last index
- JavaScript: reverse an array
- JavaScript: sort an array
- JavaScript: concatenate arrays
- JavaScript: join()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: from()
- JavaScript: check if value exists
- JavaScript: check if array
- JavaScript: slice an array
- JavaScript: splice()
- JavaScript: find()
- JavaScript: findIndex()
- JavaScript: entries()
- JavaScript: every()
- JavaScript: fill()
- JavaScript: filter()
- JavaScript: forEach()
- JavaScript: map()
- JavaScript Strings
- JavaScript: string
- JavaScript: length of string
- JavaScript: convert to lowercase
- JavaScript: convert to uppercase
- JavaScript: string concatenation
- JavaScript: search()
- JavaScript: indexOf()
- JavaScript: search() vs. indexOf()
- JavaScript: match()
- JavaScript: match() vs. search()
- JavaScript: replace()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: String()
- JavaScript: includes()
- JavaScript: substr()
- JavaScript: slice string
- JavaScript: charAt()
- JavaScript: repeat()
- JavaScript: split()
- JavaScript: charCodeAt()
- JavaScript: fromCharCode()
- JavaScript: startsWith()
- JavaScript: endsWith()
- JavaScript: trim()
- JavaScript: lastIndexOf()
- JavaScript Date and Time
- JavaScript: date and time
- JavaScript: Date()
- JavaScript: getFullYear()
- JavaScript: getMonth()
- JavaScript: getDate()
- JavaScript: getDay()
- JavaScript: getHours()
- JavaScript: getMinutes()
- JavaScript: getSeconds()
- JavaScript: getMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: getTime()
- JavaScript: getUTCFullYear()
- JavaScript: getUTCMonth()
- JavaScript: getUTCDate()
- JavaScript: getUTCDay()
- JavaScript: getUTCHours()
- JavaScript: getUTCMinutes()
- JavaScript: getUTCSeconds()
- JavaScript: getUTCMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: toDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleTimeString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleString()
- JavaScript: toUTCString()
- JavaScript: getTimezoneOffset()
- JavaScript: toISOString()
- JavaScript Regular Expression
- JavaScript: regular expression
- JavaScript: RegEx . (dot)
- JavaScript: RegEx \w and \W
- JavaScript: RegEx \d and \D
- JavaScript: RegEx \s and \S
- JavaScript: RegEx \b and \B
- JavaScript: RegEx \0
- JavaScript: RegEx \n
- JavaScript: RegEx \xxx
- JavaScript: RegEx \xdd
- JavaScript: RegEx quantifiers
- JavaScript: RegEx test()
- JavaScript: RegEx lastIndex
- JavaScript: RegEx source
- JavaScript Programs
- JavaScript Programs
JavaScript variables: definition, types, and examples
Variables in JavaScript are the containers for the data used in the program or application. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Sum of <span id="one">10</span> and <span id="two">20</span>
is <span id="res"></span></p>
<script>
var numOne = parseInt(document.getElementById("one").innerHTML);
var numTwo = parseInt(document.getElementById("two").innerHTML);
var result = numOne + numTwo;
document.getElementById("res").innerHTML = result;
</script>
</body>
</html>Sum of 10 and 20 is
In the above example, after initializing the value to a variable, say numOne, writing numOne anywhere in the program means writing the value inside it or representing the value stored in it.
Types of Variables in JavaScript
In JavaScript, a variable can be declared using any of the following three keywords:
That is, depending on the use of a keyword to declare a variable in JavaScript, there are three types of variables, which are:
- var Variable
- let Variable
- const Variable
Before describing these three types of variables in JavaScript, let's first cover the rules for naming a variable in JavaScript.
Rules for Naming a Variable in JavaScript
We should follow these rules before naming a variable in JavaScript:
- Variable names must start with a letter (A-Z or a-z), a dollar sign ($), or an underscore (_)
- Use letters, digits (0-9), underscores, and dollar signs to name a variable.
- Do not use any keyword to name a variable.
- Variable names in JavaScript are case-sensitive. Therefore, num, Num, and NUM are all different variables.
Here is a list of some valid variable names examples in JavaScript:
- num
- x
- _x
- $x
- first_name
- area34
- ar3t
- tr_$s_3_
JavaScript var: declare a global variable
The JavaScript var keyword is used to declare a global variable that can be updated as well as re-declared. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>1. <span id="span1"></span></p>
<p>2. <span id="span2"></span></p>
<p>3. <span id="span3"></span></p>
<p>4. <span id="span4"></span></p>
<p id="para1"></p>
<script>
var x = "codescracker.com";
document.getElementById("span1").innerHTML = x;
function myFun() {
document.getElementById("span2").innerHTML = x;
x = "codes cracker";
document.getElementById("span3").innerHTML = x;
}
myFun();
document.getElementById("span4").innerHTML = x;
var x = "JavaScript is Fun!";
document.getElementById("para1").innerHTML = x;
</script>
</body>
</html>1.
2.
3.
4.
Note: The default value of a variable declared using the var keyword is undefined. Therefore, accessing a var variable without its initialization returns or prints undefined. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="xyz"></p>
<script>
var a;
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = a;
</script>
</body>
</html>JavaScript var syntax
The syntax of the var keyword in JavaScript is:
var variableName = variableValue;
The variableValue is optional. That is, we can assign the value either at the time of declaration or later. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>The sum of 10 and 20 is <span id="x"></span></p>
<script>
var a = 10;
var b = 20;
var sum;
sum = a + b;
document.getElementById("x").innerHTML = sum;
</script>
</body>
</html>The sum of 10 and 20 is
As you can see from the above example, the variables a and b are initialized at the time of their declaration. where the variable sum is initialized later, after the declaration.
JavaScript let: declare a block-scoped variable
The JavaScript let keyword is used to create a block-scoped variable. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
var num = 2;
function myFun() {
for(let i=1; i<=10; i++) {
let res = num*i;
console.log(res);
}
}
myFun();
</script>
</body>
</html>The snapshot given below shows the sample output produced by the above example:
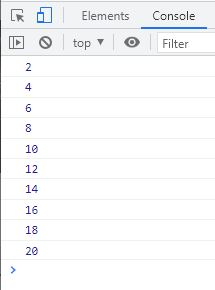
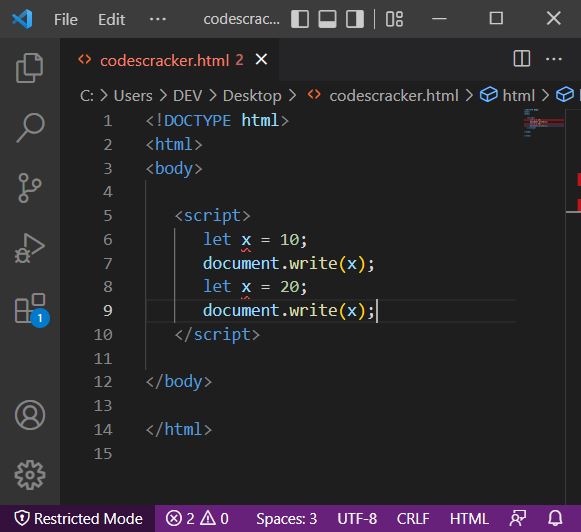
Unlike var, the let variable cannot be re-declared. If you do so, then you will get the error. For example:
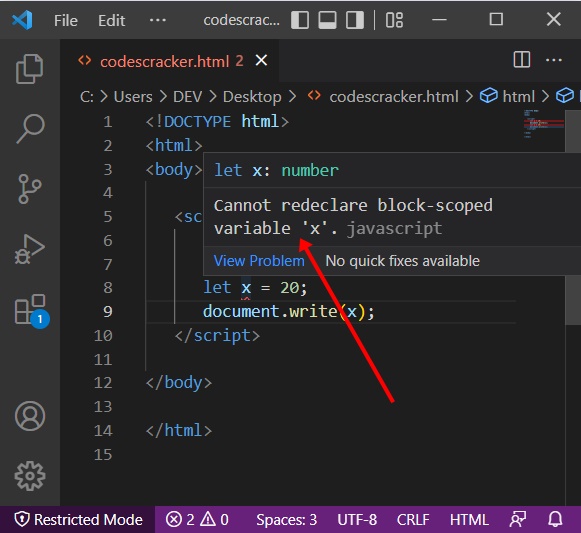
Look at the red underline next to x, the variable declared using let. If you will hover over any of the two x, then you will see:
Consider the following code as another example demonstrating the "let" keyword:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
var num = 2;
for(let i=1; i<=10; i++)
console.log(num*i);
</script>
</body>
</html>The output should be:
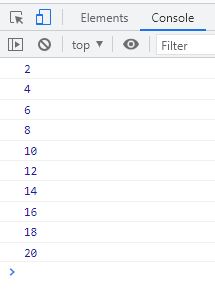
JavaScript const: create a constant variable
The JavaScript const keyword is used to create a block-scoped constant variable whose value cannot be changed or updated. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="xyz"></p>
<script>
const x = 10;
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = x;
</script>
</body>
</html>Note: The const variable can neither be updated nor re-declared.
The const variable can be used as a constant in a program. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="abc"></p>
<script>
const PI = 3.14159;
var radius = 12.8;
var area = PI * (radius*radius);
document.getElementById("abc").innerHTML = area;
</script>
</body>
</html>Also, use const variable if the value of the variable should not change further in the program. You can use const when you need to declare a new array, object, function, or RegExp.
Note: If you will use const to declare an array, then let me tell you. You can change the elements but not re-assign the array. Same goes for const object. That is, you can change the properties but not reassign the object.
Difference between var, let, and const in JavaScript
| var | let | const |
|---|---|---|
| declares a function-scoped or globally-scoped variable | declares a block-scoped local variable | declares a block-scoped variable |
| can be updated and re-declared | can be updated but cannot be re-declared | neither can be updated nor re-declared |
| can be declared without initializing any value | can be declared without initializing any value | can not be declared without initializing any value |
Note: Accessing a variable declared using the var keyword without initialization, returns undefined.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »