- JavaScript Basics
- JavaScript Tutorial
- JavaScript: where to write
- JavaScript: how to display
- JavaScript: keywords
- JavaScript: comments
- JavaScript: variables
- JavaScript: operators
- JavaScript: data types
- JavaScript Conditional Statements
- JavaScript: if-else
- JavaScript: switch
- JavaScript: for loop
- JavaScript: while loop
- JavaScript: do-while loop
- JavaScript: break and continue
- JavaScript Popup Boxes
- JavaScript: alert box
- JavaScript: confirm box
- JavaScript: prompt box
- JavaScript Popular Topics
- JavaScript: functions
- JavaScript: innerHTML
- JavaScript: getElementById()
- JavaScript: getElementsByClassName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByName()
- JavaScript: getElementsByTagName()
- JavaScript: querySelector()
- JavaScript: querySelectorAll()
- JavaScript: document.write()
- JavaScript: console.log()
- JavaScript: boolean
- JavaScript: events
- JavaScript: Math object
- JavaScript: Math.random()
- JavaScript: Number()
- JavaScript: parseInt()
- JavaScript: parseFloat()
- JavaScript Arrays
- JavaScript: array
- JavaScript: find length of array
- JavaScript: add element at beginning
- JavaScript: add element at end
- JavaScript: remove first element
- JavaScript: remove last element
- JavaScript: get first index
- JavaScript: get last index
- JavaScript: reverse an array
- JavaScript: sort an array
- JavaScript: concatenate arrays
- JavaScript: join()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: from()
- JavaScript: check if value exists
- JavaScript: check if array
- JavaScript: slice an array
- JavaScript: splice()
- JavaScript: find()
- JavaScript: findIndex()
- JavaScript: entries()
- JavaScript: every()
- JavaScript: fill()
- JavaScript: filter()
- JavaScript: forEach()
- JavaScript: map()
- JavaScript Strings
- JavaScript: string
- JavaScript: length of string
- JavaScript: convert to lowercase
- JavaScript: convert to uppercase
- JavaScript: string concatenation
- JavaScript: search()
- JavaScript: indexOf()
- JavaScript: search() vs. indexOf()
- JavaScript: match()
- JavaScript: match() vs. search()
- JavaScript: replace()
- JavaScript: toString()
- JavaScript: String()
- JavaScript: includes()
- JavaScript: substr()
- JavaScript: slice string
- JavaScript: charAt()
- JavaScript: repeat()
- JavaScript: split()
- JavaScript: charCodeAt()
- JavaScript: fromCharCode()
- JavaScript: startsWith()
- JavaScript: endsWith()
- JavaScript: trim()
- JavaScript: lastIndexOf()
- JavaScript Date and Time
- JavaScript: date and time
- JavaScript: Date()
- JavaScript: getFullYear()
- JavaScript: getMonth()
- JavaScript: getDate()
- JavaScript: getDay()
- JavaScript: getHours()
- JavaScript: getMinutes()
- JavaScript: getSeconds()
- JavaScript: getMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: getTime()
- JavaScript: getUTCFullYear()
- JavaScript: getUTCMonth()
- JavaScript: getUTCDate()
- JavaScript: getUTCDay()
- JavaScript: getUTCHours()
- JavaScript: getUTCMinutes()
- JavaScript: getUTCSeconds()
- JavaScript: getUTCMilliseconds()
- JavaScript: toDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleDateString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleTimeString()
- JavaScript: toLocaleString()
- JavaScript: toUTCString()
- JavaScript: getTimezoneOffset()
- JavaScript: toISOString()
- JavaScript Regular Expression
- JavaScript: regular expression
- JavaScript: RegEx . (dot)
- JavaScript: RegEx \w and \W
- JavaScript: RegEx \d and \D
- JavaScript: RegEx \s and \S
- JavaScript: RegEx \b and \B
- JavaScript: RegEx \0
- JavaScript: RegEx \n
- JavaScript: RegEx \xxx
- JavaScript: RegEx \xdd
- JavaScript: RegEx quantifiers
- JavaScript: RegEx test()
- JavaScript: RegEx lastIndex
- JavaScript: RegEx source
- JavaScript Programs
- JavaScript Programs
JavaScript map(): Map an Array to Create a New Updated Array
The JavaScript map() method is used when we need to create a new array after modifying or updating the elements of a specified array. For example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="xyz"></p>
<script>
const marks = [32, 43, 35, 46, 48];
document.getElementById("xyz").innerHTML = marks.map(perc);
function perc(x)
{
return x/50;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>In the above example, each elements of an array marks was divided by 50.
Note: The original array does not get affected by the map() function.
JavaScript map() syntax
The syntax of the map() method in JavaScript is:
array.map(functionName(currentElementValue, currentElementIndex, currentElementArray), thisValue)
The array, functionName, and currentElementValue are required. All others are optional.
Note: The array refers to an array whose elements are going to be updated using the function functionName.
Note: The functionName refers to a function to execute for every element of the array.
Note: The currentElementValue basically refers to a variable that will be used as an argument to the function that indicates the current value or element of the specified array.
Note: The currentElementIndex refers to the index of the current element.
Note: The currentElementArray refers to the array of the current element.
Note: The thisValue refers to a value passed to the specified function functionName as its this value. The default value is undefined.
JavaScript map() example
Consider the following code as an example demonstrating the map() method in JavaScript:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="abc"></p>
<script>
const nums = [32, 43, 35, 46, 48, 37];
const evenNums = nums.map(even);
function even(x)
{
if(x%2==0)
return x;
else
return x-1;
}
document.getElementById("abc").innerHTML = evenNums;
</script>
</body>
</html>In the above example, all odd numbers are converted into even numbers before being initialized to the evenNums array by subtracting 1.
To use all three parameters for the function used in map(). Here is an example:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="myPara"></p>
<script>
const n = [31, 43, 35, 46, 48, 37];
const en = n.map(even);
function even(x, indx, arr)
{
if(indx==0 || indx==(arr.length-1))
return x;
if(x%2==0)
return x;
else
return x-1;
}
document.getElementById("myPara").innerHTML = en;
</script>
</body>
</html>Here is another example of the map() function in JavaScript:
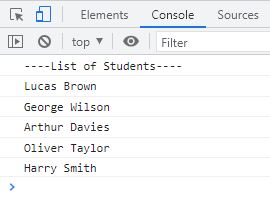
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
const students = [
{fn: "Lucas", ln: "Brown"},
{fn: "George", ln: "Wilson"},
{fn: "Arthur", ln: "Davies"},
{fn: "Oliver", ln: "Taylor"},
{fn: "Harry", ln: "Smith"}
];
const studentNames = students.map(sn);
function sn(x)
{
return [x.fn, x.ln].join(" ");
}
console.log("----List of Students----");
for(let i=0; i<studentNames.length; i++)
console.log(studentNames[i]);
</script>
</body>
</html>The snapshot given below shows the sample output produced by the above JavaScript example:
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »