- C++ Course Basics
- C++ Tutorial
- C++ Basic Syntax
- C++ Identifiers
- C++ Character Set
- C++ Input/Output Operator
- C++ Variables
- C++ Data Types
- C++ Formatting Output
- C++ Operators
- C++ Assignment Operator
- C++ Type Conversion
- C++ Program Control
- C++ if and if-else
- C++ switch
- C++ loops
- C++ break and continue
- C++ Functions
- C++ Functions
- C++ Prototype and Definition
- C++ Function Call
- C++ Function Types
- C++ Friend Function
- C++ Function Overloading
- C++ Arrays and Strings
- C++ Arrays
- C++ One-Dimensional Arrays
- C++ Strings
- C++ String Functions
- C++ Structures
- C++ Structures
- C++ Nested Structure
- C++ Structure Array
- C++ Pass Structure to Function
- C++ Pointers
- C++ Pointers
- C++ Memory Map
- C++ Declare Initialize Pointers
- C++ Pointers and Structures
- C++ Object-Oriented
- C++ Object-Oriented
- C++ Classes and Objects
- C++ Constructors and Destructors
- C++ Objects as Function Arguments
- C++ Pointers and Objects
- C++ Data Structure
- C++ Linked List
- C++ Stack
- C++ Queues
- C++ File Handling
- C++ File Handling
- C++ Opening and Closing Files
- C++ Steps to Process Files
- C++ Sequential I/O Operations
- C++ Detecting EOF
- C++ File Pointers Random Access
- C++ Binary Files Operations
- C++ Error Handling
- C++ Misc
- C++ typedef
- C++ #define
- C++ Date and Time
- C++ Examples
- C++ Examples
C++ Strings with Examples
With examples, I will explain the topic "C++ string" in this article. So, without further ado, let us begin with its definition.
What exactly are strings in C++?
Strings are character combinations. In other words, strings can be thought of as an array of characters.
Why should strings be used in our C++ program?
Strings are used to store textual data in our programs.
Declaring Strings in C++
The following is the general form to declare a string in C++:
char string_name[string_size];
Here, char is a valid C++ data type, string_name is the name of the string, and string_size is the size of the string. The string_size tells how many characters the string can hold. Here is an example.
char str[20];
The above declaration tells the compiler that a string str is declared, which can hold up to 20 characters.
C++, on the other hand, has a "string" type, which is defined in the "string" library. As a result, declaring a variable in C++ with the "string" type does not require including the size in the square bracket. As an example:
string str;
Please remember to include the "string" header file, which is similar to the "iostream" in this manner:
#include<string>
.
.
.
int main()
{
string myString;
.
.
.
return 0;
}
Initializing Strings in C++
Following is the general form to initialize a string in C++ when the string variable is declared with the "char" type.
char name[size] = {characters};
The "name" denotes the identifier, which will be the name of the string variable; the "size" denotes the number of characters that the string variable can hold; and the "characters" are the list of characters enclosed in a quote and separated by commas. As an example:
char str[6] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0'};
The preceding declaration and initialization generate a string containing the word "Hello." To hold the null character ('\0') at the end of the character array, the size of the character array containing the string must be one greater than the number of characters.
If you follow the array initialization rules, you can write the above statement as follows:
char str[] = "Hello";
The null character ('\0') is not used at the end of a string constant. When the C++ compiler initializes the array, it automatically inserts the "\0" (null character) at the end of the string. Let's try to print the preceding string:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[6] = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', '\0'};
cout<<str;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
The following should be the exact output of the above C++ program:
Hello
Let me demonstrate another use of the "string" in a C++ program. The user is permitted to enter string data into this program.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[40];
cout<<"Enter the string: ";
cin.getline(str, 40);
cout<<"\nYou entered: "<<str;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
The following snapshot shows the initial output produced by the above program:
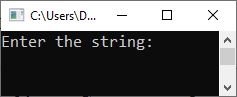
Now, type "codes cracker dot com" and press the ENTER key to get the following result:
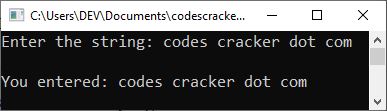
In the above program, I used
cin.getline(str, 40);
instead of
cin>>str;
to get the string content, including the space. As with "cin>>str;," where "str" is a character array, you only get the first word of the
string.
Therefore, use "getline()" as indicated in the above program to receive the whole line, regardless of whether the line contains a space or not.
Another issue is that because I set the character limit to 40, entering data longer than that results in data loss. That is, after the first 40 characters, all data will be lost. because "str" can only hold up to 40 characters of string data. But there is a solution: either increase the size or use the "string" type. As an illustration:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
cout<<"Enter the string: ";
getline(cin, str);
cout<<"\nYou entered: "<<str;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
The following snapshot shows the sample run with string input, "I had a lot of fun while learning C++."
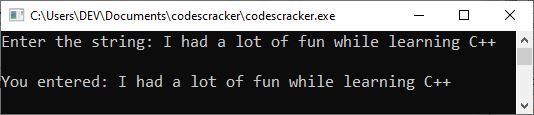
Accessing specific characters in a string in C++
We can also access any specific character in a string using its index number. As an example:
char x = str[3];
In the above statement, the code "str[3]" is used to get the character at the third index (fourth position) available in the string "str." Therefore, the character at the third index will be initialized to the variable "x." For example:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "codescracker.com";
cout<<str[0];
cout<<endl;
cout<<str[1];
cout<<endl;
cout<<str[2];
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
The following should be the exact output of the above C++ program:
c o d
The above program can also be created as:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "codescracker.com";
cout<<str[0]<<"\n"<<str[1]<<"\n"<<str[2]<<"\n";
return 0;
}
or
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[17] = "codescracker.com";
cout<<str[0]<<"\n"<<str[1]<<"\n"<<str[2]<<"\n";
return 0;
}
More Examples
- Find the length of a string in C++
- Copy string in C++
- Concatenate string in C++
- Reverse a string in C++
- Delete vowels from a string in C++
- Count the number of words in a string in C++
- Convert uppercase to lowercase in C++
- Convert lowercase to uppercase in C++
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »