- C++ Course Basics
- C++ Tutorial
- C++ Basic Syntax
- C++ Identifiers
- C++ Character Set
- C++ Input/Output Operator
- C++ Variables
- C++ Data Types
- C++ Formatting Output
- C++ Operators
- C++ Assignment Operator
- C++ Type Conversion
- C++ Program Control
- C++ if and if-else
- C++ switch
- C++ loops
- C++ break and continue
- C++ Functions
- C++ Functions
- C++ Prototype and Definition
- C++ Function Call
- C++ Function Types
- C++ Friend Function
- C++ Function Overloading
- C++ Arrays and Strings
- C++ Arrays
- C++ One-Dimensional Arrays
- C++ Strings
- C++ String Functions
- C++ Structures
- C++ Structures
- C++ Nested Structure
- C++ Structure Array
- C++ Pass Structure to Function
- C++ Pointers
- C++ Pointers
- C++ Memory Map
- C++ Declare Initialize Pointers
- C++ Pointers and Structures
- C++ Object-Oriented
- C++ Object-Oriented
- C++ Classes and Objects
- C++ Constructors and Destructors
- C++ Objects as Function Arguments
- C++ Pointers and Objects
- C++ Data Structure
- C++ Linked List
- C++ Stack
- C++ Queues
- C++ File Handling
- C++ File Handling
- C++ Opening and Closing Files
- C++ Steps to Process Files
- C++ Sequential I/O Operations
- C++ Detecting EOF
- C++ File Pointers Random Access
- C++ Binary Files Operations
- C++ Error Handling
- C++ Misc
- C++ typedef
- C++ #define
- C++ Date and Time
- C++ Examples
- C++ Examples
C++ Function Types with Examples
This article will teach you about "types of functions in C++." But before I write about this, I have a concern. This is because some people consider the type of function based on the argument, while others consider the type of function based on call by value and call by reference, and still others consider the type of function as a pre-defined and user-defined function.
Because I defined the "call by value" and "call by reference" functions in the previous article, we will go over the following types of functions one by one in this article.
In C++, there are broadly two types of functions:
However, the following can also be considered types of functions based on the parameters and return value:
- Function with no argument and no return value
- Function with no argument and a return value
- Function with argument(s) and no return value
- Function with argument(s) and a return value
Let's first define the previous two types of functions, and then we will define the function types based on their parameters and return values.
C++ built-in, pre-defined, or library functions
These functions are part of the compiler package. These are part of the standard library made available by the compiler. For example, exit(), sqrt(), pow(), strlen(), etc. are library functions (built-in functions).
Built-in functions help you use functions without declaring and defining them. To use built-in functions in a program, you have to only include the header file where the required function is defined. For example, the following program uses a built-in function named strlen(), which is defined in the "cstring" header file, to find the length of the string.
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int len;
char str[80];
cout<<"Enter the string: ";
cin.getline(str, 80);
len = strlen(str);
cout<<"\nLength = "<<len;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
The following snapshot shows the initial output produced by the above C++ example program:
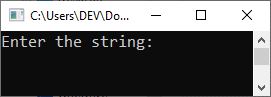
Now supply the input, say "codes cracker dot com," and hit the ENTER key to produce the following output:
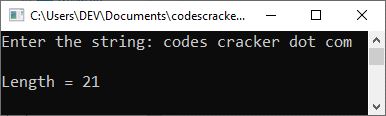
See the benefit of using the built-in function. I only included the header file where the function is defined and just used the function to make the function do its task. However, you can also self-define the function. Let's discuss it in the following section.
C++ user-defined functions
The user-defined functions are created by you, i.e., the programmer. These functions are created as per the requirements of your program.
For example, let me modify the above program. This program will do the same task as the previous program, but using a user-defined function instead of a pre-defined one.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int stringLength(char []);
int main()
{
int len;
char str[80];
cout<<"Enter the string: ";
cin.getline(str, 80);
len = stringLength(str);
cout<<"\nLength = "<<len;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
int stringLength(char x[])
{
int i=0, count=0;
while(x[i] )
{
count++;
i++;
}
return count;
}
This program does the same job as the previous program. However, in some cases, we need to use a function to perform a task that is not defined in any pre-defined or built-in function. As a result, in that case, we are forced to define that type of function ourselves.
C++ function with no argument and no return value
We can have a function without any arguments or a return value. For example, the following program uses a function that neither accepts any arguments nor returns any values:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void codescracker(void);
int main()
{
codescracker();
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
void codescracker(void)
{
cout<<"Hello there,";
}C++ function with no argument and a return value
We can have a function without any arguments but with a return value. For example, the following program uses a function that does not accept any arguments but returns a value:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int codescracker(void);
int main()
{
cout<<codescracker();
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
int codescracker(void)
{
return 10;
}C++ function with argument(s) and no return value
We can have a function with arguments but without a return value. For example, the following program uses a function that accepts arguments but does not return a value:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void codescracker(int, int);
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20;
codescracker(a, b);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
void codescracker(int x, int y)
{
cout<<x<<" + "<<y<<" = "<<x+y;
}C++ function with argument(s) and a return value
We can have a function with arguments as well as a return value. For example, the following program uses a function that accepts arguments and return a value:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int codescracker(int, int);
int main()
{
int a = 10, b = 20;
cout<<a<<" + "<<b<<" = "<<codescracker(a, b);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
int codescracker(int x, int y)
{
int res;
res = x+y;
return res;
}« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »