- C++ Course Basics
- C++ Tutorial
- C++ Basic Syntax
- C++ Identifiers
- C++ Character Set
- C++ Input/Output Operator
- C++ Variables
- C++ Data Types
- C++ Formatting Output
- C++ Operators
- C++ Assignment Operator
- C++ Type Conversion
- C++ Program Control
- C++ if and if-else
- C++ switch
- C++ loops
- C++ break and continue
- C++ Functions
- C++ Functions
- C++ Prototype and Definition
- C++ Function Call
- C++ Function Types
- C++ Friend Function
- C++ Function Overloading
- C++ Arrays and Strings
- C++ Arrays
- C++ One-Dimensional Arrays
- C++ Strings
- C++ String Functions
- C++ Structures
- C++ Structures
- C++ Nested Structure
- C++ Structure Array
- C++ Pass Structure to Function
- C++ Pointers
- C++ Pointers
- C++ Memory Map
- C++ Declare Initialize Pointers
- C++ Pointers and Structures
- C++ Object-Oriented
- C++ Object-Oriented
- C++ Classes and Objects
- C++ Constructors and Destructors
- C++ Objects as Function Arguments
- C++ Pointers and Objects
- C++ Data Structure
- C++ Linked List
- C++ Stack
- C++ Queues
- C++ File Handling
- C++ File Handling
- C++ Opening and Closing Files
- C++ Steps to Process Files
- C++ Sequential I/O Operations
- C++ Detecting EOF
- C++ File Pointers Random Access
- C++ Binary Files Operations
- C++ Error Handling
- C++ Misc
- C++ typedef
- C++ #define
- C++ Date and Time
- C++ Examples
- C++ Examples
C++ Date and Time
The C++ standard library doesn't provide any proper date types. C++ inherits the structs and functions for date and time manipulation from the C language. To access date and time-related functions and structures, you have to use or include a header file in your C++ program named "ctime."
Now, without any further description, let's first create and understand an example regarding the topic "C++ date and time."
C++ Date and Time Example
This C++ program simply prints the local and UTC date and time on the screen.
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
time_t now = time(0);
cout<<"Number of seconds since 1 January, 1970 = "<<now<<endl;
char *dt = ctime(&now);
cout<<"\nLocal date and time = "<<dt<<endl;
tm *gmtm = gmtime(&now);
dt = asctime(gmtm);
cout<<"UTC date and time = "<<dt<<endl;
return 0;
}
The following snapshot shows the sample output produced by the above example:
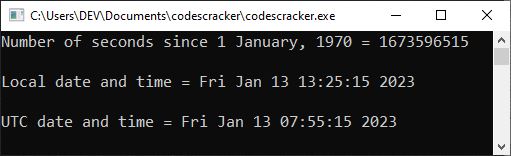
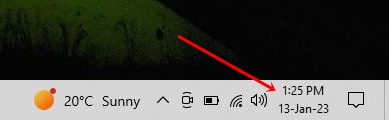
And the following photograph was taken by me. This is the time and date displayed by my system when the preceding program was executed.
The following statement applies in the preceding example:
time_t now = time(0);
declares a variable "now" of type "time_t" and initializes the current time in seconds using "time(0)." As a result, the "now" variable will not contain the number of seconds since 01-01-1970, or January 1, 1970. The "time_t" is defined in the "ctime" header file, which can be considered a type used to represent the calendar time.
Now, in the following statement:
char *dt = ctime(&now);
I used the "ctime()" method, which takes as a parameter a pointer to a "time t" object. This method returns text in the following format that represents the date and time:
Www Mmm dd hh:mm:ss yyyy
where:
- Www represents the first three letters of the weekday with the first letter in uppercase, for example, "Fri," "Wed," etc.
- Mmm represents the first three letters of the month name with the first letter in uppercase, for example, "Dec," "Feb," etc.
- dd represents the day of the month, for example, 10, 23, etc.
- hh represents the hours of the day, for example: 10, 13, etc.
- mm represents the minutes of the hour, for example: 21, 55, etc.
- ss represents the seconds of the minutes, for example: 12, 15, etc.
- yyyy represents the year in complete four-digit format, for example: 2023, 2022, etc.
Now let me describe the following statement used in the above program:
tm *gmtm = gmtime(&now);
The "gmtime()" function adjusts the specified number of seconds since January 1, 1970 to the corresponding number of seconds in the UTC, or GMT. The calendar date and time are stored in the "tm" type defined in the "ctime" header file.
Now, using the following statement:
dt = asctime(gmtm);
The given time is converted into human-readable date and time information using the "asctime()" method, and the human-readable date and time information is then initialized to the "dt" variable.
However, we can change the format of the date and time using the "tm" components. Let's create an example of getting and printing the date and time in the desired format.
C++ Date Example
This C++ program prints the current or today's date on the output screen in the format "DD/MM/YYYY."
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
time_t now = time(0);
tm *ltm = localtime(&now);
cout<<"Date: "<<ltm->tm_mday<<"/"<<1+ltm->tm_mon<<"/"<<1900+ltm->tm_year;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
While writing this post, the date is January 13, 2023; therefore, the following will be the output of the above program:
Date: 13/1/2023
I added "1" to the ltm->tm_month because the "tm_month" of the "tm" structure returns the month number of the year starting with 0 and ending with 11, where 0 indicates "January" and 11 indicates "December." A similar job was done with "tm_year." To get a complete understanding, consider the following table:
| Object | Description | Range |
|---|---|---|
| tm_sec | returns the number of seconds after the minute | 0 to 61 |
| tm_min | returns the number of minutes after the hour | 0 to 59 |
| tm_hour | returns the number of hours since midnight | 0 to 23 |
| tm_mday | returns the day of the month | 1 to 31 |
| tm_mon | returns the month number of the year | 0 to 11 (0 for January and 11 for December) |
| tm_year | returns the year since 1900 | |
| tm_wday | returns the day number of the week | 0 to 6 (0 for Sunday, 6 for Saturday) |
| tm_yday | returns the number of days elapsed since January 1 of the current year | 0 to 366 |
Another object named "tm_isdst" is available in the "tm" of "ctime," which I don't think is useful most of the time. This object returns the hours of daylight savings time.
C++ Time Example
This C++ program prints the current time on the output screen in the format "HH:MM:SS."
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
time_t now = time(0);
tm *ltm = localtime(&now);
cout<<"Time: ";
cout<<1+ltm->tm_hour<<":";
cout<<1+ltm->tm_min<<":";
cout<<1+ltm->tm_sec;
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
Since the current time while executing this program is "13:36:44", the following should be the output:
Time: 13:36:44
C++ Date and Time Complete Program
This is the full C++ version of the date and time programs (shown above). This is a menu-driven program that allows the user to continue printing the date and time, as well as its components such as the month number, year, and so on, until the user enters a number other than 1-5 or does not enter "y" to continue.
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char choice, ans;
time_t now = time(0);
tm *ltm = localtime(&now);
do
{
cout<<"1. Time\n";
cout<<"2. Date\n";
cout<<"3. Month\n";
cout<<"4. Year\n";
cout<<"5. All\n";
cout<<"6. Exit\n";
cout<<"\nEnter your choice (1-6): ";
cin>>choice;
cout<<endl;
switch(choice)
{
case '1':
cout<<"Time: "<<1+ltm->tm_hour<<":"<<1+ltm->tm_min<<":"<<1+ltm->tm_sec;
break;
case '2':
cout<<"Date: "<<ltm->tm_mday;
break;
case '3':
cout<<"Month: "<<1+ltm->tm_mon;
break;
case '4':
cout<<"Year: "<<1900+ltm->tm_year;
break;
case '5':
cout<<"Time and Date\n";
cout<<1+ltm->tm_hour<<":"<<1+ltm->tm_min<<":"<<1+ltm->tm_sec;
cout<<"\n"<<ltm->tm_mday<<"/"<<1+ltm->tm_mon<<"/"<<1900+ltm->tm_year;
break;
case '6':
exit(0);
default:
cout<<"Wrong choice!\n";
exit(0);
}
cout<<"\n\nPress 'y' to continue...";
cin>>ans;
cout<<endl;
} while(ans=='y' || ans=='Y');
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
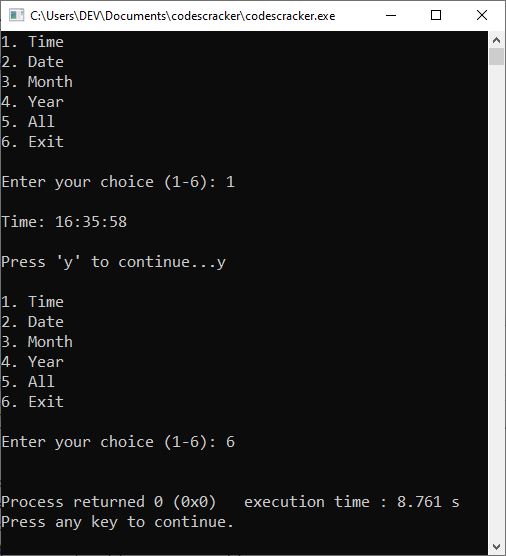
The screenshot below depicts a sample run of the above program with user inputs "1" to print the time, "y" to continue the program, and "6" to exit the program.
« Previous Tutorial CodesCracker.com »