- C++ Programming Examples
- C++ Programming Examples
- C++: Hello World
- C++: Get Input
- C++: Print Integer
- C++: Add two numbers
- C++: Add, Sub, Multiply, Div
- C++: Add Digits
- C++: Find Average and Percentage
- C++: Find Arithmetic Mean
- C++: Sum of n Natural Numbers
- C++: Sum of n Numbers
- C++: Square's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Rectangle's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Triangle's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Area and Circumference
- C++: Find Simple Interest
- C++: Fahrenheit to Celsius
- C++: Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C++: Print Prime Numbers
- C++: Reverse a Number
- C++: Swap Two Numbers
- C++: Print Multiplication Table
- C++: Find Factorial of a Number
- C++: Find Factors of a Number
- C++: Find HCF and LCM
- C++: Create a Calculator
- C++: Count Digits in a Number
- C++: First and Last Digit Sum
- C++: Product of Number Digits
- C++: Sum of Squares of Digits
- C++: Interchange Digits of Number
- C++ if-else Programs
- C++: Check Even or Odd
- C++: Check Prime or Not
- C++: Check Alphabet or Not
- C++: Check Vowel or Not
- C++: Check Leap Year or Not
- C++: Check Reverse equals Original
- C++: Check Perfect Number
- C++: Check Palindrome or Not
- C++: Check Armstrong or Not
- C++: Divisibility Test
- C++: Find Labor Wage
- C++: Find Discounted Price
- C++: Find Shipping Charge
- C++: Find Telephone Bills
- C++: Calculate Student Grade
- C++: Largest of Two Numbers
- C++: Largest of Three Numbers
- C++ Number Conversion
- C++: Decimal to Binary
- C++: Decimal to Octal
- C++: Decimal to Hexadecimal
- C++: Binary to Decimal
- C++: Binary to Octal
- C++: Binary to Hexadecimal
- C++: Octal to Decimal
- C++: Octal to Binary
- C++: Octal to Hexadecimal
- C++: Hexadecimal to Decimal
- C++: Hexadecimal to Binary
- C++: Hexadecimal to Octal
- C++ Pattern Programs
- C++: Pattern Programs
- C++: Print Diamond Pattern
- C++: Print Floyd's Triangle
- C++: Print Pascal's Triangle
- C++ Array Programs
- C++: 1D Array Program
- C++: Linear Search
- C++: Binary Search
- C++: Largest Element in an Array
- C++: Smallest Element in an Array
- C++: Find Second Largest Element
- C++: Find Second Smallest Element
- C++: Sum of All Elements
- C++: Multiply All Elements
- C++: Element in Even Position
- C++: Element in Odd Position
- C++: Print Even Numbers in Array
- C++: Print Odd Numbers in Array
- C++: Count Even or Odd Numbers
- C++: Sum of Even or Odd Numbers
- C++: Count Positive, Negative, Zero
- C++: Reverse an Array
- C++: Insert an Element
- C++: Delete an Element
- C++: Merge two Arrays
- C++: Bubble Sort
- C++: Selection Sort
- C++: Insertion Sort
- C++: Common Elements
- C++: 2D Array Programs
- C++: Add Two Matrices
- C++: Subtract Two Matrices
- C++: Transpose Matrix
- C++: Multiply Two Matrices
- C++: 3D Array Programs
- C++ String Programs
- C++: Print String
- C++: Find String Length
- C++: Compare Two Strings
- C++: Copy String
- C++: String Concatenation
- C++: Reverse a String
- C++: Delete Vowels from a String
- C++: Delete a Word from a String
- C++: Count Characters in a String
- C++: Count Words in a String
- C++: Frequency of Words
- C++: Remove Spaces from Strings
- C++: Sort a String
- C++: Uppercase to Lowercase
- C++: Lowercase to Uppercase
- C++: Swap Two Strings
- C++: Check the Anagram or Not
- C++: Capitalize All Words in a String
- C++: Get Numbers from a String
- C++ File Programs
- C++: Read a File
- C++: Write Content to a File
- C++: Append Data to a File
- C++: Read and Display File
- C++: Copy a File
- C++: Merge Two Files
- Count Characters in a File
- C++: Capitalize Every Word
- C++: List Files in Directory
- C++: Delete a File
- C++: Encrypt and Decrypt a File
- C++ Misc Programs
- C++: Print ASCII Value
- C++: Add Binary Numbers
- C++: Generate Random Numbers
- C++: Print a Smiling Face
- C++: Days into Years and Months
- C++: Add Two Numbers using Pointer
- C++: Print Fibonacci Series
- C++: Generate Armstrong Numbers
- C++: Find nCr and nPr
- C++: Get IP Address
- C++: Print Date and Time
- C++: Shutdown and Restart Computer
- C++ Programming Tutorial
- C++ Tutorial
C++ program to find the factorial of a number
In this article, you will learn and get code to find and print the factorial of a number entered by the user at run-time in C++. The factorial program is created in the following ways:
- Using a for loop, calculate the factorial of a number
- Find the factorial of a number using a while loop
- Find the factorial of a number using a user-defined function
- Find the factorial of a number using "call by reference"
How to Determine Factorial
To find the factorial of a number n, here is the formula:
factorial = n*(n-1)*(n-2)*...*3*2*1
For example, the factorial of a number, say 6, is:
6! = 6*5*4*3*2*1 = 30*12*2 = 30*24 = 720
Note: The symbol ! indicates factorial.
Find the factorial of a number in C++ using the for loop
To find the factorial of a number in C++ programming, you have to ask the user to enter the number. Then find and print the factorial of that number using the formula given above.
This program finds and prints the factorial of a number using a for loop. The question is: write a program in C++ that finds the factorial of a given number using a for loop. Here is its answer:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int num, i, fact=1; cout<<"Enter the Number: "; cin>>num; for(i=num; i>=1; i--) fact = fact*i; cout<<"\nFactorial = "<<fact; cout<<endl; return 0; }
This program was built and runs under the Code::Blocks IDE. Here is its sample run:
Now supply any number, say 5, and press the ENTER key to find and print its factorial as shown in the snapshot given below:
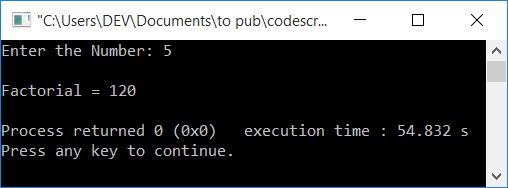
The following is the dry run of the above program with user input 5:
- fact=1 at the start.
- When the user enters 5 as input, then it gets stored in num. So num=5
- Now the evaluation of the for loop gets started after receiving the number from the user.
- That is, the value of num (5) gets initialized to i. So i=5. The initialization part (first part) of the for loop executes first, but only once.
- Now that the condition i>=1 or 5>=1 has been evaluated as true, program flow enters the loop, and fact*i or 1*5 or 5 is initialized to fact
- The program flow goes to the update part (third part) of the for loop, which decrements the value of i. So i=4
- The condition i>=1 is evaluated once more.
- Every time after updating the value of i, the condition gets evaluated.
- And each time, the program flow enters the loop after evaluating the condition, until the condition is determined to be false.
- Therefore, before its condition is evaluated to be false, here is the value of i and the fact after
each evaluation:
- i=5, fact=5
- i=4, fact=20
- i=3, fact=60
- i=2, fact=120
- i=1, fact=120
- Now, after exiting from the loop, just print the value of fact; that will be the factorial result of the given number.
In C++, using the while loop, find the factorial of a number
Here is another program to find the factorial of a number, but using the while loop in C++. In the while loop, there is only one part, which is for condition. So we have to put the initialization part before the loop and update parts inside its body.
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int num, i, fact=1; cout<<"Enter the Number: "; cin>>num; i=num; while(i>=1) { fact = fact*i; i--; } cout<<"\nFactorial = "<<fact; cout<<endl; return 0; }
This program produces the same output as the previous program.
Using a user-defined function to find the factorial of a number in C++
Now let's create the same-purpose program using a user-defined function named findFact(). This function receives a number as its argument and returns the factorial of the number.
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int findFact(int); int main() { int num, fact; cout<<"Enter the Number: "; cin>>num; fact = findFact(num); cout<<"\nFactorial = "<<fact; cout<<endl; return 0; } int findFact(int n) { int i, f=1; for(i=n; i>=1; i--) f = f*i; return f; }
Here is its sample run with user input, 6:
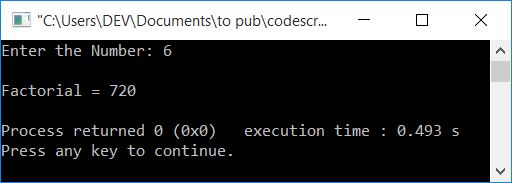
Using call-by-reference to find the factorial of a number in C++
Now this is the end of this article. This program also calculates factorial, but using the call-by-reference method. That is, the address of the variable fact gets passed as an argument to the findFact() function. So any change to this variable directly affects the original value.
#include<iostream> using namespace std; void findFact(int, int *); int main() { int num, fact=1; cout<<"Enter the Number: "; cin>>num; findFact(num, &fact); cout<<"\nFactorial = "<<fact; cout<<endl; return 0; } void findFact(int n, int *f) { int i; for(i=n; i>=1; i--) *f = (*f)*i; }
Here is its sample run with user input, 4:
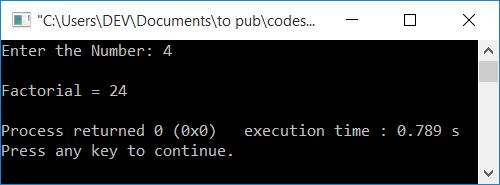
The same program in different languages
« Previous Program Next Program »