- C++ Programming Examples
- C++ Programming Examples
- C++: Hello World
- C++: Get Input
- C++: Print Integer
- C++: Add two numbers
- C++: Add, Sub, Multiply, Div
- C++: Add Digits
- C++: Find Average and Percentage
- C++: Find Arithmetic Mean
- C++: Sum of n Natural Numbers
- C++: Sum of n Numbers
- C++: Square's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Rectangle's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Triangle's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Area and Circumference
- C++: Find Simple Interest
- C++: Fahrenheit to Celsius
- C++: Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C++: Print Prime Numbers
- C++: Reverse a Number
- C++: Swap Two Numbers
- C++: Print Multiplication Table
- C++: Find Factorial of a Number
- C++: Find Factors of a Number
- C++: Find HCF and LCM
- C++: Create a Calculator
- C++: Count Digits in a Number
- C++: First and Last Digit Sum
- C++: Product of Number Digits
- C++: Sum of Squares of Digits
- C++: Interchange Digits of Number
- C++ if-else Programs
- C++: Check Even or Odd
- C++: Check Prime or Not
- C++: Check Alphabet or Not
- C++: Check Vowel or Not
- C++: Check Leap Year or Not
- C++: Check Reverse equals Original
- C++: Check Perfect Number
- C++: Check Palindrome or Not
- C++: Check Armstrong or Not
- C++: Divisibility Test
- C++: Find Labor Wage
- C++: Find Discounted Price
- C++: Find Shipping Charge
- C++: Find Telephone Bills
- C++: Calculate Student Grade
- C++: Largest of Two Numbers
- C++: Largest of Three Numbers
- C++ Number Conversion
- C++: Decimal to Binary
- C++: Decimal to Octal
- C++: Decimal to Hexadecimal
- C++: Binary to Decimal
- C++: Binary to Octal
- C++: Binary to Hexadecimal
- C++: Octal to Decimal
- C++: Octal to Binary
- C++: Octal to Hexadecimal
- C++: Hexadecimal to Decimal
- C++: Hexadecimal to Binary
- C++: Hexadecimal to Octal
- C++ Pattern Programs
- C++: Pattern Programs
- C++: Print Diamond Pattern
- C++: Print Floyd's Triangle
- C++: Print Pascal's Triangle
- C++ Array Programs
- C++: 1D Array Program
- C++: Linear Search
- C++: Binary Search
- C++: Largest Element in an Array
- C++: Smallest Element in an Array
- C++: Find Second Largest Element
- C++: Find Second Smallest Element
- C++: Sum of All Elements
- C++: Multiply All Elements
- C++: Element in Even Position
- C++: Element in Odd Position
- C++: Print Even Numbers in Array
- C++: Print Odd Numbers in Array
- C++: Count Even or Odd Numbers
- C++: Sum of Even or Odd Numbers
- C++: Count Positive, Negative, Zero
- C++: Reverse an Array
- C++: Insert an Element
- C++: Delete an Element
- C++: Merge two Arrays
- C++: Bubble Sort
- C++: Selection Sort
- C++: Insertion Sort
- C++: Common Elements
- C++: 2D Array Programs
- C++: Add Two Matrices
- C++: Subtract Two Matrices
- C++: Transpose Matrix
- C++: Multiply Two Matrices
- C++: 3D Array Programs
- C++ String Programs
- C++: Print String
- C++: Find String Length
- C++: Compare Two Strings
- C++: Copy String
- C++: String Concatenation
- C++: Reverse a String
- C++: Delete Vowels from a String
- C++: Delete a Word from a String
- C++: Count Characters in a String
- C++: Count Words in a String
- C++: Frequency of Words
- C++: Remove Spaces from Strings
- C++: Sort a String
- C++: Uppercase to Lowercase
- C++: Lowercase to Uppercase
- C++: Swap Two Strings
- C++: Check the Anagram or Not
- C++: Capitalize All Words in a String
- C++: Get Numbers from a String
- C++ File Programs
- C++: Read a File
- C++: Write Content to a File
- C++: Append Data to a File
- C++: Read and Display File
- C++: Copy a File
- C++: Merge Two Files
- Count Characters in a File
- C++: Capitalize Every Word
- C++: List Files in Directory
- C++: Delete a File
- C++: Encrypt and Decrypt a File
- C++ Misc Programs
- C++: Print ASCII Value
- C++: Add Binary Numbers
- C++: Generate Random Numbers
- C++: Print a Smiling Face
- C++: Days into Years and Months
- C++: Add Two Numbers using Pointer
- C++: Print Fibonacci Series
- C++: Generate Armstrong Numbers
- C++: Find nCr and nPr
- C++: Get IP Address
- C++: Print Date and Time
- C++: Shutdown and Restart Computer
- C++ Programming Tutorial
- C++ Tutorial
C++ program to check whether a number is divisible by another number
This article provides some programs in C++ that are used to check whether a number (entered by the user) is divisible by another number (also entered by the user) or not. These are the programs included:
- Check whether a number is divisible by another number using the if-else statement
- Check whether a number is divisible by another number using a user-defined function
- Check whether a number is divisible by another number using class
- A divisibility test program with multiple numbers in a given range entered by the user at run-time
Using if-else logic, check if a number is divisible by another
The question is, "Write a C++ program that receives two numbers as input and checks whether the second number divides first without leaving any remainder or not." The answer to this question is the program given below:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int numerator, denominator; cout<<"Enter a Number (Numerator): "; cin>>numerator; cout<<"Enter another Number (Denominator): "; cin>>denominator; if(numerator%denominator==0) cout<<endl<<numerator<<" is divisible by "<<denominator; else cout<<endl<<numerator<<" is not divisible by "<<denominator; cout<<endl; return 0; }
The snapshot given below shows the initial output produced by the above C++ program on checking whether a number (entered by the user) is divisible by another number (also entered by the user) or not:
Now enter any two numbers as the numerator and denominator to check whether the denominator completely divides the numerator (without leaving any remainder, or leaving 0 as the remainder) or not. For example, here is its sample run with user input 27 as numerator and 3 as denominator:
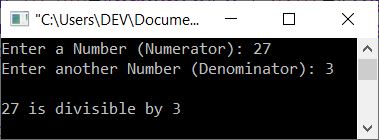
Note: The % (modulo) operator gives the remainder. For example, 10%3 gives 1, 20%10 gives 0, and 20%7 gives 6.
Therefore, if numerator%denominator gives 0, it means that the denominator divides the numerator without leaving a remainder.
Using a a user-defined function, check if a number is divisible by another
This is the same program as the previous one. That is, this program does the same job of checking whether the first number divides the second number or not. Both numbers must be entered by the user during program execution:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int check_div(int, int); int main() { int numerator, denominator, res; cout<<"Enter a Number (Numerator): "; cin>>numerator; cout<<"Enter another Number (Denominator): "; cin>>denominator; res = check_div(numerator, denominator); if(res==1) cout<<endl<<numerator<<" is divisible by "<<denominator; else cout<<endl<<numerator<<" is not divisible by "<<denominator; cout<<endl; return 0; } int check_div(int a, int b) { if(a%b==0) return 1; else return 0; }
Here is its sample run with user input of 14 as the numerator and 4 as the denominator:
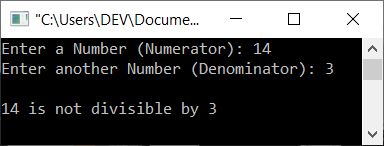
The function check_div() in the preceding program returns 1 if a%b or numerator%denominator returns 0. Otherwise, it returns 0. Based on the return value, the print statement gets performed as shown in the above program.
Using class, check if a number is divisible by another
This is another program that performs the same function as the previous two, but in a different way. That is, this program uses classes and objects, an object-oriented feature of C++.
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class CodesCracker { public: int check_div(int, int); }; int CodesCracker::check_div(int a, int b) { if(a%b==0) return 1; else return 0; } int main() { CodesCracker ob; int numerator, denominator, res; cout<<"Enter a Number (Numerator): "; cin>>numerator; cout<<"Enter another Number (Denominator): "; cin>>denominator; res = ob.check_div(numerator, denominator); if(res==1) cout<<endl<<numerator<<" is divisible by "<<denominator; else cout<<endl<<numerator<<" is not divisible by "<<denominator; cout<<endl; return 0; }
This program produces the same output as the previous program.
Divisibility Test with Multiple Numbers in a Range
The question is: write a program in C++ that finds and prints all the numbers in a given range that are divisible by a given number (entered by the user). The program given below is the answer to this question:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int tot, i, arr[100], num, j, arr_div[100]; cout<<"Enter the Size: "; cin>>tot; cout<<"Enter "<<tot<<" Numbers: "; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cin>>arr[i]; cout<<"Enter a Number to Apply Divisibility Test: "; cin>>num; for(i=0, j=0; i<tot; i++) { if(arr[i]%num==0) { arr_div[j] = arr[i]; j++; } } if(j==0) cout<<"\nAll the numbers are not divisible by "<<num; else { cout<<"\nThese are the numbers divisible by "<<num<<endl; for(i=0; i<j; i++) cout<<arr_div[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; return 0; }
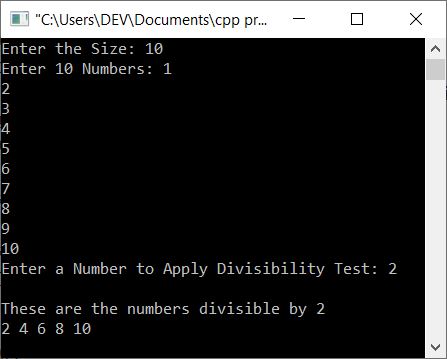
Here is its sample run with user input: 10 as size, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10 as 10 numbers, 2 as the number to apply the divisibility test with all these given 10 numbers as shown in the snapshot given below:
« Previous Program Next Program »