- C++ Programming Examples
- C++ Programming Examples
- C++: Hello World
- C++: Get Input
- C++: Print Integer
- C++: Add two numbers
- C++: Add, Sub, Multiply, Div
- C++: Add Digits
- C++: Find Average and Percentage
- C++: Find Arithmetic Mean
- C++: Sum of n Natural Numbers
- C++: Sum of n Numbers
- C++: Square's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Rectangle's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Triangle's Area and Perimeter
- C++: Area and Circumference
- C++: Find Simple Interest
- C++: Fahrenheit to Celsius
- C++: Celsius to Fahrenheit
- C++: Print Prime Numbers
- C++: Reverse a Number
- C++: Swap Two Numbers
- C++: Print Multiplication Table
- C++: Find Factorial of a Number
- C++: Find Factors of a Number
- C++: Find HCF and LCM
- C++: Create a Calculator
- C++: Count Digits in a Number
- C++: First and Last Digit Sum
- C++: Product of Number Digits
- C++: Sum of Squares of Digits
- C++: Interchange Digits of Number
- C++ if-else Programs
- C++: Check Even or Odd
- C++: Check Prime or Not
- C++: Check Alphabet or Not
- C++: Check Vowel or Not
- C++: Check Leap Year or Not
- C++: Check Reverse equals Original
- C++: Check Perfect Number
- C++: Check Palindrome or Not
- C++: Check Armstrong or Not
- C++: Divisibility Test
- C++: Find Labor Wage
- C++: Find Discounted Price
- C++: Find Shipping Charge
- C++: Find Telephone Bills
- C++: Calculate Student Grade
- C++: Largest of Two Numbers
- C++: Largest of Three Numbers
- C++ Number Conversion
- C++: Decimal to Binary
- C++: Decimal to Octal
- C++: Decimal to Hexadecimal
- C++: Binary to Decimal
- C++: Binary to Octal
- C++: Binary to Hexadecimal
- C++: Octal to Decimal
- C++: Octal to Binary
- C++: Octal to Hexadecimal
- C++: Hexadecimal to Decimal
- C++: Hexadecimal to Binary
- C++: Hexadecimal to Octal
- C++ Pattern Programs
- C++: Pattern Programs
- C++: Print Diamond Pattern
- C++: Print Floyd's Triangle
- C++: Print Pascal's Triangle
- C++ Array Programs
- C++: 1D Array Program
- C++: Linear Search
- C++: Binary Search
- C++: Largest Element in an Array
- C++: Smallest Element in an Array
- C++: Find Second Largest Element
- C++: Find Second Smallest Element
- C++: Sum of All Elements
- C++: Multiply All Elements
- C++: Element in Even Position
- C++: Element in Odd Position
- C++: Print Even Numbers in Array
- C++: Print Odd Numbers in Array
- C++: Count Even or Odd Numbers
- C++: Sum of Even or Odd Numbers
- C++: Count Positive, Negative, Zero
- C++: Reverse an Array
- C++: Insert an Element
- C++: Delete an Element
- C++: Merge two Arrays
- C++: Bubble Sort
- C++: Selection Sort
- C++: Insertion Sort
- C++: Common Elements
- C++: 2D Array Programs
- C++: Add Two Matrices
- C++: Subtract Two Matrices
- C++: Transpose Matrix
- C++: Multiply Two Matrices
- C++: 3D Array Programs
- C++ String Programs
- C++: Print String
- C++: Find String Length
- C++: Compare Two Strings
- C++: Copy String
- C++: String Concatenation
- C++: Reverse a String
- C++: Delete Vowels from a String
- C++: Delete a Word from a String
- C++: Count Characters in a String
- C++: Count Words in a String
- C++: Frequency of Words
- C++: Remove Spaces from Strings
- C++: Sort a String
- C++: Uppercase to Lowercase
- C++: Lowercase to Uppercase
- C++: Swap Two Strings
- C++: Check the Anagram or Not
- C++: Capitalize All Words in a String
- C++: Get Numbers from a String
- C++ File Programs
- C++: Read a File
- C++: Write Content to a File
- C++: Append Data to a File
- C++: Read and Display File
- C++: Copy a File
- C++: Merge Two Files
- Count Characters in a File
- C++: Capitalize Every Word
- C++: List Files in Directory
- C++: Delete a File
- C++: Encrypt and Decrypt a File
- C++ Misc Programs
- C++: Print ASCII Value
- C++: Add Binary Numbers
- C++: Generate Random Numbers
- C++: Print a Smiling Face
- C++: Days into Years and Months
- C++: Add Two Numbers using Pointer
- C++: Print Fibonacci Series
- C++: Generate Armstrong Numbers
- C++: Find nCr and nPr
- C++: Get IP Address
- C++: Print Date and Time
- C++: Shutdown and Restart Computer
- C++ Programming Tutorial
- C++ Tutorial
C++ Program for Selection Sort
In this article, you will learn and get code to implement selection sort in C++. Here is the list of programs on selection sorting available in this article:
- Selection Sort in Ascending Order
- Selection Sort in Descending Order
- Selection Sort using a User-Defined Function
- Selection Sort using Class and Object
But before creating these programs, if you're not aware of selection sort, refer to the selection sort algorithm and examples to get every required detail about it.
Selection Sort in C++
To sort an array in ascending order using the selection sort technique in C++ programming, you have to ask the user to enter the size and elements of the array. Now sort the array using the selection sort technique as shown in the program given below:
Note: Selection sort works in a way that, initially, the smallest element gets selected and moved to the very first index (0th index, because indexing in arrays starts from 0), then the second smallest element gets selected and moved to the second (1st) index, and so on.
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int tot, arr[50], i, j, temp, small, chk, index; cout<<"Enter the Size of Array: "; cin>>tot; cout<<"Enter "<<tot<<" Array Elements: "; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cin>>arr[i]; for(i=0; i<(tot-1); i++) { chk=0; small = arr[i]; for(j=(i+1); j<tot; j++) { if(small>arr[j]) { small = arr[j]; chk++; index = j; } } if(chk!=0) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = small; arr[index] = temp; } } cout<<"\nSorted Array is:\n"; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cout<<arr[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; return 0; }
This program was built and runs under the Code::Blocks IDE. Here is its sample run:
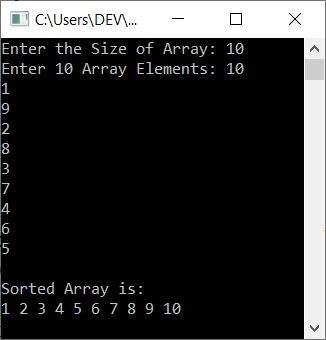
Now enter the size, say 10 and then enter any 10 array elements, say
10, 1, 9, 2, 8, 3, 7, 4, 6, and 5, and press the
ENTER key to sort the array using the selection sort technique, and then print the new sorted array as
shown in the snapshot given below:
The dry run of the above program with the same user input as in the sample run goes as follows:
- When the user enters 10 as the size, then it gets stored in tot. So tot=10
- And when the user enters 10 elements, then it gets stored in arr in this way:
- arr[0]=10
- arr[1]=1
- arr[2]=9
- and so on up until
- arr[9]=5
- Now the execution of the second for loop of the program, or the loop that is created to perform the selection sort, begins.
- That is, 0 gets initialized to i and the condition i<(tot-1) or 0<(10-1) or 0<9 evaluates to be true, therefore program flow goes inside the loop.
- Inside the loop, 0 gets initialized to chk. So chk=0
- And arr[i] or arr[0] or 10 is set to small. Because small = 10, we've taken 10 as the smallest element. Now let's compare it with elements at rest indexes.
- Every time, we supposed the element at the current index was the smallest, then compared it to the rest of the element, and if it was found to be greater than any other element, we initialized a new element as the smallest.
- Now the execution of the inner for loop begins. That is, (i+1) or 0+1 or 1 gets initialized to j, and the condition j<tot or 1<10 evaluates to be true, therefore program flow goes inside the loop.
- Inside this loop, the condition (of if) small>arr[j] or 10>arr[1] or 10>1 evaluates to be true, therefore program flow goes inside the if's body.
- And arr[j] or arr[1] or 1 is set to small. The value of chk gets incremented. So chk=1. Finally, j or 1 is assigned to index.
- Now the value of j gets incremented. So j=2 and the condition j<tot or 2<10 evaluates to be true again, therefore, program flow again goes inside the loop. This process is repeated until the condition of this for loop evaluates to false.
- Because, 1 is the smallest element, small=1 when this loop is finished. And since 1 is at the 1st index, index=1.
- After exiting from this loop, the condition (of if) chk!=0 or 1!=0 evaluates to be true, therefore arr[i] or arr[0] or 10 gets initialized to temp, small or 1 gets initialized to arr[i] or arr[0], and finally temp or 10 gets initialized to arr[index] or arr[1].
- Now the program flow goes to the update part of the outer for loop and increments the value of i. So i=1. And the condition is evaluated once more.
- That is the condition i<(tot-1) or 1<(10-1) or 1<9 evaluates to be true again, therefore program flow again goes inside the loop.
- This process continues until the condition is evaluated as false.
- In this way, selection sorting gets implemented.
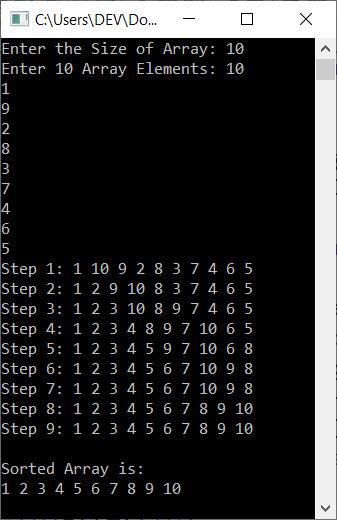
To print the array after each sort, just place the following block of code:
cout<<"Step "<<i+1<<": "; for(j=0; j<tot; j++) cout<<arr[j]<<" "; cout<<endl;
after
if(chk!=0)
{
temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = small;
arr[index] = temp;
}
That is, place the code at the end of the for loop that is created to perform the selection sort. Now the sample run with the same user input as provided in the previous sample run looks like:
Selection Sort in Descending Order
To sort an array in descending order using the selection sort technique, only replace the condition of if. That is, replace the following condition:
small>arr[j]
with the condition given below.
small<arr[j]
It is worth noticing that changing the greater than (>) and less than (<) sign flips the entire program.
But still, if you want the complete program for selection sorting in descending order, then here it is:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main() { int tot, arr[50], i, j, temp, big, chk, index; cout<<"Enter the Size of Array: "; cin>>tot; cout<<"Enter "<<tot<<" Array Elements: "; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cin>>arr[i]; for(i=0; i<(tot-1); i++) { chk=0; big = arr[i]; for(j=(i+1); j<tot; j++) { if(big<arr[j]) { big = arr[j]; chk++; index = j; } } if(chk!=0) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = big; arr[index] = temp; } } cout<<"\nSorted Array in Descending Order is:\n"; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cout<<arr[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; return 0; }
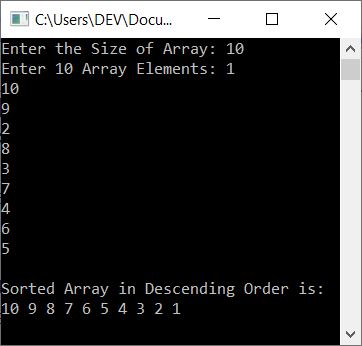
The snapshot given below shows the sample run of this program with user input, 10 as size, and 1, 10, 9, 2, 8, 3, 7, 4, 6, and 5 as 10 array elements:
Selection Sort using a User-Defined Function
Now let's create another program that does the same job as the very first program. That is, this program implements selection sort to sort an array in ascending order using the user-defined function selSort().
The function selSort() takes two arguments. The first argument is the array, whereas the second argument is its size. This function sorts an array using the selection sort technique:
#include<iostream> using namespace std; void selSort(int [], int); int main() { int tot, arr[50], i; cout<<"Enter the Size of Array: "; cin>>tot; cout<<"Enter "<<tot<<" Array Elements: "; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cin>>arr[i]; selSort(arr, tot); cout<<"\nSorted Array is:\n"; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cout<<arr[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; return 0; } void selSort(int arr[], int tot) { int i, j, temp, small, chk, index; for(i=0; i<(tot-1); i++) { chk=0; small = arr[i]; for(j=(i+1); j<tot; j++) { if(small>arr[j]) { small = arr[j]; chk++; index = j; } } if(chk!=0) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = small; arr[index] = temp; } } }
This program produces the same output as the very first program in this article. Here is its sample run, with user input of 5 as size and 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 as 5 array elements:
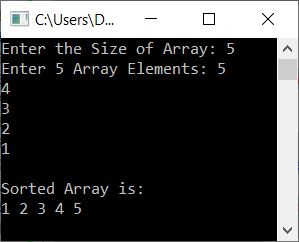
Selection sort using a class
This is the last program in this article to implement selection sort in C++. This program uses classes and objects, an object-oriented feature of C++.
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class CodesCracker { public: void selSort(int [], int); }; void CodesCracker::selSort(int arr[], int tot) { int i, j, temp, small, chk, index; for(i=0; i<(tot-1); i++) { chk=0; small = arr[i]; for(j=(i+1); j<tot; j++) { if(small>arr[j]) { small = arr[j]; chk++; index = j; } } if(chk!=0) { temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = small; arr[index] = temp; } } } int main() { CodesCracker c; int tot, arr[50], i; cout<<"Enter the Size of Array: "; cin>>tot; cout<<"Enter "<<tot<<" Array Elements: "; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cin>>arr[i]; c.selSort(arr, tot); cout<<"\nSorted Array is:\n"; for(i=0; i<tot; i++) cout<<arr[i]<<" "; cout<<endl; return 0; }
Within the main() function, an object c of type CodesCracker is created. And using this object, we've called the member function (selSort()) of the class CodesCracker using the dot (.) operator. The rest of the things are similar in function.
The same program in different languages
« Previous Program Next Program »