- Java Programming Basics
- Java Tutorial
- Java Environment Setup
- Java Separators
- Java Data Types
- Java Variables
- Java Variable Scope
- Java Type Casting
- Java Operators
- Java Increment Decrement
- Java Left Shift
- Java Right Shift
- Java Bitwise Operators
- Java Ternary Operator
- Java Control Statements
- Java if-else statement
- Java for Loop
- Java while Loop
- Java do-while Loop
- Java switch Statement
- Java break Statement
- Java continue Statement
- Java Popular Topics
- Java Arrays
- Java Multidimensional Array
- Java Strings
- Java Methods
- Java Date and Time
- Java Exception Handling
- Java File Handling
- Java OOP
- Java Classes and Objects
- Java Constructors
- Java Constructor Overloading
- Java Object as Parameter
- Java Returning Objects
- Java Encapsulation
- Java Abstraction
- Java Inheritance
- Java Polymorphism
- Java Packages
- Java Import Statement
- Java Multithreading
- Java Suspend Resume Stop Thread
- Java Programming Examples
- Java Programming Examples
Java right-shift operator
The right-shift operator, >>, shifts all of the bits in a value to the right a specified number of times. Here is the general form to use the right-shift operator in Java:
value >> num
Here, num specifies the number of positions to right-shift the value in "value," i.e., the >> moves all of the bits in the specified value to the right by the number of bit positions specified by "num."
The following code fragment shifts the value 32 to the right by two positions, resulting in a being set to 8:
int a = 32; a = a >> 2;
When a value has bits that are "shifted off," those bits are lost. For example, the next code fragment shifts the value 35 to the right two positions, which causes the two low-order bits to be lost, resulting again in a being set to 8:
int a = 35; a = a >> 2;
Looking at the same operation in binary shows more clearly how this happens:
0010001135 >>2 000010008
It divides the value by two and tosses the remainder after each shift to the right. In some circumstances, you can use this to divide an integer by 2 with high performance.
The previous contents of the top bit are filled in to the top (leftmost) bits exposed by the right shift when you shift to the right. When negative numbers are shifted to the right, the sign is maintained thanks to a technique known as sign extension. For instance, the binary equivalent of -8 >> 1 is -4.
11111000-8 >>1 11111100-4
It is interesting to note that if you shift -1 right, the result always remains -1, since sign extension keeps bringing in more ones in the high-order bits.
When shifting values to the right, sign-extending them isn't always a good idea. The following program, for instance, transforms a byte value into a hexadecimal string representation: To enable the value to be used as an index into the array of hexadecimal characters, the shifted value is masked by ANDing it with 0x0f to eliminate any sign-extended bits.
Java Right Shift Operator Example
Here is an example program that helps you understand the concept of the right-shift operator in Java:
public class JavaProgram {
public static void main(String args[]) {
char hex[] = {
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7',
'8', '9', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'
};
byte b = (byte) 0xf1;
System.out.println("b = 0x" + hex[(b >> 4) & 0x0f] + hex[b & 0x0f]);
}
}
When the above Java program is compiled and executed, it will produce the following output:
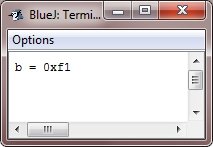
Advantages of the right-shift operator in Java
- It divides by 2 or any power of 2 faster. Shifting bits is faster than division because it's simple arithmetic.
- It is useful for manipulating binary data in low-level protocols and cryptography, where individual bits must be manipulated.
- It implements efficient data compression and decompression algorithms.
- It simplifies code writing and is easy to use.
Disadvantages of the right-shift operator in Java
- Misuse can produce unexpected results. Right-shifting a negative number replicates the sign bit (leftmost bit), which can change its value.
- Bitwise operations can confuse new programmers.
- Right shift errors are hard to debug.
- For applications that require bitwise operations beyond shifts, it may be limited.
« Previous Tutorial Next Tutorial »