- Operating Systems Course
- Operating System Tutorial
- History of the Operating System
- Personal Computer OS
- OS Processes
- OS Process Model
- OS Process Creation
- OS Deadlocks
- OS Deadlock Recovery
- OS Two-Phase Locking
- OS Memory Management
- OS Monoprogramming
- OS Shared Pages
- Operating System Input/Output
- OS Input/Output Devices
- OS Input/Output Software Layers
- OS Disk Hardware
- OS Files
- OS File Naming
- OS File Types
- OS Hierarchical Directory System
- OS Directory Operations
- OS File Operations
- Multimedia Operating System
- OS Multiprocessors
- Operating System Security
- OS User Authentication
- Computer Programming
- Learn Python
- Python Keywords
- Python Built-in Functions
- Python Examples
- Learn C++
- C++ Examples
- Learn C
- C Examples
- Learn Java
- Java Examples
- Learn Objective-C
- Web Development
- Learn HTML
- Learn CSS
- Learn JavaScript
- JavaScript Examples
- Learn SQL
- Learn PHP
File Operations in Operating System
As you are aware, files are used to store information for the purpose of using it at a later time.
The computer system is capable of carrying out a wide variety of operations pertaining to files. The following is a list of some of the most frequent file operations:
- File Create operation
- File Delete operation
- File Open operation
- File Close operation
- File Read operation
- File Write operation
- File Append operation
- File Seek operation
- File Get attribute operation
- File Set attribute operation
- File Rename operation
Now let's talk briefly about all the most common operations that can be performed with files.
File Create Operation
The creation of a file is accomplished through the use of the create operation. The creation of the file itself is the first step in the process of making one. There is no way to carry out any operation unless first a file is created.
The command can also be used to create a file. If you are using the "Windows" platform, you can use the command prompt to create files by using any of the following commands.
Don't worry; I'll include an example to help you understand how to create files using the command prompt practically. But before we get started, let's open the command prompt. To do so, press "WindowsKey+R" and then type "cmd" before pressing the "ENTER" key. The command prompt will be displayed as shown in the snapshot given below.
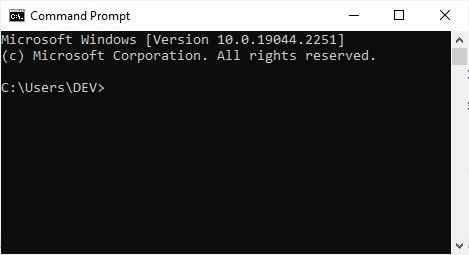
If you don't change the directory, the file will be created in the directory "DEV," which is inside the directory "Users," whose root is "C-Drive." However, if you want to change the directory and create a file in another directory, use the "cd" command as follows:
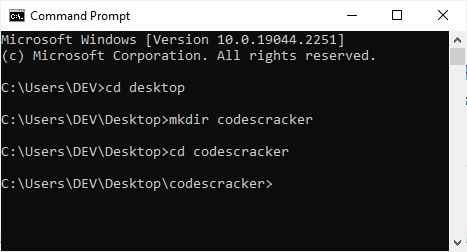
That is to say, the first command was:
cd desktop
to set the current working directory to "desktop". Then execute the command:
mkdir codescracker
is used to create a new folder named "codescracker" on the desktop. And finally, the following command:
cd codescracker
is used once more to change the current working directory to "codescracker," a newly created directory on my computer's "desktop." Now let's begin creating the files one by one using all three commands.
File Create Operation using echo
Use the "echo" command to create a file, say "one.txt," and save some text in it, such as "Hello there!" It takes the following general form:
echo content_to_save_in_file > file_name
For example:
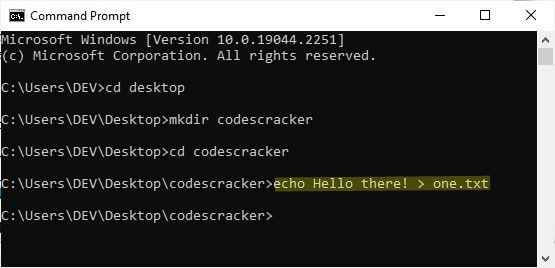
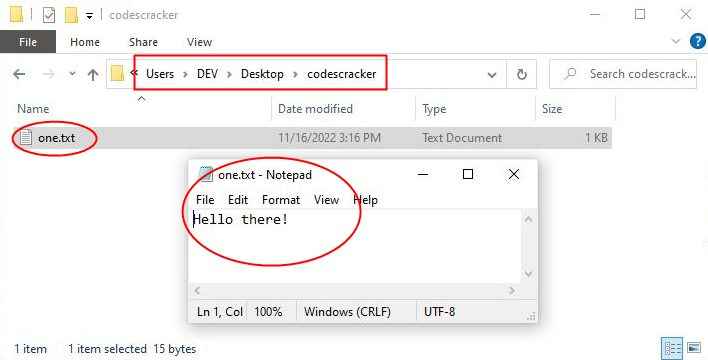
To draw your attention, I highlighted the command. If you open the folder after running this command, you will see a newly created file "one.txt" with the written text inside. In my case, here is the result of running the command:
File Create Operation using copy con
The "copy" command is equivalent to the "echo" command. The only difference is that we can keep adding content until we press the "Ctrl+Z" button. I must provide an example for your complete understanding. But, before we get to the example, let's look at the general syntax and brief description of the "copy con" command, which is used to create a file with some content.
copy con file_to_create
Simply press the "ENTER" key after typing the above command and then continue writing the content. To save three lines of text into a file, write the first line, then press the "ENTER" key, then the second line, then press the "ENTER" key, and finally the third line, then press the "ENTER" key. Finally, press "Ctrl+Z" to quit editing the newly created file. As an example:
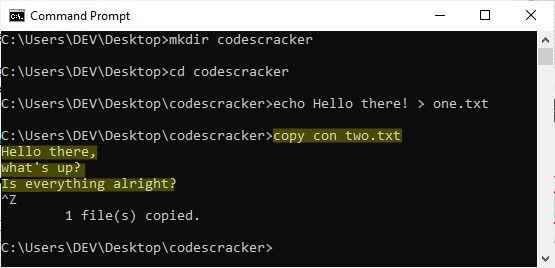
As you can see, I typed the command and then pressed the "ENTER" key. After that, I wrote three lines of text. And if you press "Ctrl+Z," you will see "^Z" appear on the command prompt, and if you hit the "ENTER" key, you will see the message "1 file(s) was copied," and the file editing will be closed. Here is a screenshot of the file after completing all of the steps to create a file with the "copy con" command at the command prompt.
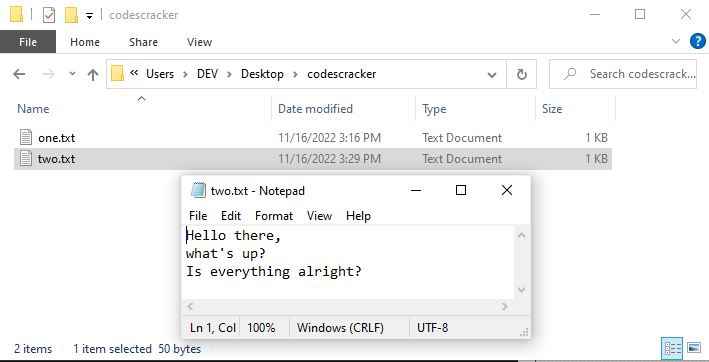
File Create Operation using notepad
Another command that can be used to create a file is "notepad." This is a little different than the previous two commands. Soon you will get it. Let's first see the general form of the "notepad" command to create a file using the command prompt.
notepad file_to_create
For example:
notepad three.txt
If you write the above command and hit the "ENTER" key, then you will see two windows appear on your system. The first one will be the confirmation window, which will ask you to click "Yes" to create the file, and the second will be the default editor of the file. Since "Notepad" is the default editor for all the files with the ".txt" extension, Therefore, in my case, the file "three.txt" opened on the notepad. Here is a snapshot of the confirmation box.
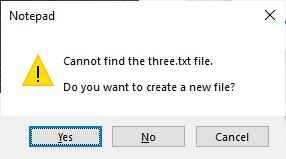
Since the second window, as already mentioned, will be the notepad, But until you chose "Yes" in the above confirmation box, the notepad opened with "Untitled." After you choose "Yes," the file "three.txt" will be opened in Notepad. Now either you can close the notepad to create an empty "three.txt" file or you can write something and then save. It is up to you.
File Delete Operation
The file is deleted using the file delete operation. To free up disc space, a file must be deleted when it is no longer required.
The file's final operation is to delete it. The file is no longer present after deletion.
To delete a file, just right-click on the file and then choose "Delete" and "Yes.". You can also use the "del" command to delete the file using the command prompt.
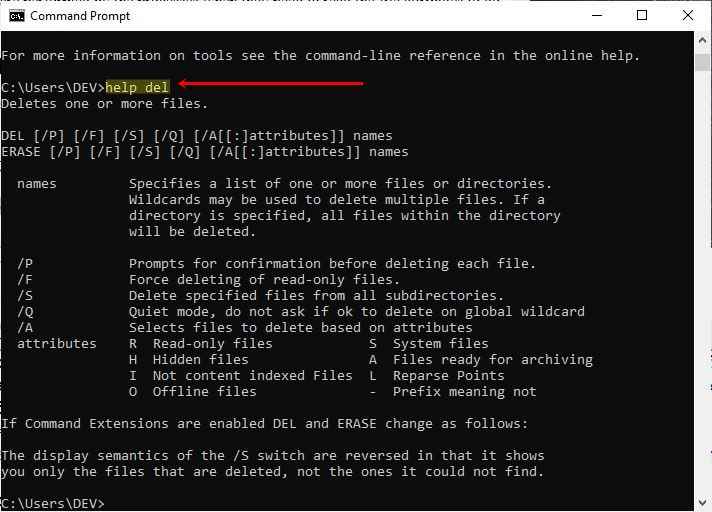
Because this "operating systems" course is intended for beginners. As a result, I won't go over each operation that can be performed on the file in detail. But, for your convenience, type "help" and press the "ENTER" key to see all the lists of commands that can be used to perform their specific task. Also use "help command_name" to get detailed information about that particular command. Below is a snapshot for your understanding.
File Open Operation
The file open operation is used to open the file. The file can be opened to read, modify, or for any other purpose. You can double-click on a file to open it.
File Close Operation
The file must be closed to free up the internal table space when all the accesses are finished and the attributes and disc addresses are no longer needed.
File Read Operation
The file read operation is only used to read the data stored in the specified file.
File Write Operation
The file write operation is used to save data to a file, usually at the current position.
File Append Operation
The file append operation is similar to the file write operation, except that it only adds data to the end of the file.
File Seek Operation
A method is required for random access files to specify where to take the data. As a result, the file seek operation handles this task.
File Get Attribute Operation
The file get attributes operation is performed by processes when they need to read the file attributes in order to complete their tasks.
File Set Attribute Operation
The file set attribute operation is used to set some of the attributes (user settable attributes) after the file has been created.
File Rename Operation
The file rename operation is used to change the name of an existing file.
« Previous Topic Next Topic »