- Computer Networking Course
- Computer Networking Tutorial
- Network Interface Unit
- Network Switch and Types
- Network Transmission Media
- Twisted Pair Cable
- Wireless Transmission Medium
- Satellite Microwave
- Data Communication Terms
- Types of Networks
- Network Topology
- Network Devices
- LAN Design
- Network Components Checklists
- Communication Protocols
- Mobile Computing
- Inter-networking Terms
- URL and Domain Names
- Web Hosting
- Web Scripting
- Software Categories
- Network Security
- Computer Programming
- Learn Python
- Python Keywords
- Python Built-in Functions
- Python Examples
- Learn C++
- C++ Examples
- Learn C
- C Examples
- Learn Java
- Java Examples
- Learn C#
- Learn Objective-C
- Web Development
- Learn HTML
- Learn CSS
- Learn JavaScript
- JavaScript Examples
- Learn SQL
- Learn PHP
Difference between domain name and URL with example
This post was written and distributed with the intention of elucidating the URL as well as the domain names. The two phrases that should be kept in mind when working with the internet.
The structure of the Internet known as the World Wide Web (WWW) is built on a protocol known as HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), as well as a language known as HTML (Hypertext Markup Language).
URL
The Uniform Resource Locator (URL) is an Internet address format that is utilized by HTTP. The URL is formatted as follows:
type://address/path
In this case, the value of type indicates the kind of server on which the file is stored, the value of address indicates the address of the server, and the value of path indicates the location of the file on the server. Take for instance the following portion of the URL:
https://codescracker.com/networking/url-domain-names.htm
Here, "https" specifies the type of server, "codescracker.com" is the address, and "networking/url-domain-names.htm" is the path. The file that will be served on the browser is "url-domain-names.htm."
Each resource on the internet has a unique address, which is specified by a uniform resource locator (URL). For example:
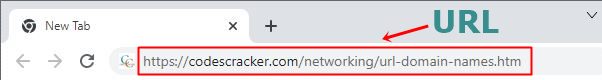
The following image depicts the various components of a URL.
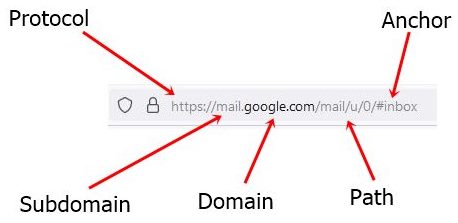
Domain Name
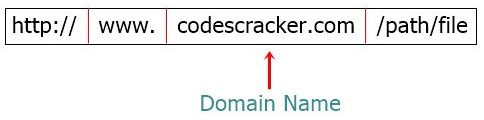
An Internet address that is character-based is called a domain name. For example: "codescracker.com", "google.com", and "youtube.com" etc. Here's a real-world example in which I indicated the domain name from the URL.
Internet Servers and Their Description
Here is a table that lists Internet servers and describes what they offer:
| Server | Protocol | Information Provides |
|---|---|---|
| ftp | File Transfer Protocol | Text and binary files that are organized in a hierarchical structure, much like a family tree |
| gopher | Transfer Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) | Text and binary files that are organized in a menu structure |
| http | Hypertext Transfer Protocol | Hypertext/hypermedia files, that is, multimedia documents that contain links to images, sounds, or other multimedia documents on the World Wide Web |
| Post Office Protocol (POP) Version 3 and Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) | Messages sent via electronic mail | |
| news | Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) | Newsgroups that are organized in a hierarchical structure. |
List of Common Domains
Here is a table listing the most common domains with their affiliations and remarks:
| Domain ID | Affiliation | Remarks |
|---|---|---|
| com | Commercial | for commercial firms |
| edu | Education | for educational firms |
| gov | Government | for government organizations |
| mil | Military | for Military |
| net | Network Resources | for ISPs/networks |
| org | Usually, non-profit organizations | for NGOs and other non-profit |
| co | Company | for listed companies |
| biz | Business | for business |
| tv | Television | for television companies and channels |
Popular country abbreviations used in domains
Sometimes a two-letter abbreviation indicating a country name may be used. For example,
https://www.google.co.uk
Here, the last uk (.uk) suggests that it is based in UK.
The table that follows provides a listing of some of the most well-known country abbreviations that are used in domain names.
| Abbreviation | Country Name |
|---|---|
| au | Australia |
| ca | Canada |
| dk | Denmark |
| fr | France |
| in | India |
| jp | Japan |
| nz | New Zealand |
| uk | United Kingdom |
« Previous Topic Next Topic »