- JavaScript Programs
- JavaScript Programs
- JavaScript Add Two Numbers
- JS Add Subtract Multiply Divide
- JavaScript Check Even/Odd
- JavaScript Add n Numbers
- JavaScript Add Number's Digit
- JavaScript Check Leap Year
- JavaScript Check Prime Number
- JavaScript Check Vowel or Not
- JavaScript Tutorial
- JavaScript Tutorial
- Computer Programming
- Learn Python
- Python Keywords
- Python Built-in Functions
- Python Examples
- Learn C++
- C++ Examples
- Learn C
- C Examples
- Learn Java
- Java Examples
- Learn C#
- Learn Objective-C
- Web Development
- Learn HTML
- Learn CSS
- Learn SQL
- Learn PHP
JavaScript Program to Find Sum of n Numbers
In this article, you will learn and get code to add n numbers entered by the user in JavaScript. Before creating the actual program, we've created a JavaScript code that shows how the program for adding n numbers looks.
Here is the list of programs you will go through:
- Add n numbers. The value of n is already initialized with 5, and 5 numbers are also initialized to an array, say arr.
- Add the number of numbers entered by the user. This program is created to get input from the user and then add all the numbers entered by the user. A live output of this program is also given.
Add n numbers in JavaScript
This is just a simple JavaScript program that doesn't allow the user to input the data. This program adds five numbers and writes the answer as an HTML output.
<!doctype html> <html> <body> <script> var i, n=5, sum=0; arr = new Array(10, 12, 13, 15, 19); for(i=0; i<5; i++) sum = sum + arr[i]; document.write(sum); </script> </body> </html>
Save this code in a file with .html extension and open it in a web browser. Here is the output you will see:
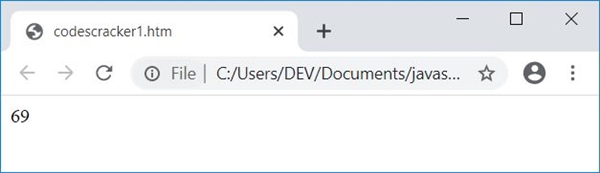
Obtain User Input Using a TextBox
Now this program allows the user to enter the data. That is, the user is asked to enter the value of n, say 5, and then again asked to enter 5 numbers.
<!doctype html> <html> <head> <script> var i=0, n, sum=0, temp; function fun() { n = parseInt(document.getElementById("n").value); if(n) { document.getElementById("nVal").innerHTML = n; document.getElementById("tme").innerHTML = i+1; i++; temp = document.getElementById("one"); temp.style.display = "none"; temp = document.getElementById("two"); temp.style.display = "block"; } } function add() { if(i==n) { temp = document.getElementById("two"); temp.style.display = "none"; temp = document.getElementById("three"); temp.style.display = "block"; } num = parseInt(document.getElementById("num").value); if(num) { sum = sum + num; document.getElementById("num").value = null; document.getElementById("tme").innerHTML = i+1; i++; } } function res() { document.getElementById("result").value = sum; } </script> </head> <body> <p id="one">Enter the Value of n: <input id="n"> <button onclick="fun()">ENTER</button></p> <p id="two" style="display:none;">Enter <span id="nVal"></span> Numbers. Input No. <span id="tme"></span>: <input id="num"><button id="btn" onclick="add()">ENTER</button></p> <p id="three" style="display:none;"><button onclick="res()">Add</button> <input id="result"></p> </body> </html>
Here is the initial output produced by the above program:
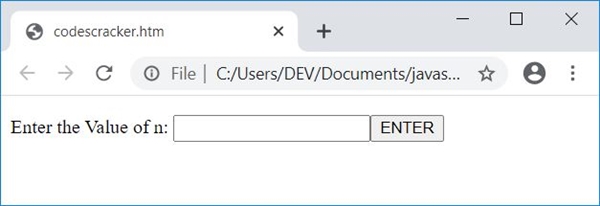
Now enter the value of n, say 5, and click on the button "Enter." After performing this, the output changes. Here is the snapshot:
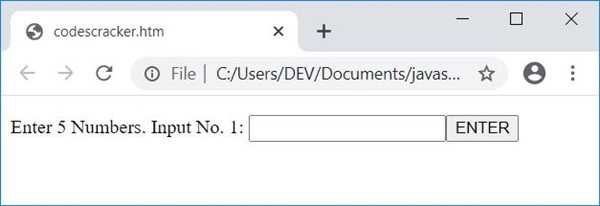
Now:
- Enter the first number, say 10, and click on the
ENTERbutton. - then the second number, say 12, and click on the
ENTERbutton. - third number, say 13, and the
ENTERbutton - fourth number, say 15, and
ENTER - fifth number, say 19, and
ENTER
Here is a snapshot of the output after performing all the above tasks:
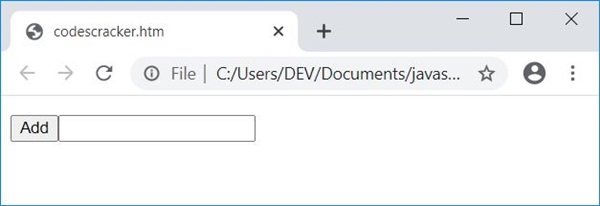
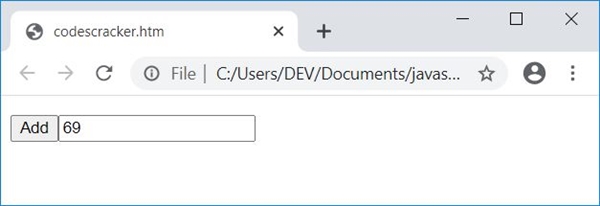
Finally, click on the "Add" button to print the sum of all five numbers entered by the user. Here is the snapshot after performing this:
The CSS code,
style="display:none;"
hides an HTML element. Because it is added in the paragraph with id, two. Then the paragraph with this id gets hidden.
When the user clicks on the button "ENTER," then a function fun() gets called. The following statement:
n = parseInt(document.getElementById("n").value);
states that the int (integer) value of an HTML element with id n gets initialized to n because the user enters 5 in the text box whose id is n. Therefore, 5 gets initialized to n. So n=5.
And the following JavaScript code for the if statement:
if(n)
states that checks whether n holds any value or is empty. The following statement:
document.getElementById("nVal").innerHTML = n;
states that the value of n gets printed in an HTML element with the id nVal. The following statement:
temp.style.display = "none";
states that an HTML element whose id is stored in temp gets hidden. And the statement given below:
temp.style.display = "block";
states that an HTML element whose id is stored in temp becomes visible.
Live Output of the Above Program
Here is the live output produced by the previous program:
Enter the Value of n:
« Previous Program Next Program »